Toursvirus (taxid:1921707)
VIRION
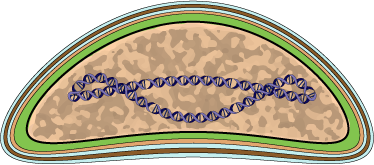
Virions consist of an envelope, a core, and an internal lipid membrane associated with the inner particle. Virion can be bacilliform, ovoidal or allantoid in shape, mesuring about 130 nm in diameter, by 200-400 nm in length. Contains at least 15 different proteins.
GENOME
Circular, dsDNA genome of 156-186 kb. The genome contains two tandem of inverted repeats.
GENE EXPRESSION
Encode for up to 180 open reading frames.
ENZYMES
- DNA-directed DNA polymerase [RT]
- Peptidase C1A [F2NYX77]
- Peptidase metallopeptidase [F2NYV8]
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase [F2NZ02, F2NYZ9]
- Endonuclease [F2NZ21]
- Metallo-beta-lactamase [F2NZ47]
- Phospholipid/glycerol acyltransferase [F2NZ10]
- Calcineurin-like phosphoesterase [F2NZ10]
- Ribonucleotide reductase [F2NYY3]
- Helicase [F2NYU9, F2NZ22, F2NZ19, F2NZ48]
- Fatty acid desaturase [F2NZ38]
- Deoxynucleoside kinase [F2NYY4]
- Nudix hydrolase [F2NYT4]
- ERV/ALR sulfhydryl oxidase [F2NYX0]
- Protein kinase [F2NZ09, F2NZ44]
- RNAse III [F2NYT2]
REPLICATION
NUCLEUS
- Attachment of the viral proteins to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the plasma membrane occurs; and the viral DNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcription of viral genes, replication of the DNA genome in the nucleus.
- Cell nucleus enlarges and ruptures.
- Assembly of new virions in the cytoplasm.
- Host cell is cleaved in cluster of virion-containing vesicles.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
The Spodoptera frugiperda ascovirus encodes a viral caspase that is able to induce apoptosis in insect cells.
