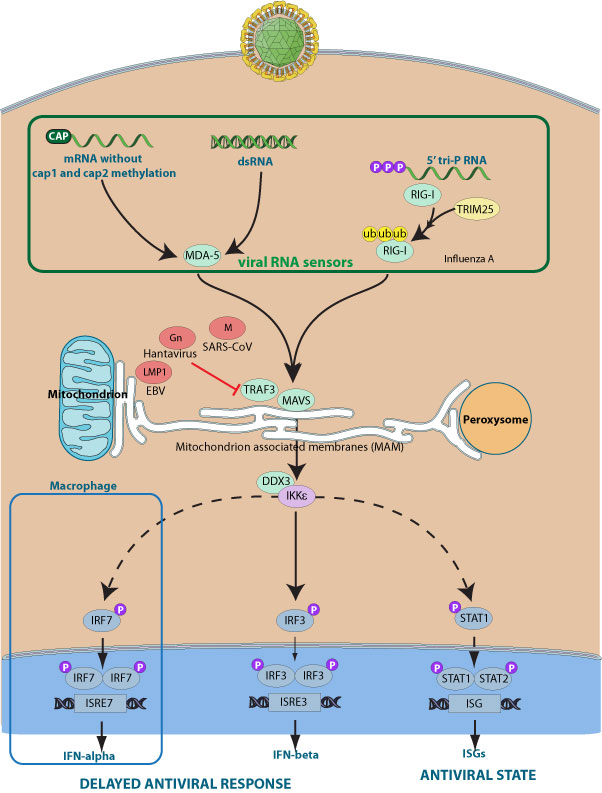
Several TRAF family members have been involved in the signaling pathway leading to the establishment of the antiviral state in the infected cells by viruses. For example, TRAF2 has been shown to be essential in RIG-I mediated expression of interferon upon Sendai virus infection in mouse fibroblasts. TRAF3 and TRAF6 are also key components of the signaling pathway downstream of MAVS.
Therefore a lot of viruses encode proteins which target the TRAF protein family. NS5A from hepatitis C virus, rotavirus VP4, hepatitis delta virus LHDAg and SHDAg, as well as vFLIP from KSVH directly interact with TRAF2. These interactions modulate production of cytokines by infected cells.
The TRAF3 protein is also the target of many viral proteins. Hantavirus Gn, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus M, and herpes virus LMP1 interact with TRAF3 and interfere with the TRAF3 / TBK1 interaction required to activate IRF3 / IRF7.

