Microtubular outwards viral transport (kw:KW-1189)
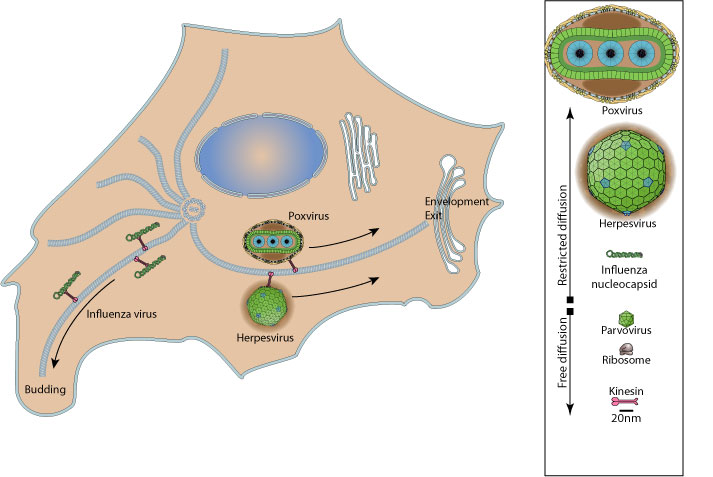
In a cell, structures exceeding 20 nm require energy-dependent motility to travel through the cytosol. Therefore viruses take advantage of molecular motors to move newly assembled viral progeny to the plasma membrane to facilitate their spread into surrounding cells  .
.
Microtubule-dependent outward transport involves motor proteins like kinesin  .
.
The taking of the cytoskeleton one two three: how viruses utilize the cytoskeleton during egress.
Virology. 2011 Mar 15;411(2):244-50. PubMed PMID: 21241997
Virology. 2011 Mar 15;411(2):244-50. PubMed PMID: 21241997
Coupling viruses to dynein and kinesin-1.
EMBO J. 2011 Aug 31;30(17):3527-39. PubMed PMID: 21878994
EMBO J. 2011 Aug 31;30(17):3527-39. PubMed PMID: 21878994
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)9 entries grouped by strain
1 entry
African swine fever virus (strain Badajoz 1971 Vero-adapted) (Ba71V) (ASFV) reference strain
1 entry
Monkeypox virus reference strain
1 entry
Vaccinia virus (strain Copenhagen) (VACV) reference strain
1 entry
Vaccinia virus (strain Western Reserve) (VACV) (Vaccinia virus (strain WR)) reference strain
1 entry
Variola virus (isolate Human/India/Ind3/1967) (VARV) (Smallpox virus) reference strain
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Pig/Kenya/KEN-50/1950) (ASFV)
1 entry
Camelpox virus (strain M-96)
1 entry
Vaccinia virus (strain Ankara) (VACV)
1 entry
