Iridoviridae (taxid:10486)
VIRION
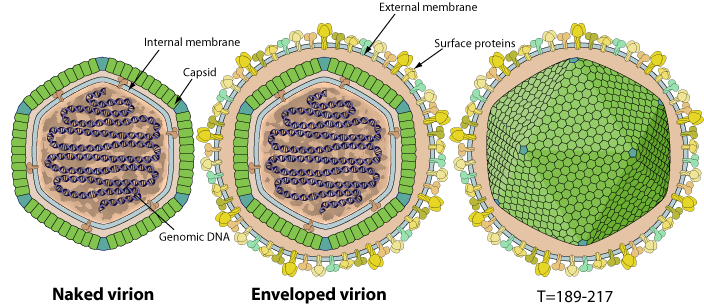
Polyhedral virions 120-350 nm in diameter. The capsid displays an icosahedral symmetry T=189-217, with an internal lipid membrane. Virions are either externally enveloped or not depending whether they budded from the cell membrane, or were arranged in paracrystaline array in the host cell cytoplasm and were released by lysis.
- Hexons: Double jelly roll-fold major capsid protein [Q05815]
- Pentons: Single jelly roll-fold [?]
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome of 140-303 kb. The genome contains terminal and redundant sequences and is circularly permuted.
Members of the genera Iridovirus and Chloriridovirus lack a highly
methylated genome. In contrast, members of the Ranavirus, Lymphocystivirus, and Megalocytivirus genera possess genomes in which approximately 25% of the cytosine residues are methylated by a virus encoded DNA methyltransferase.
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA dependent DNA polymerase [DdDp]
- DNA dependent RNA polymerase
- Cell-type capping
- Cysteine protease (Peptidase C1A) [Protease]
- Metallo protease (Peptidase M10) [Protease]
REPLICATION
NUCLEO-CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement of the viral proteins to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the DNA core into the host cytoplasm.
- Viral DNA is transported to the cell nucleus where host macromolecular synthesis is rapidly shutdown. Transcription is initiated by virally modified host RNA polymerase II.
- Parental DNA is used to produce genome and greater than genome length DNA.
- Progeny DNA is transported into cytoplasmic viral factories where large concatamers of viral DNA are formed by recombination. Transcription of very late transcripts may also take place in the cytoplasm.
- Assembly of new virions in the cytoplasm.
- Virions exit the cell by budding or cell lysis.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
Chilo iridescent virus encodes a functional inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)  . The grouper iridovirus (GIV) contains an antiapoptotic B-cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2-like gene
. The grouper iridovirus (GIV) contains an antiapoptotic B-cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2-like gene  that also inhibits host apoptosis.
that also inhibits host apoptosis.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)449 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Putative transcription factor 001R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 002L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 002R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 003L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 3R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 004R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 005L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 005R
1 entry
Putative KilA-N domain-containing protein 006L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 006R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 007R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 008L
1 entry
Putative helicase 009L (EC 3.6.4.-)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 009R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 010R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 011L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 011R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 012L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein IIV3-013L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 013R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 014R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 015R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 017L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 018L
1 entry
Putative serine/threonine-protein kinase 019R (EC 2.7.11.1)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 020R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 021L
1 entry
Transmembrane protein 022L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 023R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 024R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 025R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 026R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 027R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 028R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 029L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 029R
1 entry
uncharacterized protein 030L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 030R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 031R
3 entries
Uncharacterized protein 032R
1 entry
Transmembrane protein 033R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 034R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 035L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 036L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 037L
1 entry
uncharacterized protein 037R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 039R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 040R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 041L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 041R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 042L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 042R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 043L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 043R
1 entry
Putative serine/threonine-protein kinase 040L (EC 2.7.11.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 044R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 045L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 045R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 046L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 047L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 048L
2 entries
Putative SAP domain-containing protein 049L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 049R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 050L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 051R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 052L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 053L
1 entry
Putative myristoylated protein 053R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 054L
1 entry
Putative helicase 055L (EC 3.6.4.-)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 055R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 056R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 057L
1 entry
Putative phosphotransferase 057R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 058R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 059L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 060L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 061L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 061R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 062L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 064L
1 entry
Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 064R
1 entry
Putative collagen-like domain-containing protein 065L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 065R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 066L
1 entry
Putative uncharacterized protein 068R
1 entry
Putative Bro-N domain-containing protein 069L
1 entry
Transmembrane protein 069R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 070R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 071L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 071R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 072L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 073L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 073R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 074L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 075L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 075R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 076R
1 entry
LCDV1 orf2-like protein
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 077R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 078L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 079R
1 entry
Putative hydrolase 080R (EC 3.6.1.-)
1 entry
Putative FAS1 domain-containing protein 081L
1 entry
Putative transcription elongation factor S-II-like protein 81R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 082L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 083L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 084L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 084R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 086L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 087L
1 entry
Putative FAD-linked sulfhydryl oxidase 088R (EC 1.8.3.2)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 089L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 89R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 092R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 093L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 094L
2 entries
Probable matrix metalloproteinase 095L (EC 3.4.24.-)
1 entry
Putative RAD2-like endonuclease 095R (EC 3.1.-.-)
1 entry
Putative FAS1 domain-containing protein 096L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 096R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 097R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 098R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 101L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 102R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 103L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 104L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 106L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 107L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 108L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 110R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 111R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 113L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 114L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 116L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 116R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 117L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 118R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 119R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 120L
1 entry
Putative RING finger protein 121R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 122R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 123L
1 entry
Putative tyrosine phosphatase 123R (EC 3.1.3.-)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 124R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 125R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 126R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 127L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 130R
1 entry
Putative zinc finger protein 132L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 135R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 137R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 138R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 139L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 140L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 141R
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 146R
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 148R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 149L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 156R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 159L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 160L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 162R
1 entry
Putative metalloproteinase 165R (EC 3.4.24.-)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 169L
1 entry
Putative helicase 172L (EC 3.6.4.-)
1 entry
Putative RING finger protein 175R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 192R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 195L
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 200R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 206L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 209R
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 211L
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 212L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 216R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 218R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 221L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 226R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 227L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 228L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 234R
1 entry
Putative methyltransferase 235L (EC 2.1.1.-)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 236L
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 238R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 240R
1 entry
Cysteine-rich uncharacterized protein 241L
1 entry
Putative GIY-YIG domain-containing protein 242L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 246L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 247L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 249R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 250L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 253L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 254L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 255L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 261R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 272L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 273R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 284R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 285L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 287R
1 entry
Putative Bro-N domain-containing protein 289L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 293R
1 entry
Transmembrane protein 300R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 301L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 308L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 312R
1 entry
Putative KilA-N domain-containing protein 313L
1 entry
Putative KilA-N domain-containing protein 315L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 317L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 322R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 325L
1 entry
Uncharacterized RING finger protein 332L
1 entry
DRBM domain-containing protein 340R
1 entry
Probable DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit 343L (EC 2.7.7.6)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 346R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 348R
1 entry
Probable cysteine proteinase 361L (EC 3.4.22.-)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 366R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 368R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 373L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 374R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 375R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 384L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 385L
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 388R
1 entry
Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase 389L (EC 2.7.11.1)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 400R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 404L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 411L
1 entry
Putative RING finger protein 413R
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 420R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 422L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 423L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 426R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 437L
1 entry
Probable deoxyuridine 5'-triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase (dUTPase) (EC 3.6.1.23) (dUTP pyrophosphatase)
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 441R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 443R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 451L
1 entry
Putative DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit 454R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 457L
1 entry
Putative myristoylated membrane protein 458R
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 460R
1 entry
Probable lipid hydrolase 463L (EC 3.1.1.-)
1 entry
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 468L
1 entry
Putative deoxynucleoside kinase (EC 2.7.1.-)
1 entry
Probable DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.37) (Orphan methyltransferase M.Fvi3IP) (M.Fvi3IP)
4 entries
DNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.7)
1 entry
Putative deoxyuridine 5'-triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase (dUTPase) (EC 3.6.1.23)
1 entry
Putative exonuclease 059L (EC 3.1.11.-)
1 entry
Putative exonuclease 012L (EC 3.1.11.-)
1 entry
High mobility group protein homolog
1 entry
Immediate-early protein ICP-18
3 entries
Immediate-early protein ICP-46 homolog
1 entry
Putative thymidylate kinase 251L (EC 2.7.4.9) (dTMP kinase)
9 entries
Major capsid protein (MCP) (P50)
1 entry
Putative helicase 022R (EC 3.6.4.-)
1 entry
Putative poly
3 entries
Putative ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase large subunit (EC 1.17.4.1) (Ribonucleotide reductase large subunit)
4 entries
Probable ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase small subunit 048L (EC 1.17.4.1) (Ribonucleotide reductase small subunit)
3 entries
Putative ribonuclease 3 (EC 3.1.26.3) (Ribonuclease III) (RNase III)
3 entries
Probable DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 homolog (EC 2.7.7.6)
3 entries
Probable DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB2 homolog (EC 2.7.7.6)
2 entries
DNA topoisomerase 2 (EC 5.6.2.2) (DNA topoisomerase II)
1 entry
Probable thymidylate synthase 225R (EC 2.1.1.45)
2 entries
Transmembrane protein 010R
2 entries
Uncharacterized 15.9 kDa protein in MSP 5'region
2 entries
Putative MSV199 domain-containing protein 093L
2 entries
Putative helicase 022L (EC 3.6.4.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 030L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 050L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 004R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 075L
2 entries
Putative zinc finger protein 034R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 038R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 031R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 107R
2 entries
Putative myristoylated protein 006R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 042R
2 entries
Putative kinase protein 029R (EC 2.7.-.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 050L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 113L
2 entries
Putative RING finger protein 027R
2 entries
Putative helicase 109L (EC 3.6.4.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 170L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 035R
2 entries
Putative helicase 121R (EC 3.6.4.-)
2 entries
Apoptosis inhibitor 193R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 020R
2 entries
Putative tyrosine phosphatase 067L (EC 3.1.3.48)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 069L
2 entries
Putative Bro-N domain-containing protein 019R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 085L
2 entries
Putative DNA ligase 052L (EC 6.5.1.2)
2 entries
Transmembrane protein 213R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 036R
2 entries
Probable cysteine proteinase 024R (EC 3.4.22.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 229L
2 entries
Putative ubiquitin thioesterase 232R (EC 3.4.19.12)
2 entries
Putative phosphoesterase 078R (EC 3.1.-.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 071L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 074L
2 entries
Putative transcription factor 079L
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein 056L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 016R
2 entries
Putative zinc finger protein 012R
2 entries
Putative SWIB domain-containing protein 070L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 033L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 063R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 099R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 017R
2 entries
Putative membrane protein 047R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 115R
2 entries
Putative FAD-linked sulfhydryl oxidase 096R (EC 1.8.3.2)
2 entries
Putative transcription elongation factor S-II-like protein 055R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 026R
2 entries
Putative CTD phosphatase-like protein 355R (EC 3.1.3.-)
2 entries
Transmembrane protein 066L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 083L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 105R
2 entries
Probable RAD2-like endonuclease 076L (EC 3.1.-.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 100L
2 entries
Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase 010L (EC 2.7.11.1)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 058R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 001R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 091L
1 entry
High mobility group protein homolog 068R
2 entries
Putative hydrolase 111R (EC 3.6.1.-)
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 018L
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 060L
2 entries
Probable kinase 098L (EC 2.7.-.-)
2 entries
Putative thioredoxin-like protein 041R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 112R
2 entries
Uncharacterized protein 061R
1 entry
Integrase homolog
1 entry
Putative ubiquitin thioesterase L96 (EC 3.4.19.12)
1 entry
