Eukaryotic host transcription shutoff by virus (kw:KW-1191)
Host RNA polymerase II (RNA pol-II) is the major enzyme responsible for transcription of mRNA from a DNA template strand.
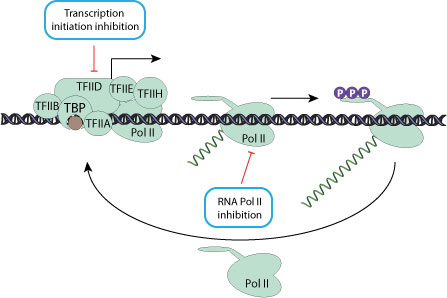
Some viruses interfere with host RNA pol-II function. They may either mediate its ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation, or inhibit RNA pol-II phosphorylation thereby lowering its efficiency. They can as well interfere with initiation factors. Inhibiting host transcription eventually leads to shutoff of host proteins expression and gives viruses transcripts a competitive edge for access to the cellular translation machinery. Preventing the expression of host proteins is also a strategy to counteract the antiviral response.
Viruses inhibiting transcription:
| Family | Virus | Viral protein | Transcription inhibition strategy | references |
| Herpesviridae | HHV-1 | ICP22 | Counteracts CTD Ser-2 phosphorylation |

|
| Bunyaviridae | Bunyamwera virus | NSs | Counteracts CTD Ser-2 phosphorylation |

|
| Orthomyxoviridae | Influenza virus | Polymerase PB1, PB2, PA | RNA pol-II ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation |

|
| Papillomaviridae, alphapapillomavirus | HPV16 | E7 | Inhibition of TBP |

|
| Picornaviridae | Poliovirus | 3C | Cleavage of TBP |

|
| Bunyaviridae, Phlebovirus | Rift valley fever virus | NSs | Downregulates TFIIH subunit p62 |

|
| Herpesviridae, Varicellovirus | Varicella virus | IE63 | Disruption of the transcriptional pre-initiation complex |

|
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)348 entries grouped by protein
2 entries
Early E1A protein (Early E1A 32 kDa protein)
3 entries
Transcriptional regulator ICP22 (Immediate-early protein IE68) (Infected cell protein 22) (ICP22)
6 entries
Non-structural protein NS-S
98 entries
Polymerase acidic protein (EC 3.1.-.-) (RNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit P2)
97 entries
Polymerase basic protein 2 (RNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit P3)
5 entries
Genome polyprotein
25 entries
Polyprotein P1234 (P1234) (Non-structural polyprotein)
12 entries
Structural polyprotein (p130)
99 entries
RNA-directed RNA polymerase catalytic subunit (EC 2.7.7.48) (Polymerase basic protein 1) (PB1) (RNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit P1)
1 entry
