Viral penetration via lysis of host organellar membrane (kw:KW-1174)
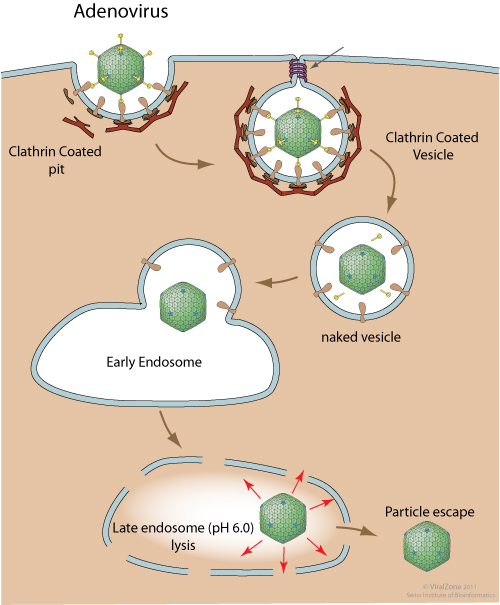
Non-enveloped viruses transfer their genetic material from endosome compartment to cell cytoplasm through membrane permeabilization or lysis.
Lysis occurs when a viral capsid induces rupture of endosomal membrane. This process occurs after capsid protein conformational change triggered by endosomal acidic pH or upon receptor binding. The result is either viral particle escape to the cytoplasm (Adenovirus 2 and 5)  or release of viral genome into the cytoplasm (Human rhinovirus)
or release of viral genome into the cytoplasm (Human rhinovirus)
Adenovirus membrane penetration: Tickling the tail of a sleeping dragon
Christopher M. Wiethoff, Glen R. Nemerow
Virology May 2015; 479-480: 591-599
Christopher M. Wiethoff, Glen R. Nemerow
Virology May 2015; 479-480: 591-599
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)11 entries grouped by strain
1 entry
Fowl adenovirus A serotype 1 (strain CELO / Phelps) (FAdV-1) (Avian adenovirus gal1 (strain Phelps)) reference strain
1 entry
Human adenovirus A serotype 12 (HAdV-12) (Human adenovirus 12) reference strain
1 entry
Human adenovirus C serotype 2 (HAdV-2) (Human adenovirus 2) reference strain
1 entry
Human adenovirus C serotype 5 (HAdV-5) (Human adenovirus 5) reference strain
1 entry
Human adenovirus F serotype 40 (HAdV-40) (Human adenovirus 40) reference strain
1 entry
Snake adenovirus serotype 1 (SnAdV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Canine adenovirus serotype 1 (strain CLL) (CAdV-1) (Canine adenovirus 1 (strain CLL))
1 entry
Canine adenovirus serotype 1 (strain RI261) (CAdV-1) (Canine adenovirus 1 (strain RI261))
1 entry
Human adenovirus F serotype 41 (HAdV-41) (Human adenovirus 41)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 14 (HRV-14)
1 entry
