Viral penetration into host cytoplasm (kw:KW-1162)
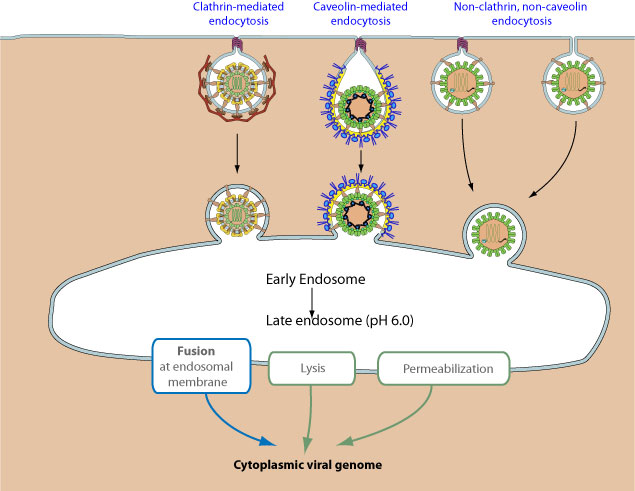
Translocation of the virion or its genetic material from the extracellular space into the host cell cytoplasm. Entry is achieved through pore formation, membrane fusion and/or endocytosis mechanisms.
Penetration reactions occur mainly in five locations: the cell
membrane, early and late endosomes, caveosomes, and the ER. Many viruses are able to utilize multiple uptake pathways, simultaneously, or depending on the host cell type targeted.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)1349 entries grouped by strain
11 entries
Vaccinia virus (strain Copenhagen) (VACV) reference strain
11 entries
Vaccinia virus (strain Western Reserve) (VACV) (Vaccinia virus (strain WR)) reference strain
11 entries
Variola virus (isolate Human/India/Ind3/1967) (VARV) (Smallpox virus) reference strain
9 entries
Monkeypox virus reference strain
8 entries
Fowlpox virus (strain NVSL) (FPV) reference strain
7 entries
Escherichia phage lambda (Bacteriophage lambda) reference strain
6 entries
Bacillus phage SPP1 (Bacteriophage SPP1) reference strain
6 entries
Escherichia phage T7 (Bacteriophage T7) reference strain
6 entries
Lactococcus phage SK1 (Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage SK1) reference strain
6 entries
Salmonella phage P22 (Bacteriophage P22) reference strain
5 entries
Acyrthosiphon pisum secondary endosymbiont phage 1 (Bacteriophage APSE-1) reference strain
5 entries
Escherichia phage Mu (Bacteriophage Mu) reference strain
5 entries
Escherichia phage N15 (Bacteriophage N15) reference strain
4 entries
Bacillus phage phi29 (Bacteriophage phi-29) reference strain
4 entries
Enterobacteria phage PRD1 (Bacteriophage PRD1) reference strain
4 entries
Enterobacteria phage T4 (Bacteriophage T4) reference strain
4 entries
Escherichia phage P2 (Bacteriophage P2) reference strain
4 entries
Escherichia phage T5 (Enterobacteria phage T5) reference strain
3 entries
African swine fever virus (strain Badajoz 1971 Vero-adapted) (Ba71V) (ASFV) reference strain
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage HK97 (Bacteriophage HK97) reference strain
3 entries
Enterobacteria phage S13 (Bacteriophage S13) reference strain
3 entries
Enterobacteria phage phiX174 (Isolate Sanger) (Bacteriophage phi-X174) reference strain
3 entries
Equine arteritis virus (strain Bucyrus) (EAV) reference strain
3 entries
Escherichia phage G4 (Bacteriophage G4) reference strain
3 entries
Escherichia phage alpha3 (Bacteriophage alpha-3) reference strain
3 entries
Psittacid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Amazon parrot/-/97-0001/1997) (PsHV-1) (Pacheco's disease virus) reference strain
3 entries
Vibrio phage KVP40 (isolate Vibrio parahaemolyticus/Japan/Matsuzaki/1991) (KVP40) (Bacteriophage KVP40) reference strain
2 entries
Adeno-associated virus 2 (isolate Srivastava/1982) (AAV-2) reference strain
2 entries
Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 (strain C500) (AlHV-1) (Malignant catarrhal fever virus) reference strain
2 entries
Bacillus phage SP01 (Bacteriophage SP01) reference strain
2 entries
Bacteroides phage crAss001 (Bacteroides phage PhiCrAss001) reference strain
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 10 (isolate USA) (BTV 10) reference strain
2 entries
Chikungunya virus (strain S27-African prototype) (CHIKV) reference strain
2 entries
Clostridium phage phiCD119 (strain Clostridium difficile/United States/Govind/2006) (Bacteriophage phiCD119) reference strain
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage HK620 (Bacteriophage HK620) reference strain
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage M13 (Bacteriophage M13) reference strain
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage SP6 (Bacteriophage SP6) reference strain
2 entries
Epstein-Barr virus (strain AG876) (HHV-4) (Human herpesvirus 4) reference strain
2 entries
Epstein-Barr virus (strain B95-8) (HHV-4) (Human herpesvirus 4) reference strain
2 entries
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain Ab4p) (EHV-1) (Equine abortion virus) reference strain
2 entries
Equine herpesvirus 2 (strain 86/87) (EHV-2) reference strain
2 entries
Escherichia phage If1 (Bacteriophage If1) reference strain
2 entries
Fowl adenovirus A serotype 1 (strain CELO / Phelps) (FAdV-1) (Avian adenovirus gal1 (strain Phelps)) reference strain
2 entries
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain Chicken/Md5/ATCC VR-987) (GaHV-2) (Marek's disease herpesvirus type 1) reference strain
2 entries
Guinea pig cytomegalovirus (strain 22122) (GPCMV) reference strain
2 entries
Human adenovirus A serotype 12 (HAdV-12) (Human adenovirus 12) reference strain
2 entries
Human adenovirus C serotype 2 (HAdV-2) (Human adenovirus 2) reference strain
2 entries
Human adenovirus C serotype 5 (HAdV-5) (Human adenovirus 5) reference strain
2 entries
Human cytomegalovirus (strain AD169) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5) reference strain
2 entries
Human cytomegalovirus (strain Merlin) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain 17) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain HG52) (HHV-2) (Human herpes simplex virus 2) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 6A (strain Uganda-1102) (HHV-6 variant A) (Human B lymphotropic virus) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 6B (strain Z29) (HHV-6 variant B) (Human B lymphotropic virus) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 7 (strain JI) (HHV-7) (Human T lymphotropic virus) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 8 type P (isolate GK18) (HHV-8) (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus) reference strain
2 entries
JC polyomavirus (JCPyV) (JCV) reference strain
2 entries
Murid herpesvirus 1 (strain Smith) (MuHV-1) (Mouse cytomegalovirus) reference strain
2 entries
Pseudomonas phage Pf1 (Bacteriophage Pf1) reference strain
2 entries
Pseudomonas phage Pf3 (Bacteriophage Pf3) reference strain
2 entries
Pseudomonas phage phiKMV reference strain
2 entries
Saimiriine herpesvirus 2 (strain 11) (SaHV-2) (Herpesvirus saimiri) reference strain
2 entries
Salmonella phage IKe (Bacteriophage IKe) reference strain
2 entries
Salmonella phage ViI reference strain
1 entry
Semliki forest virus (SFV) reference strain
2 entries
Simian virus 40 (SV40) reference strain
2 entries
Sindbis virus (SINV) reference strain
2 entries
Snake adenovirus serotype 1 (SnAdV-1) reference strain
2 entries
Staphylococcus phage Twort (strain DSM 17442 / HER 48) (Bacteriophage Twort) reference strain
2 entries
Varicella-zoster virus (strain Dumas) (HHV-3) (Human herpesvirus 3) reference strain
2 entries
Xanthomonas phage phiLf (Bacteriophage phi-Lf) reference strain
1 entry
Aedes albopictus densovirus (isolate Boublik/1994) (AalDNV) reference strain
1 entry
Alethinophid 1 reptarenavirus (isolate AlRrV1/Boa/USA/BC/2009) (Golden Gate virus) reference strain
1 entry
Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (strain G) (ADV) reference strain
1 entry
Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus (AmEPV) reference strain
1 entry
Aquareovirus C (isolate Golden shiner/USA/GSRV/1977) (AQRV-C) reference strain
1 entry
Aquareovirus G (isolate American grass carp/USA/PB01-155/-) (AQRV-G) reference strain
1 entry
Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) reference strain
1 entry
Avian infectious bronchitis virus (strain Beaudette) (IBV) reference strain
1 entry
Avian leukosis virus subgroup A (isolate RSA) (ALV-A RSA) reference strain
1 entry
Avian metapneumovirus (isolate Canada goose/Minnesota/15a/2001) (AMPV) reference strain
1 entry
Bacillus phage Nf (Bacteriophage Nf) reference strain
1 entry
Bacillus phage SPR (Bacteriophage SPR) reference strain
1 entry
Bacillus phage SPbeta (Bacillus phage SPBc2) (Bacteriophage SP-beta) reference strain
1 entry
Bat coronavirus HKU4 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/HKU4/2004) reference strain
1 entry
Bat coronavirus HKU5 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/HKU5/2004) reference strain
1 entry
Bat coronavirus HKU9 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/HKU9) reference strain
1 entry
Bdellovibrio phage phiMH2K (Bacteriophage phiMH2K) reference strain
1 entry
Beak and feather disease virus (BFDV) reference strain
1 entry
Bhanja virus (BHAV) reference strain
1 entry
Bordetella phage BPP-1 reference strain
1 entry
Borna disease virus (strain V) (BDV) reference strain
1 entry
Bovine papillomavirus type 1 reference strain
1 entry
Bovine papillomavirus type 3 reference strain
1 entry
Bovine papillomavirus type 5 reference strain
1 entry
Bovine parvovirus 1 (BPV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Bovine polyomavirus (BPyV) (Bos taurus polyomavirus 1) reference strain
1 entry
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus (strain A51908) (BRS) reference strain
1 entry
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (isolate NADL) (BVDV) (Mucosal disease virus) reference strain
1 entry
Breda virus 1 (BRV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Budgerigar fledgling disease virus (BFPyV) (Aves polyomavirus 1) reference strain
1 entry
Bunyamwera virus (BUNV) reference strain
1 entry
Bunyavirus La Crosse reference strain
1 entry
Burkholderia phage BcepMu (isolate -/United States/Summer/2002) (Bacteriophage BcepMu) reference strain
1 entry
Camelpox virus (strain CMS) reference strain
1 entry
Canary circovirus (CaCV) reference strain
1 entry
Canine oral papillomavirus (strain Y62) (COPV) reference strain
1 entry
Chicken anemia virus (isolate Germany Cuxhaven-1) (CAV) reference strain
1 entry
Chlamydia phage 1 (Bacteriophage Chp1) reference strain
1 entry
Cottontail rabbit papillomavirus (strain Kansas) (CRPV) (Papillomavirus sylvilagi) reference strain
1 entry
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (strain Nigeria/IbAr10200/1970) (CCHFV) reference strain
1 entry
Cupixi mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Brasil/BeAn 119303/1970) (CPXV) reference strain
1 entry
Dengue virus type 1 (strain Nauru/West Pac/1974) (DENV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Drosophila melanogaster sigma virus (isolate Drosophila/USA/AP30/2005) (DMelSV) reference strain
1 entry
Duck hepatitis B virus (isolate Shanghai/DHBVQCA34) (DHBV) reference strain
1 entry
Duck hepatitis B virus (strain United States/DHBV-16) (DHBV) reference strain
1 entry
Dugbe virus (isolate ArD44313) (DUGV) reference strain
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage GA (Bacteriophage GA) reference strain
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage I2-2 (Bacteriophage I2-2) reference strain
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage N4 (Bacteriophage N4) reference strain
1 entry
Enterococcus phage phiEF24C (Enterococcus bacteriophage phi-EF24C) reference strain
1 entry
Escherichia phage MS2 (Bacteriophage MS2) reference strain
1 entry
Escherichia phage T1 (Bacteriophage T1) reference strain
1 entry
European elk papillomavirus (EEPV) reference strain
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O (FMDV) reference strain
1 entry
Goose circovirus (GoCV) reference strain
1 entry
Haemophilus phage HP1 (strain HP1c1) (Bacteriophage HP1) reference strain
1 entry
Halomonas phage phiHAP-1 (isolate -/Gulf of Mexico/-/2001) (Bacteriophage phiHAP-1) reference strain
1 entry
Hantaan virus (strain 76-118) (Korean hemorrhagic fever virus) reference strain
1 entry
Hazara virus (isolate JC280) reference strain
1 entry
Helicobacter pylori bacteriophage KHP30 reference strain
1 entry
Hendra virus (isolate Horse/Autralia/Hendra/1994) reference strain
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ayr (isolate Human/Japan/Okamoto/-) (HBV-C) reference strain
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate France/Tiollais/1979) (HBV-D) reference strain
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate Japan/JYW796/1988) (HBV-D) reference strain
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1a (isolate H77) (HCV) reference strain
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 (isolate Caribbea HS-35 subtype A) (HTLV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 (strain Japan ATK-1 subtype A) (HTLV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 2 (HTLV-2) reference strain
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 3 (strain 2026ND) (HTLV-3) reference strain
1 entry
Human adenovirus F serotype 40 (HAdV-40) (Human adenovirus 40) reference strain
1 entry
Human associated cyclovirus 1 (isolate Homo sapiens/Pakistan/PK5510/2007) (HuCyV-1) (Cyclovirus PK5510) reference strain
1 entry
Human astrovirus-1 (HAstV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human coronavirus HKU1 (isolate N5) (HCoV-HKU1) reference strain
1 entry
Human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype A (isolate MAL) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate ARV2/SF2) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BRU/LAI) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate HXB2) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate MN) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate RF/HAT3) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (strain 89.6) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype C (isolate 92BR025) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype C (isolate ETH2220) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype D (isolate ELI) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype F1 (isolate 93BR020) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype F1 (isolate VI850) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype H (isolate 90CF056) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group N (isolate YBF30) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group O (isolate ANT70) (HIV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate BEN) (HIV-2) reference strain
1 entry
Human metapneumovirus (strain CAN97-83) (HMPV) reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 11 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 15 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 21 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 22 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 23 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 24 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 27 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 29 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 30 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 31 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 35 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 39 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 4 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 44 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 5 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 56 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 62 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 7 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 9 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 1 (Human papillomavirus type 1a) reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 10 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 16 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 18 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 26 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 32 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 34 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 41 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 48 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 50 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 54 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 60 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 61 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 63 reference strain
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 70 reference strain
1 entry
Human parainfluenza 2 virus (strain Toshiba) (HPIV-2) reference strain
1 entry
Human parvovirus B19 (strain HV) (HPV B19) reference strain
1 entry
Human respiratory syncytial virus B (strain B1) reference strain
1 entry
Human rhinovirus A serotype 89 (strain 41467-Gallo) (HRV-89) reference strain
1 entry
Infectious salmon anemia virus (isolate Atlantic salmon/Norway/810/9/99) (ISAV) reference strain
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Aichi/2/1968 H3N2) reference strain
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Goose/Guangdong/1/1996 H5N1 genotype Gs/Gd) reference strain
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1) reference strain
1 entry
Influenza B virus (strain B/Lee/1940) reference strain
1 entry
Influenza C virus (strain C/Ann Arbor/1/1950) reference strain
1 entry
Junonia coenia densovirus (isolate pBRJ/1990) (JcDNV) reference strain
1 entry
Lake Victoria marburgvirus (strain Musoke-80) (MARV) (Marburg virus (strain Kenya/Musoke/1980)) reference strain
1 entry
Lassa virus (strain Mouse/Sierra Leone/Josiah/1976) (LASV) reference strain
1 entry
Latino mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Bolivia/MARU 1924/1965) (LATV) reference strain
1 entry
Lymantria dispar multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus (LdMNPV) reference strain
1 entry
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (strain Armstrong) (LCMV) reference strain
1 entry
Macaca mulata papillomavirus 1 (Rhpv 1) (Rhesus papillomavirus type 1) reference strain
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Ichinose-B95a) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus) reference strain
1 entry
Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (isolate United Kingdom/H123990006/2012) (MERS-CoV) (Betacoronavirus England 1) reference strain
1 entry
Molluscum contagiosum virus subtype 1 (MOCV) (MCVI) reference strain
1 entry
Moloney murine leukemia virus (isolate Shinnick) (MoMLV) reference strain
1 entry
Mouse mammary tumor virus (strain BR6) (MMTV) reference strain
1 entry
Mouse mammary tumor virus (strain C3H) (MMTV) reference strain
1 entry
Mumps virus genotype B (strain Miyahara vaccine) (MuV) reference strain
1 entry
Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (MHV-A59) (Murine hepatitis virus) reference strain
1 entry
Murine minute virus (strain MVM prototype) (MVM) (Murine minute virus (strain MVM(p))) reference strain
1 entry
Murine pneumonia virus (strain 15) (MPV) reference strain
1 entry
Murine polyomavirus (strain A2) (MPyV) reference strain
1 entry
Mycobacterium phage Bxz1 (Mycobacteriophage Bxz1) reference strain
1 entry
Mycobacterium phage D29 (Mycobacteriophage D29) reference strain
1 entry
Mycobacterium phage L5 (Mycobacteriophage L5) reference strain
1 entry
Myxoma virus (strain Lausanne) (MYXV) reference strain
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Chicken/United States/B1/48) (NDV) reference strain
1 entry
Nodamura virus (strain Mag115) (NoV) reference strain
1 entry
Odocoileus virginianus papillomavirus 1 (DPV) (Deer papillomavirus) reference strain
1 entry
Oliveros mammarenavirus (isolate Mouse/Argentina/RIID 3229/1990) (OLVV) reference strain
1 entry
Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid polyhedrosis virus (OpMNPV) reference strain
1 entry
Parainfluenza virus 5 (strain W3) (PIV5) (Simian virus 5) reference strain
1 entry
Parana mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Paraguay/12056/1965) (PARV) (Paran mammarenavirus) reference strain
1 entry
Pirital mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Venezuela/VAV-488/1995) (PIRV) reference strain
1 entry
Poliovirus type 1 (strain Mahoney) reference strain
1 entry
Porcine adenovirus A serotype 3 (PAdV-3) (Porcine adenovirus 3) reference strain
1 entry
Porcine circovirus 1 (PCV1) reference strain
1 entry
Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) reference strain
1 entry
Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (strain 67N) (HEV-67N) reference strain
1 entry
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (strain Lelystad) (PRRSV) reference strain
1 entry
Pseudomonas phage PAJU2 reference strain
1 entry
Pseudomonas phage phi6 (Bacteriophage phi-6) reference strain
1 entry
Puumala virus (strain Sotkamo/V-2969/81) reference strain
1 entry
Pygmy chimpanzee papillomavirus type 1 (PCPV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Rabbit fibroma virus (strain Kasza) (RFV) (Shope fibroma virus (strain Kasza)) reference strain
1 entry
Reovirus type 1 (strain Lang) (T1L) (Mammalian orthoreovirus 1) reference strain
1 entry
Rift valley fever virus (strain ZH-548 M12) (RVFV) reference strain
1 entry
Rinderpest virus (strain RBOK) (RDV) reference strain
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Monkey/South Africa/SA11-H96/1958/G3P5B[2]) (RV-A) (Simian Agent 11 (isolate SI/South Africa/H96/58)) reference strain
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/United States/D/1974/G1P1A[8]) (RV-A) reference strain
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/SA11-Both/G3P5B[2]) (RV-A) (Simian Agent 11 (strain Both)) reference strain
1 entry
Rotavirus C (isolate RVC/Human/United Kingdom/Bristol/1989) (RV-C) reference strain
1 entry
Rotavirus X (strain RVX/Human/China/NADRV-J19/1997/GXP[X]) (RV ADRV-N) (Rotavirus (isolate novel adult diarrhea rotavirus-J19)) reference strain
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain Therien) (RUBV) reference strain
1 entry
SFTS phlebovirus (isolate SFTSV/Human/China/HB29/2010) (Severe fever with thrombocytopenia virus) reference strain
1 entry
Salmonella phage ST64T (Bacteriophage ST64T) reference strain
1 entry
Salmonella phage epsilon15 reference strain
1 entry
Sendai virus (strain Ohita) (SeV) reference strain
1 entry
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) reference strain
1 entry
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (2019-nCoV) (SARS-CoV-2) reference strain
1 entry
Shigella phage Sf6 (Shigella flexneri bacteriophage VI) (Bacteriophage SfVI) reference strain
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate CPZ GAB1) (SIV-cpz) (Chimpanzee immunodeficiency virus) reference strain
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate EK505) (SIV-cpz) (Chimpanzee immunodeficiency virus) reference strain
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate MB66) (SIV-cpz) (Chimpanzee immunodeficiency virus) reference strain
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate TAN1) (SIV-cpz) (Chimpanzee immunodeficiency virus) reference strain
1 entry
Simian virus 41 (SV41) reference strain
1 entry
Spiroplasma virus 4 (SpV4) reference strain
1 entry
Spring viremia of carp virus (Rhabdovirus carpia) reference strain
1 entry
Squirrel monkey polyomavirus reference strain
1 entry
Staphylococcus phage 44AHJD reference strain
1 entry
Streptomyces phage phiC31 (Bacteriophage phi-C31) reference strain
1 entry
Tacaribe virus (strain Franze-Fernandez) (TCRV) reference strain
1 entry
Tibrogargan virus (strain CS132) (TIBV) reference strain
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Brazilian Br-01) (TSWV) reference strain
1 entry
Tupaia virus (isolate Tupaia/Thailand/-/1986) (TUPV) reference strain
1 entry
Uukuniemi virus (strain S23) (UUKV) reference strain
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain San Juan) (VSIV) reference strain
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus (strain Ogden subtype Concan) (VSNJV) reference strain
1 entry
WU polyomavirus (WUPyV) reference strain
1 entry
Walleye dermal sarcoma virus (WDSV) reference strain
1 entry
White bream virus (isolate Blicca bjoerkna L./Germany/DF24/00) (WBV) reference strain
1 entry
Whitewater Arroyo mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/United States/AV 9310135/1995) (WWAV) reference strain
1 entry
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 8) (WHV) reference strain
1 entry
Xenotropic MuLV-related virus (isolate VP62) (XMRV) reference strain
1 entry
Yaba monkey tumor virus (strain VR587) (YMTV) reference strain
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain 17D vaccine) (YFV) reference strain
1 entry
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Mayinga-76) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus) reference strain
1 entry
Zika virus (ZIKV) reference strain
1 entry
Monkeypox virus
8 entries
Vaccinia virus (strain Ankara) (VACV)
8 entries
Variola virus
6 entries
Lactococcus phage p2 (Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage p2)
3 entries
Bacillus phage B103 (Bacteriophage B103)
3 entries
Bacillus phage PZA (Bacteriophage PZA)
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage HK97 (Bacteriophage HK97)
3 entries
Enterobacteria phage phiK (Bacteriophage phi-K)
3 entries
Vaccinia virus (strain Tian Tan) (VACV)
2 entries
BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) (Human polyomavirus 1)
2 entries
BK polyomavirus (strain AS) (BKPyV)
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 1 (isolate Australia) (BTV 1)
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 1 (isolate South Africa) (BTV 1)
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 11 (isolate USA) (BTV 11)
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 13 (isolate USA) (BTV 13)
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 17 (isolate USA) (BTV 17)
2 entries
Canine adenovirus serotype 1 (strain CLL) (CAdV-1) (Canine adenovirus 1 (strain CLL))
2 entries
Canine adenovirus serotype 1 (strain RI261) (CAdV-1) (Canine adenovirus 1 (strain RI261))
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage f1 (Bacteriophage f1)
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage fd (Bacteriophage fd)
2 entries
Epstein-Barr virus (strain GD1) (HHV-4) (Human gammaherpesvirus 4)
2 entries
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain Jaoars982) (JEV)
2 entries
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain M28) (JEV)
2 entries
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain SA(v)) (JEV)
2 entries
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain SA-14) (JEV)
2 entries
Murine adenovirus A serotype 1 (MAdV-1) (Murine adenovirus 1)
2 entries
Nipah virus
1 entry
Semliki forest virus (SFV)
2 entries
Serratia phage KSP20 (Serratia marcescens bacteriophage KSP20)
2 entries
Simian virus 12 (strain wt100) (SV-12) (Baboon polyomavirus 1)
2 entries
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Kaplan) (SuHV-1) (Pseudorabies virus (strain Kaplan))
2 entries
Varicella-zoster virus (strain Oka vaccine) (HHV-3) (Human herpesvirus 3)
1 entry
AKV murine leukemia virus (AKR (endogenous) murine leukemia virus)
1 entry
Aedes densonucleosis virus (strain GKV 002 002) (Aedes densovirus)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus (AHSV) (Orbivirus alphaequi)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 6 (AHSV-6)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 9 (AHSV-9)
1 entry
Alkhumra hemorrhagic fever virus (ALKV) (Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever virus)
1 entry
Allpahuayo mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Peru/CLHP-2472/1997) (ALLV)
1 entry
Alphavirus salmon subtype 1 (SAV1) (Salmon pancreas disease virus subtype 1)
1 entry
Alphavirus salmon subtype 2 (SAV2) (Sleeping disease virus)
1 entry
Alphavirus salmon subtype 3 (SAV3) (Norwegian salmonid alphavirus)
1 entry
Andes orthohantavirus (ANDV) (Andes virus)
1 entry
Aura virus (AURAV)
1 entry
Avian infectious bronchitis virus (strain 6/82) (IBV)
1 entry
Avian infectious bronchitis virus (strain D274) (IBV)
1 entry
Avian infectious bronchitis virus (strain KB8523) (IBV)
1 entry
Avian infectious bronchitis virus (strain M41) (IBV)
1 entry
Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus
1 entry
Avian spleen necrosis virus
1 entry
B-lymphotropic polyomavirus (LPV)
1 entry
Baboon endogenous virus (strain M7)
1 entry
Banzi virus (BANV)
1 entry
Barmah forest virus (BFV)
1 entry
Bat coronavirus 133/2005 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/133/2005)
1 entry
Bat coronavirus 279/2005 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/279/2005)
1 entry
Bat coronavirus HKU3 (BtCoV) (SARS-like coronavirus HKU3)
1 entry
Bat coronavirus Rp3/2004 (BtCoV/Rp3/2004) (SARS-like coronavirus Rp3)
1 entry
Bear Canyon mammarenavirus (isolate Mouse/United States/AV A0070039/2000) (BCNV)
1 entry
Berne virus (BEV)
1 entry
Black Creek Canal orthohantavirus (BCCV) (Black Creek Canal virus)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 1 (isolate South Africa vaccine) (BTV 1)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 2 (isolate USA) (BTV 2)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 3 (isolate South Africa vaccine) (BTV 3)
1 entry
Boolarra virus (BoV)
1 entry
Borna disease virus 1 (BoDV-1)
1 entry
Bos taurus papillomavirus 2 (Bovine papillomavirus 2)
1 entry
Bos taurus papillomavirus 4 (Bovine papillomavirus 4)
1 entry
Bovine Schmallenberg virus (isolate Bovine/BH80/Germany/2011) (SBV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain 98TXSF-110-ENT) (BCoV-ENT) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain 98TXSF-110-LUN) (BCoV-LUN) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain F15) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain L9) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain LSU-94LSS-051) (BCoV-LSU) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain LY-138) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain Mebus) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain OK-0514) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain Quebec) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine coronavirus (strain vaccine) (BCoV) (BCV)
1 entry
Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) (BEV)
1 entry
Bovine herpesvirus 1.1 (strain Cooper) (BoHV-1) (Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (isolate American FLK) (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (isolate American VDM) (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (isolate Australian) (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (isolate Belgium LB285) (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (isolate Belgium LB59) (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine leukemia virus (isolate Japanese BLV-1) (BLV)
1 entry
Bovine parainfluenza 3 virus (BPIV-3)
1 entry
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus (strain Copenhagen) (BRS)
1 entry
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus (strain Rb94) (BRS)
1 entry
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (strain CP7) (BVDV) (Mucosal disease virus)
1 entry
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (strain SD-1) (BVDV) (Mucosal disease virus)
1 entry
Broadhaven virus (BRD)
1 entry
Bunyavirus germiston
1 entry
Bunyavirus snowshoe hare
1 entry
Bussuquara virus (BUSV)
1 entry
Camelpox virus (strain M-96)
1 entry
Canine distemper virus (strain Onderstepoort) (CDV)
1 entry
Canine parvovirus type 2 (CPV-2)
1 entry
Canine parvovirus type 2 (isolate Dog/United States/CPV-N/1978) (CPV-2)
1 entry
Canine parvovirus type 2 (isolate Dog/United States/CPV-b/1978) (CPV-2)
1 entry
Canine parvovirus type 2 (strain Dog/United States/780929/-) (CPV-2)
1 entry
Canine parvovirustype 2 (isolate Dog/United States/CPV-d/1988) (CPV-2)
1 entry
Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus
1 entry
Chapare mammarenavirus (isolate Human/Bolivia/810419/2003)
1 entry
Chicken anemia virus (isolate Australia) (CAV)
1 entry
Chicken anemia virus (isolate Australia/CAU269-7/2000) (CAV)
1 entry
Chicken anemia virus (isolate Japan 82-2) (CAV)
1 entry
Chicken anemia virus (isolate USA 26p4) (CAV)
1 entry
Chicken anemia virus (isolate USA CIA-1) (CAV)
1 entry
Chikungunya virus (strain 37997) (CHIKV)
1 entry
Chikungunya virus (strain Nagpur) (CHIKV)
1 entry
Chimpanzee hepatitis B virus (isolate United Kingdom/LSH/1988) (HBVcpz)
1 entry
Choristoneura fumiferana nuclear polyhedrosis virus (CfMNPV)
1 entry
Classical swine fever virus (strain Alfort/Tuebingen) (CSFV) (Hog cholera virus)
1 entry
Classical swine fever virus (strain Brescia) (CSFV) (Hog cholera virus)
1 entry
Cowpox virus (strain Brighton Red) (CPV)
1 entry
Cowpox virus (strain GRI-90 / Grishak) (CPV)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A16 (strain G-10)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A16 (strain Tainan/5079/98)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A21 (strain Coe)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A24 (strain EH24/70)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A9 (strain Griggs)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B1 (strain Japan)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B2 (strain Ohio-1)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B3 (strain Nancy)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B3 (strain Woodruff)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B4 (strain E2)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B4 (strain JVB / Benschoten / New York/51)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B5 (strain Peterborough / 1954/UK/85)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B6 (strain Schmitt)
1 entry
Dabie bandavirus (Severe fever with thrombocytopenia virus) (Huaiyangshan banyangvirus)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 1 (strain Brazil/97-11/1997) (DENV-1)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 1 (strain Singapore/S275/1990) (DENV-1)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (isolate Thailand/0168/1979) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain 16681-PDK53) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Jamaica/1409/1983) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Peru/IQT2913/1996) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Puerto Rico/PR159-S1/1969) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Thailand/16681/1984) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Thailand/NGS-C/1944) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain China/80-2/1980) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Martinique/1243/1999) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Philippines/H87/1956) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Singapore/8120/1995) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Sri Lanka/1266/2000) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Dominica/814669/1981) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Philippines/H241/1956) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Singapore/8976/1995) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Thailand/0348/1991) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Thailand/0476/1997) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Diatraea saccharalis densovirus (DsDNV)
1 entry
Dobrava-Belgrade orthohantavirus (DOBV) (Dobrava virus)
1 entry
Duck hepatitis B virus (isolate brown Shanghai duck S5) (DHBV)
1 entry
Duck hepatitis B virus (isolate white Shanghai duck S31) (DHBV)
1 entry
Duck hepatitis B virus (strain China) (DHBV)
1 entry
Duck hepatitis B virus (strain Germany/DHBV-3) (DHBV)
1 entry
Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV) (Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus)
1 entry
Eastern equine encephalitis virus (strain Florida 91-469) (EEEV) (Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus)
1 entry
Eastern equine encephalitis virus (strain PE-0.0155) (EEEV) (Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus)
1 entry
Eastern equine encephalitis virus (strain PE-3.0815) (EEEV) (Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus)
1 entry
Eastern equine encephalitis virus (strain va33[ten broeck]) (EEEV) (Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus)
1 entry
Echovirus 1 (strain Human/Egypt/Farouk/1951) (E-1)
1 entry
Echovirus 11 (strain Gregory)
1 entry
Echovirus 12 (strain Travis)
1 entry
Echovirus 30 (strain Bastianni)
1 entry
Echovirus 5 (strain Noyce)
1 entry
Echovirus 6 (strain Charles)
1 entry
Echovirus 9 (strain Barty)
1 entry
Echovirus 9 (strain Hill)
1 entry
Ectromelia virus (strain Moscow) (ECTV) (Mousepox virus)
1 entry
Edge Hill virus (EHV)
1 entry
Elephantid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Asian elephant/Berlin/Kiba/1998) (EIHV-1) (Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus)
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage P21 (Bacteriophage 21) (Bacteriophage P21)
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage T3 (Bacteriophage T3)
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage T6 (Bacteriophage T6)
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage fr (Bacteriophage fr)
1 entry
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus 1 (EHDV-1)
1 entry
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain HVS25A) (EHV-1) (Equine abortion virus)
1 entry
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain V592) (EHV-1) (Equine abortion virus)
1 entry
Equine herpesvirus 4 (strain 1942) (EHV-4) (Equine rhinopneumonitis virus)
1 entry
Escherichia phage SECphi27
1 entry
Feline endogenous virus ECE1
1 entry
Feline herpesvirus 1 (FeHV-1) (Feline viral rhinotracheitis virus)
1 entry
Feline leukemia virus (isolate CFE-6)
1 entry
Feline leukemia virus (strain A/Glasgow-1)
1 entry
Feline leukemia virus (strain B/lambda-B1)
1 entry
Feline leukemia virus (strain C/Sarma)
1 entry
Feline panleukopenia virus (FPV)
1 entry
Feline panleukopenia virus (strain 193) (FPV)
1 entry
Feline sarcoma virus (strain Gardner-Arnstein) (Ga-FeSV) (Gardner-Arnstein feline leukemia oncovirus B)
1 entry
Feline sarcoma virus (strain SM) (Sm-FeSV)
1 entry
Flock house virus (FHV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate -/Azerbaijan/A22-550/1965 serotype A) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate -/Brazil/C3Indaial/1971 serotype C) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate -/Germany/A5Westerwald/1951 serotype A) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate -/Germany/C1Oberbayen/1960 serotype C) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate -/Spain/S8c1SantaPau/1970 serotype C) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate Bovine/Brazil/A24Cruzeiro/1955 serotype A) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate Bovine/United Kingdom/A12Valle119/1932 serotype A) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (isolate Swine/Taiwan/OTai/1997 serotype O) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (strain A10/Holland/1961 serotype A) (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype Asia-1 (FMDV)
1 entry
Foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype SAT-2 (FMDV)
1 entry
Fowl adenovirus C serotype 10 (strain SA2) (FAdV-10) (Fowl adenovirus 10)
1 entry
Friend murine leukemia virus (isolate 57) (FrMLV)
1 entry
Friend murine leukemia virus (isolate FB29) (FrMLV)
1 entry
Friend murine leukemia virus (isolate PVC-211) (FrMLV)
1 entry
Friend spleen focus-forming virus (isolate 502) (FSFFV)
1 entry
Friend spleen focus-forming virus (strain BB6) (FSFFV)
1 entry
Friend spleen focus-forming virus (strain Lilly-Steeves) (FSFFV)
1 entry
Galleria mellonella densovirus (GmDNV)
1 entry
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain GA) (GaHV-2) (Marek's disease herpesvirus type 1)
1 entry
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain RB-1b) (GaHV-2) (Marek's disease herpesvirus type 1)
1 entry
Getah virus (GETV)
1 entry
Gibbon ape leukemia virus (GALV)
1 entry
Gibbon hepatitis B virus subtype ayw3q (isolate Hope) (HBVgbn)
1 entry
Gorilla hepatitis B virus (isolate Cameroon/gor97) (HBVgor)
1 entry
Ground squirrel hepatitis virus (strain 27) (GSHV)
1 entry
Guanarito mammarenavirus (isolate Human/Venezuela/NH-95551/1990) (GTOV)
1 entry
Hamster parvovirus H1
1 entry
Hamster polyomavirus (HaPyV) (Mesocricetus auratus polyomavirus 1)
1 entry
Hantaan virus (strain B-1) (Korean hemorrhagic fever virus)
1 entry
Hantaan virus (strain Hojo) (Hojo virus) (Korean hemorrhagic fever virus)
1 entry
Hantaan virus (strain Lee) (Lee virus) (Korean hemorrhagic fever virus)
1 entry
Heartland virus (HTRV)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A1 subtype adw (isolate Philippines/pFDW294/1988) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A1 subtype adw2 (isolate South Africa/84/2001) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A1 subtype adw2 (isolate Southern-Africa/Cai) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 (isolate Japan/11D11HCCW/1998) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 subtype adw (isolate Japan/Nishioka/1983) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 subtype adw2 (isolate Germany/991/1990) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 subtype adw2 (strain Rutter 1979) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A3 (isolate Cameroon/CMR711/1994) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A3 (isolate Cameroon/CMR983/1994) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B/C subtype adw (isolate Okinawa/pODW282/1998) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B1 (isolate Japan/Ry30/2002) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B1 (isolate Japan/Yamagata-2/1998) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B1 subtype adw (isolate Japan/pJDW233/1988) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 (isolate Indonesia/pIDW420/1988) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 (isolate Vietnam/16091/1992) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 (isolate Vietnam/9873/1997) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 subtype adw (isolate China/patient4/1996) (HBV-B)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C (isolate Vietnam/3270/2000) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ad (isolate Japan/S-179/1988) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate China/NC-1/1988) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate Japan/A4/1994) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate Japan/Nishioka/1983) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate Korea/Kim/1989) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (strain Japan/adr4/1983) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ar (isolate Japan/S-207/1988) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ayw (isolate Australia/AustRC/1992) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ayw (isolate China/Tibet127/2002) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D (isolate France/alpha1/1989) (HBV-D)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D (isolate Germany/1-91/1991) (HBV-D)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979) (HBV-D)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate Australia/AustKW/1991) (HBV-D)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate Italy/CI/1992) (HBV-D)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype E (isolate Cote d'Ivoire/ABI-129/2003) (HBV-E)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype E (isolate Cote d'Ivoire/ABI-212/2003) (HBV-E)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype E subtype ayw4 (isolate Kou) (HBV-E)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype F1 (isolate Argentina/sa11/2000) (HBV-F)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype F2 (isolate Argentina/sa16/2000) (HBV-F)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype F2 (isolate Brazil/w4B) (HBV-F)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype F2 subtype adw4q (isolate Senegal/9203) (HBV-F)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype G (isolate IG29227/2000) (HBV-G)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype H (isolate United States/LAS2523/2002) (HBV-H)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype H subtype adw4 (isolate Nicaragua/1853Nic/1997) (HBV-H)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype H subtype adw4 (isolate Nicaragua/2928Nic/1997) (HBV-H)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1a (isolate 1) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate BK) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate Con1) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate HC-J1) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate HC-JT) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate HCR6) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate Japanese) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (isolate Taiwan) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (strain HC-J4) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1c (isolate HC-G9) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1c (isolate India) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 2a (isolate HC-J6) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 2a (isolate JFH-1) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 2b (isolate HC-J8) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 2b (isolate JPUT971017) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 2c (isolate BEBE1) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 2k (isolate VAT96) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 3a (isolate NZL1) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 3a (isolate k3a) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 3b (isolate Tr-Kj) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 3k (isolate JK049) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 4a (isolate ED43) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 5a (isolate EUH1480) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 5a (isolate SA13) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6a (isolate 6a33) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6a (isolate EUHK2) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6b (isolate Th580) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6d (isolate VN235) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6g (isolate JK046) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6h (isolate VN004) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6k (isolate VN405) (HCV)
1 entry
Hepatitis GB virus B (GBV-B) (GB virus B)
1 entry
Heron hepatitis B virus (HHBV)
1 entry
Hortulanus murine leukemia virus (HoMuLV) (Mus hortulanus virus)
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 (isolate Caribbea CH subtype A) (HTLV-1)
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 (isolate Melanesia mel5 subtype C) (HTLV-1)
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 (isolate Zaire EL subtype B) (HTLV-1)
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 (strain Japan MT-2 subtype A) (HTLV-1)
1 entry
Human T-cell leukemia virus 3 (strain Pyl43) (HTLV-3)
1 entry
Human adenovirus F serotype 41 (HAdV-41) (Human adenovirus 41)
1 entry
Human astrovirus VA1 (HAstV-VA1) (Mamastrovirus 9)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-2 (HAstV-2)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-3 (HAstV-3)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-4 (HAstV-4)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-5 (HAstV-5)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-6 (HAstV-6)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-7 (HAstV-7)
1 entry
Human astrovirus-8 (HAstV-8)
1 entry
Human coronavirus HKU1 (isolate N1) (HCoV-HKU1)
1 entry
Human coronavirus HKU1 (isolate N2) (HCoV-HKU1)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 1042) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 119) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 2387) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 4654) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 5035) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 5040) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 5160) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 5508) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain PT) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human cytomegalovirus (strain Towne) (HHV-5) (Human herpesvirus 5)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 70 (strain J670/71) (EV70) (EV-70)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 71 (EV71) (EV-71)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 71 (strain 7423/MS/87) (EV71) (EV-71)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 71 (strain USA/BrCr/1970) (EV71) (EV-71)
1 entry
Human enterovirus D68 (EV68) (EV-68)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain F) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain HFEM) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain KOS) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 6A (strain GS) (HHV-6 variant A) (Human B lymphotropic virus)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype A (isolate Z321) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BH10) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BH8) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BRVA) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate CDC-451) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate HXB3) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate JH32) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate JRCSF) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate KB-1/ETR) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate LW123) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate MFA) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate NY5) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate OYI) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate SC) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate SF162) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate SF33) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate WMJ1) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate WMJ22) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate YU-2) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype D (isolate NDK) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype D (isolate Z2/CDC-Z34) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype D (isolate Z6) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype D (isolate Z84) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype F2 (isolate MP255) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype F2 (isolate MP257) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype G (isolate 92NG083) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype H (isolate VI991) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype J (isolate SE9173) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype J (isolate SE9280) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype K (isolate 96CM-MP535) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype K (isolate 97ZR-EQTB11) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype U (isolate Z3) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group N (isolate YBF106) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group O (isolate MVP5180) (HIV-1)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate CAM2) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate D194) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate Ghana-1) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate KR) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate NIH-Z) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate ROD) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate SBLISY) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate ST) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate ST/24.1C#2) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype B (isolate D205) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype B (isolate EHO) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype B (isolate UC1) (HIV-2)
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 12
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 13
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 14
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 17
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 19
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 20
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 25
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 28
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 3
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 33
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 36
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 37
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 38
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 40
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 42
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 43
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 45
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 47
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 51
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 52
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 57
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 58
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 65
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 66
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 67
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 68
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 69
1 entry
Human papillomavirus 82
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 2a
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 49
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 53
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 55
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 5b
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 6a
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 6b
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type 8
1 entry
Human papillomavirus type ME180
1 entry
Human parainfluenza 1 virus (strain C39) (HPIV-1)
1 entry
Human parainfluenza 2 virus (HPIV-2)
1 entry
Human parainfluenza 2 virus (strain Greer) (HPIV-2)
1 entry
Human parainfluenza 3 virus (strain Wash/47885/57) (HPIV-3) (Human parainfluenza 3 virus (strain NIH 47885))
1 entry
Human parechovirus 1 (strain Harris) (HPeV-1) (Echovirus 22)
1 entry
Human parvovirus B19 (isolate AU) (HPV B19)
1 entry
Human respiratory syncytial virus
1 entry
Human respiratory syncytial virus A (strain A2)
1 entry
Human respiratory syncytial virus A (strain RSS-2)
1 entry
Human respiratory syncytial virus B (strain 18537)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 14 (HRV-14)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 16 (HRV-16)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 1A (HRV-1A)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 1B (HRV-1B)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 2 (HRV-2)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 3 (HRV-3)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus C (strain C15) (HRV-C15)
1 entry
Ilheus virus (ILHV)
1 entry
Impatiens necrotic spot virus (INSV)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Beijing/353/1989 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Beijing/39/1975 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Brazil/11/1978 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Brevig Mission/1/1918 H1N1) (Influenza A virus (strain A/South Carolina/1/1918 H1N1))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Budgerigar/Hokkaido/1/1977 H4N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Alabama/1/1975 H4N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Germany/n/1949 H10N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/220/1997 H5N1 genotype Gs/Gd)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/1/1983 H5N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Scotland/1959 H5N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Victoria/1/1985 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Weybridge H7N7) (Influenza A virus (strain A/FPV/Weybridge H7N7))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chile/1/1983 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/China:Nanchang/11/1996 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Alberta/28/1976 H4N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Alberta/35/1976 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Alberta/60/1976 H12N5)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Alberta/78/1976 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Australia/749/1980 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Czechoslovakia/1956 H4N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/England/1/1956 H11N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Germany/1949 H10N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Hokkaido/8/1980 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Hong Kong/2986.1/2000 H5N1 genotype C)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Ireland/113/1983 H5N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Memphis/928/1974 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/New Zealand/31/1976 H4N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Ukraine/1/1963 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/England/321/1977 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Algiers/1972 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/C.Detroit/1/1964 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Cambridge/1/1963 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Cambridge/1/1973 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Detroit/1/1964 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Fontainebleau/1976 H3N8) (Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/France/1/1976 H3N8))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Jillin/1/1989 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Kentucky/1/1981)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Kentucky/1/1987 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Kentucky/2/1986 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Lexington/1/1966 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/London/1416/1973 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Miami/1/1963 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/New Market/1/1977 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/New Market/1976 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Prague/1/1956 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Romania/1980 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Santiago/1/1985 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Sao Paulo/1/1976 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Suffolk/1989 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Switzerland/137/1972 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Tennessee/5/1986 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Tokyo/1971 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Uruguay/1/1963 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Fowl plague virus/Rostock/8/1934 H7N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Grey teal/Australia/2/1979 H4N4)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Astrakhan/227/1984 H13N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Maryland/704/1977 H13N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Minnesota/945/1980 H13N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Henry/1936 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Herring gull/DE/677/1988 H2N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hickox/1940 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/1/1968 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/156/1997 H5N1 genotype Gs/Gd)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/5/1983 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/India/6263/1980 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Japan/305/1957 H2N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Kiev/59/1979 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Korea/426/1968 H2N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Leningrad/1/1954 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Malaysia:Malaya/302/1954 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/Astrakhan/263/1982 H14N5) (Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/Gurjev/263/1982 H14N5))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/New York/6750/1978 H2N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/New York/6874/1978 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/Ohio/556/1987 H5N9)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/1/1971 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/101/1972 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/102/1972 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/110/1976 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/18/1978 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/2/1978 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/4/1980 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/6/1986 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/New Zealand:South Canterbury/35/2000 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Northern Territory/60/1968 H3N2) (Influenza A virus (strain NT60)) (Influenza A virus (strain A/NT/60/1968 H3N2))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Port Chalmers/1/1973 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Ruddy Turnstone/New Jersey/47/1985 H4N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Russia:St.Petersburg/8/2006 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Seal/Massachusetts/1/1980 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Seal/Massachusetts/133/1982 H4N5)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Shearwater/Australia/1972 H6N5)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Singapore/1/1957 H2N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Starling/Victoria/5156/1985 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Colorado/1/1977 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Indiana/1726/1988 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Iowa/15/1930 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Netherlands/12/1985 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/New Jersey/11/1976 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Ukkel/1/1984 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Wisconsin/1/1961 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Wisconsin/1/1967 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Tern/South Africa/1961 H5N3)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Ireland/1378/1983 H5N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Minnesota/1661/1981 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Minnesota/833/1980 H4N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Ontario/6118/1968 H8N4)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Ontario/7732/1966 H5N9)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Oregon/1971 H7N3)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Wisconsin/1/1966 H9N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Albany/12/1951 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Huston/AA/1945 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Iowa/1943 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Memphis/10/1996 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Phila/1935 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Texas/UR06-0195/2007 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/USSR/90/1977 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Udorn/307/1972 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Victoria/3/1975 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Whale/Maine/328/1984 H13N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Wilson-Smith/1933 H1N1) (Influenza A virus (strain A/WS/1933 H1N1))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/X-31 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza B virus (strain B/Beijing/1/1987)
1 entry
Influenza B virus (strain B/England/222/1982)
1 entry
Influenza B virus (strain B/Oregon/5/1980)
1 entry
Influenza B virus (strain B/Singapore/222/1979)
1 entry
Influenza B virus (strain B/Victoria/2/1987)
1 entry
Influenza C virus (strain C/California/1978)
1 entry
Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966)
1 entry
Influenza C virus (strain C/Nara/2/1985)
1 entry
Influenza C virus (strain C/Yamagata/4/1988)
1 entry
Ippy mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Central African Republic/Dak An B 188 d/1970) (IPPYV)
1 entry
Junin mammarenavirus (JUNV) (Junn mammarenavirus)
1 entry
KI polyomavirus (isolate Stockholm 350) (KIPyV)
1 entry
KI polyomavirus (isolate Stockholm 380) (KIPyV)
1 entry
KI polyomavirus (isolate Stockholm 60) (KIPyV)
1 entry
Koala retrovirus (KoRV)
1 entry
Kokobera virus (KOKV)
1 entry
Kunjin virus (strain MRM61C)
1 entry
Kyasanur forest disease virus (KFDV)
1 entry
Lactococcus phage F4-1 (Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage F4-1)
1 entry
Lake Victoria marburgvirus (strain Angola/2005) (MARV)
1 entry
Lake Victoria marburgvirus (strain Ozolin-75) (MARV) (Marburg virus (strain South Africa/Ozolin/1975))
1 entry
Lake Victoria marburgvirus (strain Popp-67) (MARV) (Marburg virus (strain West Germany/Popp/1967))
1 entry
Lake Victoria marburgvirus (strain Ravn-87) (MARV) (Marburg virus (strain Kenya/Ravn/1987))
1 entry
Langat virus (strain TP21)
1 entry
Lassa virus (strain GA391) (LASV)
1 entry
Louping ill virus (Li)
1 entry
Lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV)
1 entry
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (strain WE) (LCMV)
1 entry
Machupo virus (MACV)
1 entry
Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (MPMV) (Simian Mason-Pfizer virus)
1 entry
Mayaro virus (strain Brazil) (MAYV)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Edmonston B) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Edmonston) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Edmonston-AIK-C vaccine) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Edmonston-Zagreb vaccine) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Halle) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain IP-3-Ca) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Leningrad-16) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Philadelphia-26) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Measles virus (strain Yamagata-1) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
1 entry
Meleagrid herpesvirus 1 (MeHV-1) (Turkey herpesvirus)
1 entry
Middelburg virus
1 entry
Mink astrovirus 1 (MAstV-1)
1 entry
Mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus
1 entry
Mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus (isolate CI-3)
1 entry
Mink enteritis virus (strain Abashiri) (MEV)
1 entry
Mobala mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/Central African Republic/Acar 3080/1983) (MOBV)
1 entry
Monkeypox virus (strain Zaire-96-I-16) (MPX)
1 entry
Mopeia virus (MOPV)
1 entry
Mouse intracisternal a-particle MIAE (IAP-MIAE)
1 entry
Mouse mammary tumor virus (strain GR) (MMTV)
1 entry
Mumps virus (strain Kilham) (MuV)
1 entry
Mumps virus (strain RW) (MuV)
1 entry
Mumps virus (strain SBL) (MuV)
1 entry
Mumps virus (strain SBL-1) (MuV)
1 entry
Mumps virus genotype N (strain L-Zagreb vaccine) (MuV)
1 entry
Murid herpesvirus 1 (strain K181) (MuHV-1) (Mouse cytomegalovirus)
1 entry
Murine coronavirus (strain 4) (MHV-4) (Murine hepatitis virus)
1 entry
Murine coronavirus (strain JHM) (MHV-JHM) (Murine hepatitis virus)
1 entry
Murine coronavirus (strain JHMV / variant CL-2) (MHV) (Murine hepatitis virus)
1 entry
Murine minute virus (strain MVMi) (MVM) (Murine parvovirus)
1 entry
Murine polyomavirus (strain A3) (MPyV)
1 entry
Murine polyomavirus (strain Crawford small-plaque) (MPyV)
1 entry
Murine polyomavirus (strain Kilham) (MPyV) (Murine pneumotropic virus)
1 entry
Murine polyomavirus (strain P16 small-plaque) (MPyV)
1 entry
Murray valley encephalitis virus (strain MVE-1-51) (MVEV)
1 entry
Myeloproliferative leukemia virus (MpLV)
1 entry
Myxoma virus (strain Uriarra) (MYXV)
1 entry
New York virus (NYV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain B1-Hitchner/47) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Beaudette C/45) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Chicken/Australia-Victoria/32) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Chicken/Northern Ireland/Ulster/67) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Chicken/United States(TX)/GB/48) (NDV) (Newcastle disease virus (strain Texas g.b./48))
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Chicken/United States/LaSota/46) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain D26/76) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Her/33) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Italien/45) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Miyadera/51) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Queensland/66) (NDV)
1 entry
Newcastle disease virus (strain Texas) (NDV)
1 entry
O'nyong-nyong virus (strain Gulu) (ONNV)
1 entry
O'nyong-nyong virus (strain Igbo Ora) (ONNV) (Igbo Ora virus)
1 entry
O'nyong-nyong virus (strain SG650) (ONNV)
1 entry
Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus (OHFV)
1 entry
Orangutan hepatitis B virus (isolate Somad) (HBVoru)
1 entry
Ovine astrovirus 1 (OAstV-1)
1 entry
Pariacoto virus (PaV)
1 entry
Parvovirus LuIII
1 entry
Phocine distemper virus (PDV)
1 entry
Pichinde mammarenavirus (PICV) (Pichind mammarenavirus)
1 entry
Pigeon circovirus (PiCV) (Columbid circovirus)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 1 (strain Sabin)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 2 (strain Lansing)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 2 (strain W-2)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 3 (strain 23127)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 3 (strains P3/Leon/37 and P3/Leon 12A[1]B)
1 entry
Porcine astrovirus 1 (PAstV-1)
1 entry
Porcine enterovirus 9 (strain UKG/410/73)
1 entry
Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (strain IAF-404) (HEV)
1 entry
Porcine parvovirus (strain 90HS) (PPV)
1 entry
Porcine parvovirus (strain Kresse) (PPV)
1 entry
Porcine parvovirus (strain NADL-2) (PPV)
1 entry
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (isolate Pig/United States/SD 01-08/2001) (PRRSV)
1 entry
Prospect Hill virus (PHV)
1 entry
Punta toro phlebovirus
1 entry
Puumala virus (strain Bank vole/Russia/CG1820/1984)
1 entry
Puumala virus (strain K27)
1 entry
Puumala virus (strain P360)
1 entry
Rabbitpox virus (strain Utrecht) (RPV)
1 entry
Radiation murine leukemia virus
1 entry
Radiation murine leukemia virus (strain Kaplan)
1 entry
Rat coronavirus (strain 681) (RCV-SDAV) (Sialodacryoadenitis virus SDAV-681)
1 entry
Rauscher mink cell focus-inducing virus
1 entry
Rauscher spleen focus-forming virus (RSFFV)
1 entry
Reovirus type 2 (strain D5/Jones) (T2J) (Mammalian orthoreovirus 2)
1 entry
Reovirus type 3 (strain Dearing) (T3D) (Mammalian orthoreovirus 3)
1 entry
Reston ebolavirus (strain Philippines-96) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
1 entry
Reston ebolavirus (strain Reston-89) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
1 entry
Reston ebolavirus (strain Siena/Philippine-92) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
1 entry
Rift valley fever virus (RVFV)
1 entry
Rinderpest virus (strain Kabete O) (RDV)
1 entry
Rinderpest virus (strain L) (RDV)
1 entry
Rinderpest virus (strain RBT1) (RDV)
1 entry
Rocio virus (ROCV)
1 entry
Ross river virus (strain NB5092) (RRV)
1 entry
Ross river virus (strain T48) (RRV)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cat/Japan/FRV-1/1986/G3P3[9]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (isolate FRV1))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cat/Japan/FRV64/1989/G3P5B[3]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/Germany/993/1983/G18P[17]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/India/Hg18/2000/G15P[21]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/Japan/KK3/1983/G10P8[11]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/South/Africa/Offal agent/1965/G8P6[1]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/Thailand/61A/1988/G10P7[5]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/Thailand/A44/1988/G10P8[11]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/Thailand/A5/1988/G8P6[1]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/United States/B223/1983/G10P8[11]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Cow/United States/VMRI/1988/G6P[5]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Dog/United States/Cu-1/1982/G3P5A[3]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Dog/United States/K9/1981/G3P5A[3]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Equine/Japan/HO-5/1980/G3P[X]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Equine/United Kingdom/H2/1976/G3P4[12]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (isolate H-2))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Equine/United Kingdom/L338/1988/G13P12[18]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/Australia/McN13/1980/G3P2A[6]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/Belgium/B4106/2000/G3P11[14]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (isolate B4106))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/India/116E/1986/G9P8[11]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/Israel/RO1845/1993/G3P5A[3]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/Italy/VA70/1975/G4P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/Sweden/1076/1983/G2P2A[6]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/Thailand/Mc35/1992/G10P11[14]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/United Kingdom/A64/1987/G10P11[14]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Human/United States/WI61/1983/G9P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Monkey/United States/TUCH/2003/G3P[24]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Mouse/Brazil/EHP/1981/G16P[20]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Mouse/United States/Eb/1982/G16P10[16]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Pig/Australia/CRW-8/1987/G3P9[7]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Pig/Venezuela/A46/1985/G5P13[13]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Cow/Canada/C486/1977/G6P6[1]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Cow/France/RF/1975/G6P6[1]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Cow/United Kingdom/UK/1975/G6P7[5]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Cow/United States/B641/XXXX/G6P7[5]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Cow/United States/NCDV-Lincoln/1969/G6P6[1]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain Nebraska calf diarrhea virus))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Cow/United States/WC3/1981/G6P7[5]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus (strain Wistar calf 3))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Equine/United States/FI-14/1980/G3P4[12]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain FI14))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Australia/RV-5/1981/G2P1B[4]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain RV5))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Indonesia/69M/1980/G8P4[10]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Japan/AU-1/1982/G3P3[9]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Japan/K8/1977/G1P3A[9]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Japan/KU/1995/G1P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Japan/MO/1982/G3P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Japan/YO/1977/G3P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Philippines/L26/1987/G12P1B[4]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/United Kingdom/ST3/1975/G4P2A[6]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain St. Thomas 3))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/United States/DS-1/1976/G2P1B[4]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain DS1))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/United States/P/1974/G3P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/United States/Wa/1974/G1P1A[8]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Human/Venezuela/M37/1982/G1P2A[6]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Pig/Mexico/YM/1983/G11P9[7]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Pig/United States/Gottfried/1983/G4P2B[6]) (RV-A)
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Pig/United States/OSU/1977/G5P9[7]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain Ohio State University))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Rabbit/United States/ALA/XXXX/G3P11[14]) (RV-A) (Rotavirus A (strain Alabama))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/SA11-4F/G3P6[1]) (RV-A) (Simian Agent 11 (strain 4F))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/SA11-FEM/G3P6[1]) (RV-A) (Simian Agent 11 (strain FEM))
1 entry
Rotavirus A (strain RVA/SA11-SEM/G3P5B[2]) (RV-A) (Simian Agent 11 (strain SEM))
1 entry
Rotavirus B (isolate RVB/Human/China/ADRV/1982) (RV-B) (Rotavirus B (isolate adult diarrhea rotavirus))
1 entry
Rotavirus B (isolate RVB/Rat/United States/IDIR/1984/G1P[X]) (RV-B) (Rotavirus B (isolate infectious diarrhea of infant rats))
1 entry
Rotavirus C (isolate RVC/Cow/Japan/Shintoku/1991/G2P[3]) (RV-C)
1 entry
Rotavirus C (strain RVC/Pig/United States/Cowden/1980) (RV-C)
1 entry
Rotavirus X (isolate RVX/Human/Bangladesh/NADRV-B219/2002/GXP[X]) (RV ADRV-N) (Rotavirus (isolate novel adult diarrhea rotavirus-B219))
1 entry
Rous sarcoma virus subgroup B (strain Schmidt-Ruppin) (RSV-SR-B)
1 entry
Rous sarcoma virus subgroup C (strain Prague) (RSV-Pr-C)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain BRD1) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain BRDII) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain Cendehill) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain M33) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain RA27/3 vaccine) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain RN-UK86) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain TO-336 vaccine) (RUBV)
1 entry
Rubella virus (strain TO-336) (RUBV)
1 entry
Sabia mammarenavirus (isolate Human/Brasil/SPH114202/1990) (SABV) (Sabi mammarenavirus)
1 entry
Sagiyama virus (SAGV)
1 entry
Sendai virus (strain Fushimi) (SeV)
1 entry
Sendai virus (strain Hamamatsu) (SeV)
1 entry
Sendai virus (strain Harris) (SeV)
1 entry
Sendai virus (strain Z) (SeV) (Sendai virus (strain HVJ))
1 entry
Seoul virus (strain 80-39)
1 entry
Seoul virus (strain R22)
1 entry
Seoul virus (strain SR-11) (Sapporo rat virus)
1 entry
Serratia phage KSP90 (Serratia marcescens bacteriophage KSP90)
1 entry
Sheep pulmonary adenomatosis virus (Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus) (JSRV)
1 entry
Sheeppox virus (strain KS-1) (SPPV) (Capripoxvirus (strain KS-1))
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate F236/smH4) (SIV-sm) (Simian immunodeficiency virus sooty mangabey monkey)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate GB1) (SIV-mnd) (Simian immunodeficiency virus mandrill)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate K6W) (SIV-mac) (Simian immunodeficiency virus rhesus monkey)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate K78) (SIV-mac) (Simian immunodeficiency virus rhesus monkey)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate Mm142-83) (SIV-mac) (Simian immunodeficiency virus rhesus monkey)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate Mm251) (SIV-mac) (Simian immunodeficiency virus rhesus monkey)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus (isolate PBj14/BCL-3) (SIV-sm) (Simian immunodeficiency virus sooty mangabey monkey)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus agm.grivet (isolate AGM gr-1) (SIV-agm.gri) (Simian immunodeficiency virus African green monkey grivet)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus agm.vervet (isolate AGM TYO-1) (SIV-agm.ver) (Simian immunodeficiency virus African green monkey vervet)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus agm.vervet (isolate AGM155) (SIV-agm.ver) (Simian immunodeficiency virus African green monkey vervet)
1 entry
Simian immunodeficiency virus agm.vervet (isolate AGM3) (SIV-agm.ver) (Simian immunodeficiency virus African green monkey vervet)
1 entry
Simian retrovirus SRV-1
1 entry
Simian retrovirus SRV-2
1 entry
Simian retrovirus SRV-2 (isolate 2R-18B1)
1 entry
Sin Nombre orthohantavirus (SNV) (Sin Nombre virus)
1 entry
Sindbis virus subtype Ockelbo (strain Edsbyn 82-5) (OCKV) (Ockelbo virus)
1 entry
Squirrel monkey retrovirus (SMRV-H) (SMRV-HLB)
1 entry
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Boniface-76) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus)
1 entry
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Human/Uganda/Gulu/2000) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus)
1 entry
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Maleo-79) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus)
1 entry
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Indiana-Funkhauser / Becker) (SuHV-1) (Pseudorabies virus (strain Indiana-Funkhauser / Becker))
1 entry
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain NIA-3) (SuHV-1) (Pseudorabies virus (strain NIA-3))
1 entry
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Rice) (SuHV-1) (Pseudorabies virus (strain Rice))
1 entry
Swine vesicular disease virus (strain H/3 '76) (SVDV)
1 entry
Swine vesicular disease virus (strain UKG/27/72) (SVDV)
1 entry
Tacaribe virus (strain TRVL 11598) (TCRV)
1 entry
Tacaribe virus (strain V5) (TCRV)
1 entry
Tacaribe virus (strain V7) (TCRV)
1 entry
Tai Forest ebolavirus (strain Cote d'Ivoire-94) (TAFV) (Cote d'Ivoire Ebola virus)
1 entry
Tamiami mammarenavirus (isolate Rat/United States/W 10777/1964) (TAMV)
1 entry
Tembusu virus (TMUV)
1 entry
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (strain Hypr) (TBEV)
1 entry
Tick-borne encephalitis virus European subtype (strain Neudoerfl) (NEUV) (Neudoerfl virus)
1 entry
Tick-borne encephalitis virus Far Eastern subtype (strain Sofjin) (SOFV) (Sofjin virus)
1 entry
Tick-borne powassan virus (strain LB) (POWV) (Powassan virus)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (isolate D) (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Regular2A) (TSWV)
1 entry
Tula orthohantavirus (TULV) (Tula virus)
1 entry
Turkey rhinotracheitis virus (TRTV)
1 entry
Usutu virus (USUV)
1 entry
Vaccinia virus (strain L-IVP) (VACV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain 3880) (VEEV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain Everglades Fe3-7c) (VEEV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain Mena II) (VEEV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain P676) (VEEV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain TC-83) (VEEV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain Trinidad donkey) (VEEV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 85CLB South America) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 94GUB Central America) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 98COE North America) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain Glasgow) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain Mudd-Summers) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain Orsay) (VSIV)
1 entry
Wesselsbron virus (WSLV)
1 entry
West Nile virus (WNV)
1 entry
West Nile virus (strain NY-99) (WNV) (West Nile virus (strain NY-1999))
1 entry
Western equine encephalitis virus (WEEV)
1 entry
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 1) (WHV)
1 entry
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 2) (WHV)
1 entry
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 59) (WHV)
1 entry
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 7) (WHV)
1 entry
Woolly monkey hepatitis B virus (isolate Louisville) (WMHBV)
1 entry
Xenotropic MuLV-related virus (isolate VP35) (XMRV)
1 entry
Xenotropic MuLV-related virus (isolate VP42) (XMRV)
1 entry
Yaba-like disease virus (YLDV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Angola/14FA/1971) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Ethiopia/Couma/1961) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Ivory Coast/1999) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Ivory Coast/85-82H/1982) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Uganda/A7094A4/1948) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain French neurotropic vaccine FNV) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain Ghana/Asibi/1927) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain Trinidad/TRINID79A/1979) (YFV)
1 entry
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Eckron-76) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
1 entry
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Gabon-94) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
1 entry
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Kikwit-95) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
1 entry
Zika virus (isolate ZIKV/Human/Cambodia/FSS13025/2010) (ZIKV)
1 entry
