Inhibition of host complement factors by virus (kw:KW-1087)
The complement system is a major non-specific mechanism of humoral immunity. The activation of complement involves the sequential proteolyis of proteins to generate enzymes with catalytic activities. The biological functions of the complement include opsonization, inflammation, lysis of immune complexes, or enhancement of the humoral immune response.
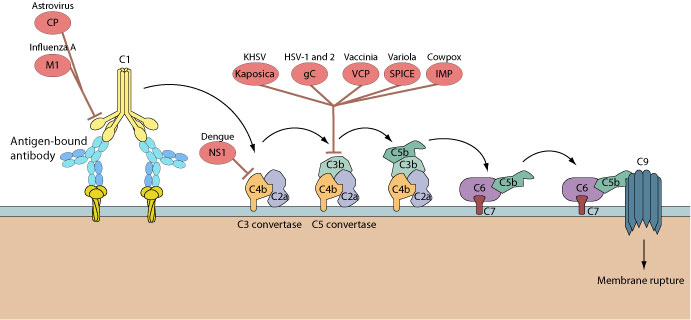
Members of the herpesvirus, orthopoxvirus and retrovirus families mimic or interact with complement regulatory proteins to block complement activation and neutralization of virus particles. For example, vaccinia and variola viruses encode secreted proteins that block C3 convertase assembly. Influenza A virus instead blocks the complement pathway via M1 protein interacting with and inhibiting host C1qA protein.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)18 entries grouped by protein
3 entries
Capsid polyprotein VP90
11 entries
Envelope glycoprotein C
1 entry
Complement control protein (KCP)
1 entry
Genome polyprotein
2 entries
