Fusion of virus membrane with host endosomal membrane (kw:KW-1170)
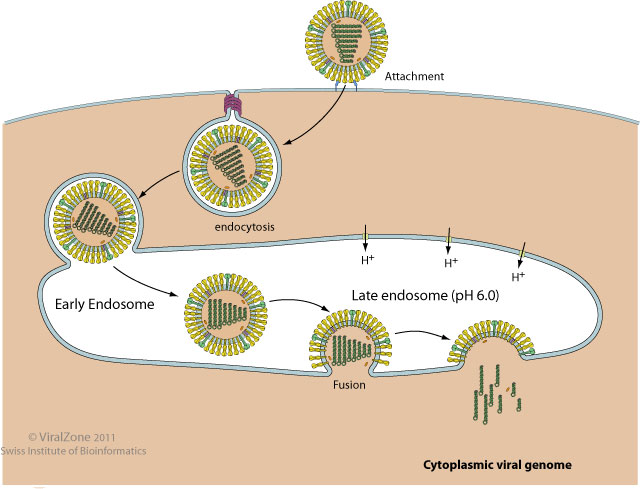
Enveloped viruses use specialized machinery to fuse viral and host cell membranes after internalization through the endosomal pathway.
Viral fusion proteins drive this fusion reaction by undergoing major conformational change. The specific trigger depends on the virus and very often involves the exposure to the low pH of the late endosome.
All fusion proteins are active in a trimeric conformation. Most of them are natively trimeric, some of them are dimers on the virion surface but are converted to trimers upon activation  .
.
Fusion proteins have to be produced in an inactive state in order to avoid to trigger fusion in the Golgi or other compartments upon synthesis and transport to the cell surface. Many are activated in the trans.Golgi network or at the cell surface by proteolytic cleavage which reveals the fusion peptide.
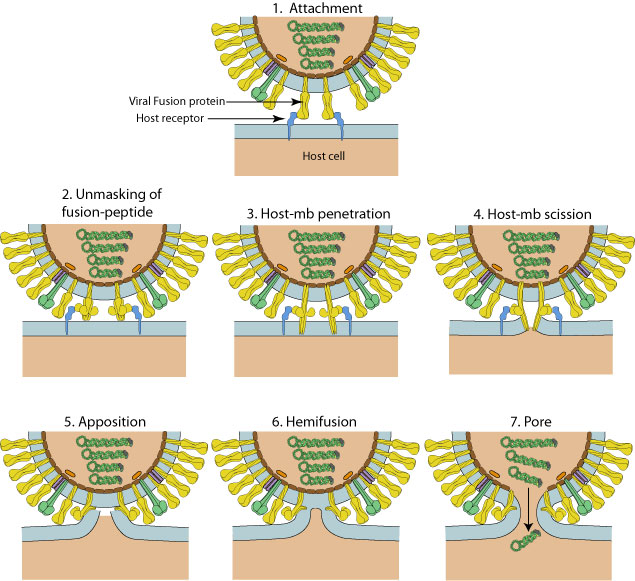
Fusion mechanism according to the "viral fusion pore" model of Lee K.  . A different model has been described with PIV5
. A different model has been described with PIV5
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)538 entries grouped by protein
66 entries
Envelope glycoprotein gp160 (Env polyprotein)
3 entries
Major envelope glycoprotein (gp64)
27 entries
Pre-glycoprotein polyprotein GP complex (Pre-GP-C)
12 entries
Glycoprotein
39 entries
Envelopment polyprotein (M polyprotein)
57 entries
Large envelope protein (L glycoprotein) (L-HBsAg) (LHB) (Large S protein) (Large surface protein) (Major surface antigen)
135 entries
Hemagglutinin
97 entries
Genome polyprotein
45 entries
Structural polyprotein (p130)
3 entries
Frameshifted structural polyprotein (p130)
36 entries
Spike glycoprotein (S glycoprotein) (E2) (Peplomer protein)
2 entries
Envelope glycoprotein p57 (gp84) (gp94)
16 entries
