Orthopoxvirus (taxid:10242)
VIRION
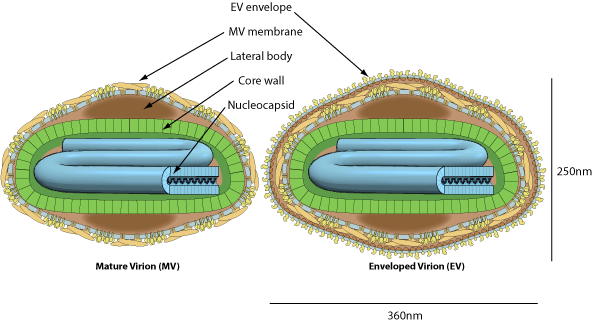
Enveloped, brick-shaped virion, 250nm long and 200nm wide. The surface membrane displays surface tubules or surface filaments. Two distinct infectious virus particles exists: the intracellular mature virus (IMV) and the extracellular enveloped virus (EEV).
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome of 170-250kb. The linear genome is flanked by inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequences which form covalently closed hairpin termini at each extremity.
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA-directed DNA polymerase [E9L (OPG071)]
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase [E4L (OPG066)]
- Cell-type capping
- RNA TPase [D1R (OPG113)]
- GTase [D1R (OPG113)]
- N7MTase [D1R (OPG113) + D12L (OPG124)]
- 2'O methylase [J3R (OPG102)]
- Core protease (Peptidase C57) [I7 (OPG083)]
- Metalloprotease (Peptidase M44) [G1L (OPG085)]
- Phospholipase [F13 (OPG057)]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement of the viral proteins to host glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell. The virus can be uptaked also by apoptotic mimicry
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the core into the host cytoplasm.
- Early phase: early genes are transcribed in the cytoplasm by viral RNA polymerase. Early expression begins at 30 minutes post-infection.
- Core is completely uncoated as early expression ends, viral genome is now free in the cytoplasm.
- Intermediate phase: Intermediate genes are expressed, triggering genomic DNA replication at approximately 100 minutes post-infection.
- Late phase: Late genes are expressed from 140 min to 48 hours post-infection, producing all structural proteins.
- Assembly of progeny virions starts in cytoplasmic viral factories, producing an spherical immature particle. This virus particle matures into brick-shaped intracellular mature virion (IMV).
- IMV virion can be released upon cell lysis, or can acquire a second double membrane from trans-Golgi and bud as external enveloped virion (EEV).
Host-virus interaction
Adaptive immune response inhibition
The vaccinia virus A35R localizes to host endosomes and inhibits MHC class II antigen presentation  .
.
Apoptosis modulation
Several poxviral proteins are dedicated to the inhibition of host apoptosis. Vaccinia F1L functions both as a suppressor of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins and as an inhibitor of caspase-9  .
.
Autophagy modulation
Vaccinia virus actively disrupts the cellular autophagy through a mechanism that involves aberrant LC3 lipidation and a direct conjugation between ATG12 and ATG3  .
.
NF-kappa-B modulation
The B14 protein from vaccinia virus functions by binding to the IKK complex via an interaction with IKK-beta and preventing the phosphorylation of IKK-beta on its activation loop. In turn, IKK-beta is not activated and fails to phosphorylate IkB-beta, leaving IkB-beta able to retain NF-kappa-B in the cytoplasm  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Poxviruses inhibit the cascade leading to production of interferon-beta by mainly targeting the host IRF3 protein. For instance, vaccinia virus protein C6 inhibits IRF3 activation downstream of TBK1  .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
Cowpox virus taxid:10243
Cowpox virus (strain Brighton Red) taxid:265872
Horsepox virus taxid:397342
Raccoon poxvirus taxid:10256
Vaccinia virus taxid:10245
Vaccinia virus (strain Ankara) taxid:126794
Vaccinia virus (strain Copenhagen) taxid:10249
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Protein OPG157 | ma-jd-viral-44671 |
| Scaffold protein OPG125 (62 kDa protein) (Rifampicin resistance protein) | ma-jd-viral-18034 |
Vaccinia virus (strain L-IVP) taxid:31531
Vaccinia virus (strain Tian Tan) taxid:10253
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Phosphoprotein OPG062 (Phosphoprotein F17) | ma-jd-viral-63871 |
