CRISPR-cas system evasion by virus (kw:KW-1257)
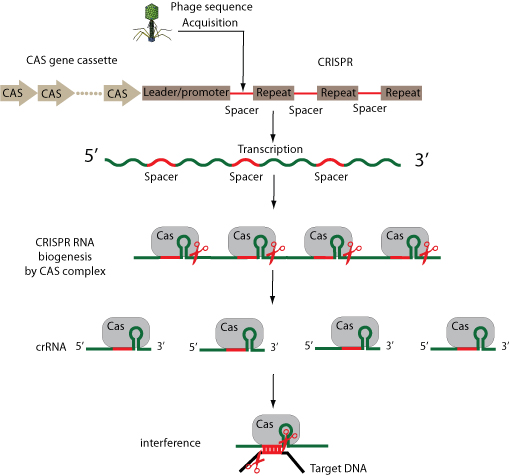
CRISPR/Cas (clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats /CRISP-associated proteins) system is a prokaryotic antiviral resistance mechanism which constitutes the only documented bacterial adaptive immune system. The adaptive feature of CRISPR-Cas immune system relies on its ability to integrate foreign short DNA sequences of invading molecules and integrate them in between the repetitive sequences of the CRISPR array in the form of
spacers.
Following transcription and processing of these loci, the CRISPR antisens RNAs (crRNAs) guide the Cas proteins to complementary invading nucleic acid, which results in target interference.
The acquisition of new spacers allows the CRISPR-Cas immune system to rapidly adapt against new threats 


 .
.
Wikipedia
Bacterial viruses have developed strategies to circumvent this bacterial defense 
 . Gene 35 from the Pseudomonas phage JBD30 encodes a protein able to suppress the CRISPR system, most probably after the crRNA biogenesis
. Gene 35 from the Pseudomonas phage JBD30 encodes a protein able to suppress the CRISPR system, most probably after the crRNA biogenesis .
.
The vibrio cholera phage ICP1 instead encodes its own CRISPR/Cas system to counteract a phage inhibitory chromosomal island of the bacterial host
 .
.
Joe Bondy-Denomy, April Pawluk, Karen L Maxwell, Alan R Davidson
Nature January 17, 2013; 493: 429-432
Joe Bondy-Denomy, April Pawluk, Karen L Maxwell, Alan R Davidson
Nature January 17, 2013; 493: 429-432.
Joseph Bondy-Denomy, Alan R Davidson
Trends Microbiol. February 26, 2014;
Katharina Stummeyer, David Schwarzer, Heike Claus, Ulrich Vogel, Rita Gerardy-Schahn, Martina M?hlenhoff
Mol. Microbiol. June 2006; 60: 1123-1135
Timothy R Sampson, Sunil D Saroj, Anna C Llewellyn, Yih-Ling Tzeng, David S Weiss
Nature May 9, 2013; 497: 254-257
Joe Bondy-Denomy, April Pawluk, Karen L Maxwell, Alan R Davidson
Nature January 17, 2013; 493: 429-432
Barrangou R, Marraffini LA
Mol Cell. Apr 24, 2014; 54(2):234-44
April Pawluk, Joseph Bondy-Denomy, Vivian H. W. Cheung, Karen L. Maxwell, Alan R. Davidson
MBio 2014; 5: e00896
Kimberley D Seed, David W Lazinski, Stephen B Calderwood, Andrew Camilli
Nature February 28, 2013; 494: 489-491
Alexandra L. Bryson, Young Hwang, Scott Sherrill-Mix, Gary D. Wu, James D. Lewis, Lindsay Black, Tyson A. Clark, Frederic D. Bushman
MBio 2015; 6: e00648
Joseph Bondy-Denomy, Bianca Garcia, Scott Strum, Mingjian Du, MaryClare F. Rollins, Yurima Hidalgo-Reyes, Blake Wiedenheft, Karen L. Maxwell, Alan R. Davidson
Nature October 1, 2015; 526: 136?139
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)3 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Anti-CRISPR protein 30 (Gene product 30) (gp30)
1 entry
Anti-CRISPR protein 31 (ACR3112-31) (Gene product 31) (gp31)
1 entry
