Some bacterial viruses encode factors that modulate the virulence of bacterial host against a third organism. This change in properties of the host can occur at different levels including bacterial adhesion, spread through human tissues, exotoxin production or protection against immune defenses. These virulence factors are mostly expressed from integrated viral genomes and provide strong advantages to the bacterial host that carry them.
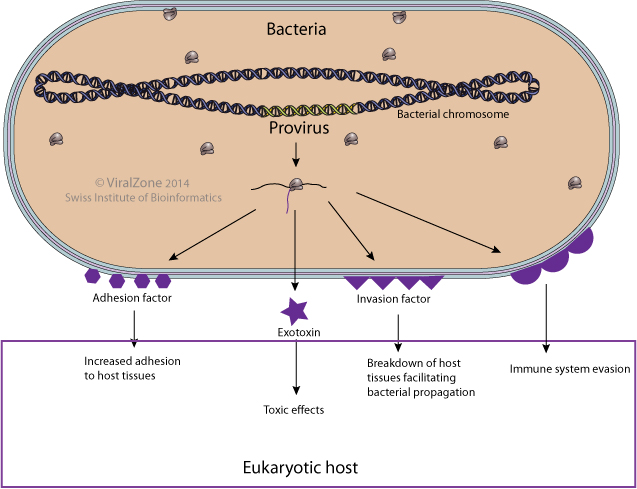
Adhesion
- The phage SM1 encode PblA and PblB that promote binding of Streptococcus mitis to human platelets
- The phage lambda lom gene product promotes adhesion to buccal epithelial cells
Survival of intracellular bacteria
- The phage Gifsy-2 encodes a periplasmic copper- and zinc-cofactored superoxyde dismutase protecting the intracellular bacterium from oxydative stress  .
.
Exotoxin
- Phage encoded Shiga toxin (Stx) acts as a bacterial defense against the eukaryotic predator Tetrahymena
- Phage encoded diphteria toxin causes the disease diphtheria in humans by gaining entry into the cytoplasm of cells and inhibiting protein synthesis.
Invasion
Some phages encode invasins that allow the bacteria to penetrate the eukaryotic host tissue layers or cells.
Some of these proteins catalyze the breakdown of tissues in the eukaryotic host. From a confined site of infection, the bacteria can thus spread to other parts of the organism.
- Hyaluronidase for example breaks down hyaluronan, a constituent of the extracellular matrix to increase tissue permeability and allow bacterial spread.
- The complex formed by staphylokinase and plasminogen (PLG) displays a plasmin-like proteolytic activity which lyses fibrin and causes dissolution if fibrin clots. This activity may improve bacterial invasion of host tissues.
- The gifsy-1 phage encodes gipA helps the bacteria to colonize the small intestine and invade the intestinal epithelium
- Other protein like SopE are invasion factors that are injected in the eukaryotic cell to subvert host key signaling pathways for the benefit of the invading bacteria.
The salmonella phage encoded sopE protein promotes uptake of its host in intestinal epithelial cells

Eukaryotic host immune system evasion
Some phage encoded virulence factor allow the bacteria to evade the eukaryotic host immune system. These factors can alter bacterial antigenicity and thus recognition by the host immune system or provide serum resistance.
Phage-encoded virulence factors
Source:Common themes among bacteriophage-encoded virulence factors and diversity among the bacteriophages involved 
Boyd EF, Brussow H
Trends Microbiol. 2002 Nov;10(11):521-9
| Virus | Host bacteria | Virulence factor | Gene | Type/function |
| β-phage | Corynebacterium diphtheriae | Diphtheria toxin | tox | Exotoxin |
| Phage C1 | Clostridium botulinum | Neurotoxin | C1 | Exotoxin |
| Phage H-19B, Enterobacteria phage 933W | Escherichia coli | Shiga toxin 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B | stx1AB stx2AB |
Exotoxin |
| Phage CTXΦ | Vibrio cholerae | Cholera toxin A, B | ctxAB | Exotoxin |
| Phage ΦC3208 | Escherichia coli | Hemolysin | hly2 stx2AB |
Exotoxin |
| Phage ΦCTX | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Cytotoxin | ctx | Exotoxin |
| Phage N315 | Staphylococcus aureus | Enterotoxin P | sep | Exotoxin |
| Phage Mu50A | Staphylococcus aureus | Enterotoxin A | sea | Exotoxin |
| Phage Φ13 | Staphylococcus aureus | Enterotoxin A | entA | Exotoxin |
| Phage ΦETA | Staphylococcus aureus | Exfoliative toxin A | eta | Exotoxin |
| Phage ΦPVL | Staphylococcus aureus | Panton-Valentine leukocidin S, F | lukS | Exotoxin/Invasin |
| Phage T12 | Streptococcus pyogenes | Toxin A | speA | Exotoxin |
| Phage CS112 | Streptococcus pyogenes | Toxin C | speC | Exotoxin |
| Phage Ε34 | Salmonella enterica | Glucosylation | rfb | Antigenicity modulator |
| Phage P22 | Salmonella enterica | Glucosylation | gtr | Antigenicity modulator |
| Phage sf6 | Shigella flexneri | O-antigen acetylase | oac | Antigenicity modulator |
| Phage SfX | Shigella flexneri | Glucosyl transferase | gtrB | Antigenicity modulator |
| Phage SopEΦ | Salmonella typhimurium | Type III secretion effector | sopE | Invasin |
| Phage Gifsy-2 | Salmonella typhimurium | Type III secretion effector | ssel | Invasin |
| Phage SopEΦ | Salmonella typhimurium | Type III secretion effector | sopE | Invasin |
| Phage Gifsy-1 | Salmonella enterica | Type III secretion effector | gogB | Invasin |
| Phage Sp4 | Escherichia coli | Superoxyde dismutase | sodC | Intracellular survival (macrophages) |
| Phage Gifsy-2 | Salmonella typhimurium | Superoxyde dismutase | sodC | Intracellular survival (macrophages) |
| Phage Fels-1 | Salmonella enterica | Superoxyde dismutase | sodC-III | Intracellular survival (macrophages) |
| Phage Φ13 | Salmonella aureus | Staphylokinase | sak | Invasin |
| Phage H4489A | Streptococcus pyogenes | Hyaluronidase | hylP | Invasin |
| Phage lambda | Escherichia coli | Outer membrane protein Lom | lom | Adhesin |
| Phage lambda | Escherichia coli | Outer membrane protein Bor | bor | Resistance factor to serum complement killing |
| Phage lambda-like | Escherichia coli | Outer membrane protein | eib | Resistance factor to serum complement killing |
| Phage MAV-1 | Mycoplasma arthritidis | Vir | vir | Adhesin |
| Phage SM1 | Streptococus mitis | Capsid proteins pblA, pblB | pbla, pblb | Adhesin |
| Phage VPIΦ | Vibrio cholerae | TCP pilus | tcp | Adhesin |
| Phage Gifsy-1 | Salmonella typhimurium | GipA | gipA | Invasin |

