Orbivirus (taxid:10892)
VIRION
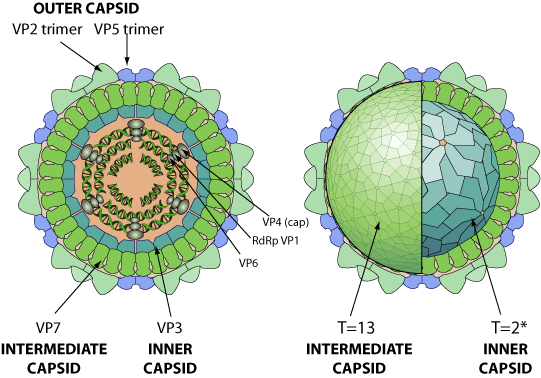
Non enveloped, icosahedral, non-turreted virion with a triple capsid structure, about 80 nm in diameter. The intermediate capsid has a T=13 icosahedral symmetry, the inner capsid a T=2* icosahedral symmetry.
GENOME
Segmented linear dsRNA genome. Contains 10 segments coding for 12 proteins. Segments size range from 822 to 3,954 bp (BTV). Genome total size is 19,200 bp (BTV).
GENE EXPRESSION
The dsRNA genome is never completely uncoated, to prevent activation of antiviral state by the cell in response to dsRNA. The viral polymerase VP1 synthesizes a capped mRNA from each dsRNA segment. This capped mRNA is translocated to the cell cytoplasm where it is translated. VP6(a), NS3(a) and NS4 are presumably expressed by leaky scanning
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [VP1]
- Cell-type capping:
- Helicase [VP6A]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment to host receptors mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of virus into host cell.
- Particles are partially uncoated in endolysosomes, but not entirely, and penetrate in the cytoplasm.
- Early transcription of the dsRNA genome by viral polymerase occurs inside this sub-viral particle (naked core), so that dsRNA is never exposed to the cytoplasm.
- Full-length plus-strand transcripts from each of the dsRNA segments are synthesized. These plus-strand transcripts are used as templates for translation.
- Viral proteins and genomic RNAs aggregates in cytoplasmic viral factories.
- (+)RNAs are encapsidated in a sub-viral particle, in which they are transcribed to give RNA (-) molecules with which they become base-paired to produce dsRNA genomes.
- The capsid is assembled on the sub-viral particle.
- Mature virions are released presumably following cell death and associated breakdown of host plasma membrane.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
Bluetongue virus mediates host cell apoptosis via caspases activaton (caspases-8, caspases-9, caspase-3, and caspase-7)  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Bluetongue virus NS4 protein might also be involved in counteracting the antiviral response of the host
 .
.
Mourad Belhouchet, Fauziah Mohd Jaafar, Andrew E. Firth, Jonathan M. Grimes, Peter P. C. Mertens, Houssam Attoui
PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e25697
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)101 entries grouped by strain
10 entries
Bluetongue virus 10 (isolate USA) (BTV 10) reference strain
10 entries
African horse sickness virus (AHSV) (Orbivirus alphaequi) reference strain
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 10 (isolate USA) (BTV 10)
8 entries
Bluetongue virus 1 (isolate South Africa) (BTV 1)
8 entries
Bluetongue virus 11 (isolate USA) (BTV 11)
8 entries
Bluetongue virus 13 (isolate USA) (BTV 13)
8 entries
Bluetongue virus 17 (isolate USA) (BTV 17)
7 entries
Bluetongue virus 2 (isolate USA) (BTV 2)
6 entries
Bluetongue virus 1 (isolate Australia) (BTV 1)
4 entries
African horse sickness virus 6 (AHSV-6)
4 entries
African horse sickness virus 9 (AHSV-9)
4 entries
Broadhaven virus (BRD)
4 entries
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus 1 (EHDV-1)
3 entries
African horse sickness virus 4 (AHSV-4)
2 entries
African horse sickness virus 3 (AHSV-3)
2 entries
Bluetongue virus 13 (isolate 13B89Z) (BTV 13)
2 entries
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus 2 (strain Alberta) (EHDV-2)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 1 (AHSV-1)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 2 (AHSV-2)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 5 (AHSV-5)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 7 (AHSV-7)
1 entry
African horse sickness virus 8 (AHSV-8)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 1 (isolate South Africa vaccine) (BTV 1)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 10 (BTV 10)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 20 (isolate Australia) (BTV 20)
1 entry
Bluetongue virus 3 (isolate South Africa vaccine) (BTV 3)
1 entry
