Trichomonasvirus (taxid:674952)
VIRION
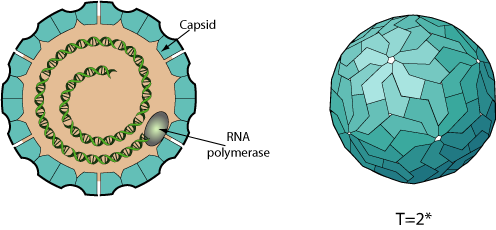
Non enveloped, icosahedral virion composed of a single capsid protein (CP), about 36 nm in diameter. The capsid has a T=2* icosahedral symmetry.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear dsRNA genome of 4.6-4.9 kb. The genome has two large, overlapping ORFs on the positive strand encoding the capsid (gag) and polymerase (pol) proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The dsRNA genome is never completely uncoated, to prevent activation of antiviral state by the cell in response to dsRNA. The viral polymerase synthesizes a mRNA, which is translocated to the cell cytoplasm where it is translated.
Translation is initiated on a unique internal ribosome entry site (IRES) element situated at the 5'-UTR.
The plus-strand viral transcript is flanked by a 5'untranslated region (5'-UTR) and a 3'-UTR and directs the translation of a major CP (Gag) and a minor fusion protein CP-RdRP (Gag-Pol) via a +1 or -2 ribosomal frameshift.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Cell to cell transmission of the virus through small extracellular vesicles.

- Transcription of the dsRNA genome by viral polymerase occurs inside the virion, so that dsRNA is never exposed to the cytoplasm. This plus-strand transcript is used as template for translation.
- (+)RNAs are encapsidated in a sub-viral particle, in which they are transcribed to give RNA (-) molecules with which they become base-paired to produce dsRNA genomes.
- Mature virions are released from the host cell.
Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1 taxid:674953
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-62208 |
| Capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-62208 |
| RNA-directed RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.48) | ma-jd-viral-32338 |
Trichomonas vaginalis virus 2 taxid:674954
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-62207 |
| RNA-directed RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.48) | ma-jd-viral-32339 |
