VIRION
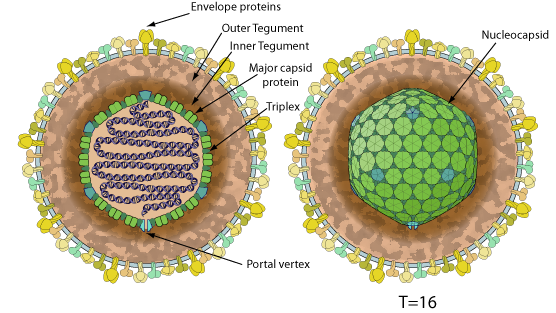
Enveloped, spherical to pleomorphic, 150-200 nm in diameter, T=16 icoseadral symmetry. Capsid consists of 162 capsomers. Glycoproteins complexes are embeded in the lipid envelope.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, dsDNA genome of 134 kb. The genome contains terminal and internal reiterated sequences.
GENE EXPRESSION
Each viral transcript usually encodes a single protein and has a promoter/regulatory sequence, a TATA box, a transcription initiation site, a 5' leader sequence of 30-300 bp (not translated), a 3' nontranslated sequence of 10-30 bp, and a poly A signal. There are many gene overlaps. There are only few spliced genes. Some of the expressed ORFs are antisense to each other. Some ORFs can be accessed from more than one promoter. There are some non-coding genes.
ENZYMES
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- Primase
- Ribonucleotide reductase
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
Lytic replication:
- Virus attaches to host receptors through gB, gC, gD and gH .
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the core and the tegument proteins into the host cytoplasm.
- The capsid is transported to the nuclear pore where the viral DNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcription of immediate early genes which promote transcription of early genes.
- Transcription of early viral mRNA by host polymerase II, transport into the cytoplasm and translation into early proteins.
- Early proteins are involved in replication of the viral DNA and are transported back into the nucleus.
- Synthesis of multiple copies of viral DNA by the viral DNA-dependent DNA polymerase.
- Transcription of late mRNAs by host polymerase II, transport into the cytoplasm and translation into late proteins.
- Late proteins are structural or core proteins and are transported back into the nucleus.
- Assembly of the virus and budding through the inner lamella of the nuclear membrane which has been modified by the insertion of herpes glycoproteins, throughout the Golgi and final release at the plasma membrane.
Latent replication : replication of circular viral episome in tandem with the host cell DNA using the host cell replication machinery.

