Ribosomal skipping (kw:KW-1197)
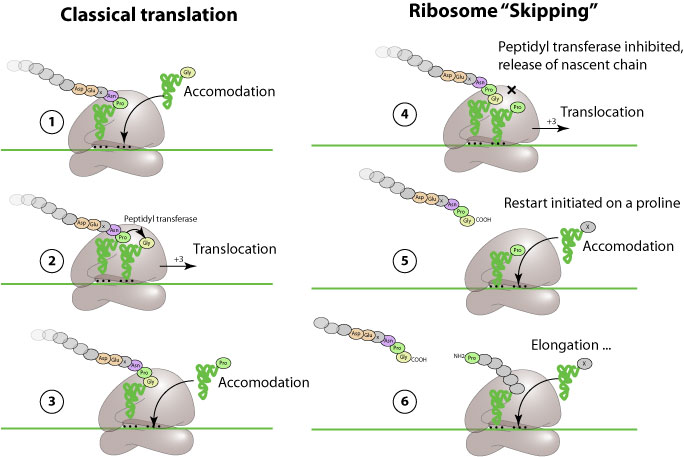
Ribosomal "skipping" is an alternate mechanism of translation in which a specific viral peptide prevents the ribosome from covalently linking a new inserted aa, and let it continue translation. This result in apparent co-translational cleavage of the polyprotein.
This process is induced by a "2A-like", or CHYSEL (cis-acting hydrolase element) sequence. This sequence comprises a non-conserved sequence of amino-acids with a strong alpha-helical propensity followed by the consensus sequence -D(V/I)ExNPG P, where x= any amino acid. The apparent cleavage occurs between G and P.
Ribosomal "skipping" has been observed only in +ssRNA and dsRNA viruses, whose hosts are animals, plant or insect. The conserved motif has been identified also in trypanosoma and in some fungus proteins.
Ribosomal "skipping" is functioning both in vitro and in vivo when translated by eukaroytic ribosomes, but is inactive when translated by prokaryotic ribosomes.
| Family | Genus | Virus | Sequence ( |= apparent cleavage ) | Frequency | UniProt | |
| Picornaviridae | Aphthovirus | Foot-and-mouth disease virus | PSDARHKQRIVAPAKQLLNFDLLKLAGDVESNPG|P | 99% | Q9DLK1 | |
| Avisivirus | Avisivirua A | ARRTLEWARREVGAIDETDHKDILLGGDIEENPG|P | 99% | M4PJD6 | ||
| Avihepatovirus | Duck hepatitis A virus | RLKTLAFELNLEIESDQIRNKKDLTTEGVEPNPG|P | 99% | Q0ZQM1 | ||
| Cardiovirus | Encephalomyocarditis virus | VREENVFGLYRIFNAHYAGYFADLLIHDIETNPG|P | 99% | Q66765 | ||
| Cosavirus | Cosavirus A | IMADSVLPRPLTRAERDVARDLLLIAGDIESNPG|P | 99% | B8XTP8 | ||
| Erbovirus | Equine rhinitis B virus 1 | SEPIPEATLSTILSEGATNFSLLKLAGDVELNPG|P | 99% | Q66776 | ||
| Erbovirus | Seneca Valley virus | RYKNARAWCPSMLPFRSYKQKMLMQSGDIETNPG|P | 99% | Q155Z9 | ||
| Hunnivirus | Hunnivirus A | CPRPGMAIDPPAQSSGATNFSLLRLAGDVELNPG|P | 99% | F4YYF3 | ||
| Kunsagivirus | Kunsagivirus A | SPRSLLHFLIGRPRPRVPPSPSLLLSGDVEPNPG|P | NA | S4VD62 | ||
| Mischivirus | Mischivirus A | DSYPASGEEEEDDFHDMEDHSDILLGGDVEENPG|P | 99% | I3VR62 | ||
| Mosavirus | Mosavirus A2 | TNSRAKLMVDEDYVIQRSAHRSVLLDGDVESNPG|P | 99% | X2L6K2 | ||
| Pasivirus | Pasivirus A1 | DIPSFQRDFINWLGSKEELQNMILQCGDVEQNPG|P | 99% | I6YQK4 | ||
| Teschovirus | Porcine teschovirus 1 | EGLSSAMTVMAFQGPGATNFSLLKQAGDVEENPG|P | 99% | Q9WJ28 | ||
| Iflaviridae | Iflavirus | Infectious flacherie virus | NYPLVPSIGNVARTLTRAEIEDELIRAGIESNPG|P | 99% | O70710 | |
| Tetraviridae | Betatetravirus | Thosea asigna virus | RSRRLRGPRPQNLGVRAEGRGSLLTCGDVEENPG|P | 94-99% | Q9YK87 | |
| Dicistroviridae | Cripavirus | Cricket paralysis virus | FQQWKLVSSNDECRAFLRKRTQLLMSGDVESNPG|P | 88% | Q9IJX4 | |
| Reoviridae | Rotavirus | Human rotavirus C | LKKHNGAGYPLIVANSKFQIDKILISGDIELNPG|P | 82% | Q9PY95 | |
| Cypovirus | Lymantria dispar cypovirus 1 | TDFLSMTAFDFQQAVFRSNYDLLKLCGDVESNPG|P | 99% | Q91ID7 |
References
Luke GA, de Felipe P, Lukashev A, Kallioinen SE, Bruno EA, Ryan MD.
*Occurrence, function and evolutionary origins of '2A-like' sequences in virus
genomes*.
J Gen Virol. 2008 Apr;89(Pt 4):1036-42. PubMed
Doronina VA, de Felipe P, Wu C, Sharma P, Sachs MS, Ryan MD, Brown JD.
Dissection of a co-translational nascent chain separation event.
Biochem Soc
Trans. 2008 Aug;36(Pt 4):712-6. PubMed
Martin D. Ryan, Michelle Donnelly, Arwel Lewis, Amit P. Mehrotra, John Wilkie, David Gani.
A Model for Nonstoichiometric, Cotranslational Protein Scission in Eukaryotic Ribosomes.
Bioorganic Chemistry, Volume 27, Issue 1, February 1999, 55-79
link
