VIRION
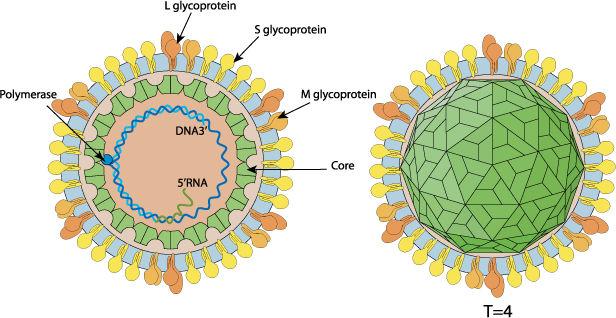
Enveloped, spherical. Diameter from about 42nm. Icosahedric capsid with a T=4 symmetry.
GENOME
Partially dsDNA circular genome, about 3.2 kb in size. Encodes for 7 proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The minichromosome is transcribed by cellular RNA polymerase II under the control of four promoters (the core, pre-S1, pre-S2/S, and X promoters) and two enhancer regions (ENH1 and ENH2). The early transcript encodes HBx, all others are late transcripts. The pre-genomic RNA is alternatively spliced. The unspliced form is exported from the nucleus through a PRE motif possibly by capsid protein. The Polymerase and short S proteins are expressed by leaky scanning from the pg mRNA and the S mRNA respectively.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [P]
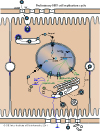
REPLICATION
NUCLEO-CYTOPLASMIC
- Virus attaches to host receptors through major surface antigen and enters the cell by an unknown mechanism.
- Relaxed circular DNA (RC-DNA) and capsid are transported via microtubules to the nucleus where DNA is released through the nuclear pore, and repaired to form covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA).
- Transcription by RNA polymerase II of the viral mRNAs and the pregenomic RNA (pgRNA).
- The unspliced pregenomic RNA leaves the nucleus by nuclear pore export.
- In the cytoplasm pgRNA is encapsidated, together with the P protein, and reverse-transcribed inside the nucleocapsid in new RC-DNA.
- Transport to the nucleus of new RC-DNA leads to cccDNA amplification; alternatively, the RC-DNA containing nucleocapsids are enveloped at the ER, and new virions are released by exocytosis.