Inhibition of host proteasome antigen processing by virus (kw:KW-1117)
The proteasome plays an essential role in MHC class I antigen presentation pathway. The processing of foreign proteins leads to the presentation of viral peptides by MHC class I molecules to cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
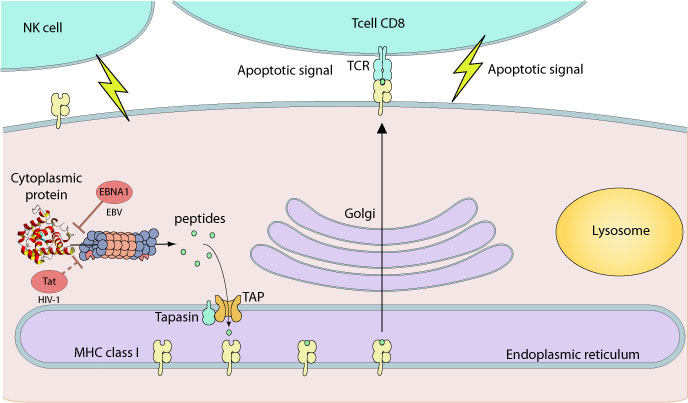
Several viruses have managed to avoid degradation by the proteasome using different tricks. Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-1 contains for example an internal repeat exclusively composed of glycines and alanines that inhibits proteasomal degradation. HIV TAT also acts at the transcriptional level by modifying proteasome composition by upregulating the LMP7 and MECL1 subunits and downregulating the LMP2 subunit, thereby promoting presentation of cryptic and subdominant CTL epitopes.
