Topocuvirus (taxid:220339)
VIRION
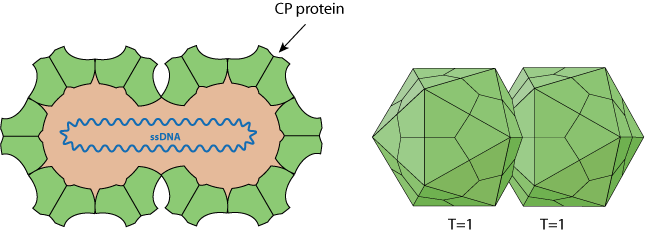
Non-enveloped, about 38 nm in length and 22 nm in diameter (for MSV), twinned (geminate) incomplete T=1 icosahedral symmetry capsid that contains 22 pentameric capsomers made of 110 capsid proteins (CP). Each geminate particle contains only a single circular ssDNA.
GENOME
Monopartite, circular, ssDNA genome (+) genome of 2.86 kb. 3' terminus has no poly(A) tract. There are coding regions in both the virion (positive) and complementary (negative) sense strands.
The genome is replicated through double-stranded intermediates. The replication (Rep) protein initiates and terminates rolling circle replication, the host DNA polymerase being used for DNA replication itself. There is a potential stem-loop structure in the intergenic region that includes a conserved nonanucleotide sequence (TAATATTAC) where ssDNA synthesis is initiated.
GENE EXPRESSION
Transcription is bidirectional from the common region (CR), which corresponds to the non-coding region common for topocu- and begomoviruses. 6 proteins are produced. In the V-sense: V2 and CP. In the C-sense: Rep, C2, C3 and C4.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
- Virus penetrates into the host cell.
- Uncoating, the viral ssDNA genome penetrates into the nucleus.
- The ssDNA is converted into dsDNA with the participation of cellular factors.
- bidirectional dsDNA transcription from the IR promoter produces viral mRNAs and translation of viral proteins.
- Replication is initiated by cleavage of the (+)strand by REP, and occurs by rolling circle producing ssDNA genomes.
- These newly synthesized ssDNA can either
a) be converted to dsDNA and serve as a template for transcription/replication
b) be encapsidated by capsid protein and form virions released by cell lysis
c) be transported outside the nucleus, to a neighboring cell through plasmodesmata (cell-cell movement) with the help of viral movement proteins.
Host-virus interaction
Cell-cycle modulation
Topocuvirus protein Rep is probably responsible for inhibiting host retinoblastoma protein and inducing transition from the G1 to S phase in preparation for virus replication since the virus targets differentiated non-dividing cells.
 .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)6 entries grouped by strain
6 entries
