Poxviridae (taxid:10240)
VIRION
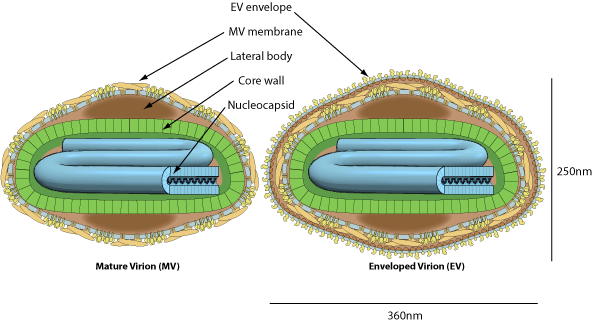
Enveloped, brick-shaped or ovoid virion, 220-450 nm long and 140-260 nm wide. The surface membrane displays surface tubules or surface filaments. Two distinct infectious virus particles exists: the intracellular mature virus (IMV) and the extracellular enveloped virus (EEV).
- Major core protein [OPG 136]
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome of 130-375kb. The linear genome is flanked by inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequences which are covalently-closed at their extremities.
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA-directed DNA polymerase B [E9L (OPG071)]
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase [E4L (OPG066)]
- Cell-type capping
- RNA TPase [D1R (OPG113)]
- GTase [D1R (OPG113)]
- N7MTase [D1R (OPG113) + D12L (OPG124)]
- 2'O methylase [J3R (OPG102)]
- Core protease (Peptidase C57) [I7 (OPG083)]
- Metalloprotease (Peptidase M44) [G1L (OPG085)]
- Phospholipase [F13 (OPG057)]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment of the viral proteins to host glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the core into the host cytoplasm.
- Early phase: early genes are transcribed in the cytoplasm by viral RNA polymerase. Early expression begins at 30 minutes post-infection.
- Core is completely uncoated as early expression ends, viral genome is now free in the cytoplasm.
- Intermediate phase: Intermediate genes are expressed, triggering genomic DNA replication at approximately 100 minutes post-infection.
- Late phase: Late genes are expressed from 140 min to 48 hours post-infection, producing all structural proteins.
- Assembly of progeny virions starts in cytoplasmic viral factories, producing an spherical immature particle. This virus particle matures into brick-shaped intracellular mature virion (IMV).
- IMV virion can be released upon cell lysis, or can acquire a second double membrane from trans-Golgi and bud as external enveloped virion (EEV).
Host-virus interaction
Adaptive immune response inhibition
The vaccinia virus A35R localizes to host endosomes and inhibits MHC class II antigen presentation  . Additionally, the poxviral E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase LAP promotes ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of host MHC-I and CD4 molecules
. Additionally, the poxviral E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase LAP promotes ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of host MHC-I and CD4 molecules 
 .
.
Apoptosis modulation
Several poxviral proteins are dedicated to the inhibition of host apoptosis. For example Myxoma virus M11L alters the pathway by preventing the conformational activation of host Bax at the mitochondria  .
.
Vaccinia F1L functions both as a suppressor of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family of proteins and as an inhibitor of caspase-9  .
.
Molluscipoxviruses encode a viral FLICE-inhibitory protein (v-FLIP) that prevents apoptosis induced by death receptors  .
.
FPV039 inhibits apoptosis by sequestering and inactivating multiple proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, including Bak and Bax  .
.
Autophagy modulation
Vaccinia virus actively disrupts the cellular autophagy through a mechanism that involves aberrant LC3 lipidation and a direct conjugation between ATG12 and ATG3  .
.
Cell-cycle modulation
The myxomavirus Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein M-T5 is an adapter of SKP1-containing E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases which mediate the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of host target proteins including CDKN1B. Disappearance of host CDKN1B correlates with cell cycle progression through the G0/G1 checkpoint  .
.
NF-kappa-B modulation
The B14 protein from vaccinia virus functions by binding to the IKK complex via an interaction with IKK-beta and preventing the phosphorylation of IKK-beta on its activation loop. In turn, IKK-beta is not activated and fails to phosphorylate IkB-beta, leaving IkB-beta able to retain NF-kappa-B in the cytoplasm  . MC159 protein from the molluscum contagiosum instead inhibits NF-kappa-B activation by interacting with the IkB kinase complex
. MC159 protein from the molluscum contagiosum instead inhibits NF-kappa-B activation by interacting with the IkB kinase complex  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Poxviruses inhibit the cascade leading to production of interferon-beta by mainly targeting the host IRF3 protein. For instance, vaccinia virus protein C6 inhibits IRF3 activation downstream of TBK1  .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
Adoxophyes honmai entomopoxvirus 'L' taxid:1293540
Alphaentomopoxvirus acuprea taxid:62099
BeAn 58058 virus taxid:67082
Choristoneura biennis entomopoxvirus taxid:10288
Cotia virus SPAn232 taxid:930275
Cowpox virus taxid:10243
Cowpox virus (strain Brighton Red) taxid:265872
Deerpox virus (strain Mule deer/United States/W-848-83/1983) taxid:305674
Horsepox virus taxid:397342
Molluscum contagiosum virus subtype 1 taxid:10280
Mythimna separata entomopoxvirus 'L' taxid:1293572
Nile crocodilepox virus (isolate Crocodylus niloticus/Zimbabwe/Ume/2001) taxid:1289473
Orf virus taxid:10258
Orf virus (strain Goat/Texas/SA00/2000) taxid:647330
Parapoxvirus red deer/HL953 taxid:1579460
Penguinpox virus taxid:648998
Pigeonpox virus taxid:10264
Pteropox virus taxid:1873698
Raccoon poxvirus taxid:10256
Salmon gill poxvirus taxid:1680908
Sheeppox virus taxid:10266
Sheeppox virus (strain InS-1) taxid:10268
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Protein B14 homolog (Protein T3A) | ma-jd-viral-13479 |
| Protein B14 homolog (Protein T3A) | ma-jd-viral-13481 |
Sheeppox virus (strain KS-1) taxid:10269
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope protein A28 homolog (Protein HM3) | ma-jd-viral-31661 |
Sheeppox virus (strain Turkey/TU-V02127) taxid:654928
Turkeypox virus taxid:336486
Vaccinia virus taxid:10245
Vaccinia virus (strain Ankara) taxid:126794
Vaccinia virus (strain Copenhagen) taxid:10249
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Protein OPG157 | ma-jd-viral-44671 |
| Scaffold protein OPG125 (62 kDa protein) (Rifampicin resistance protein) | ma-jd-viral-18034 |
Vaccinia virus (strain L-IVP) taxid:31531
Vaccinia virus (strain Tian Tan) taxid:10253
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Phosphoprotein OPG062 (Phosphoprotein F17) | ma-jd-viral-63871 |
