Orthoflavivirus (taxid:3044782)
VIRION
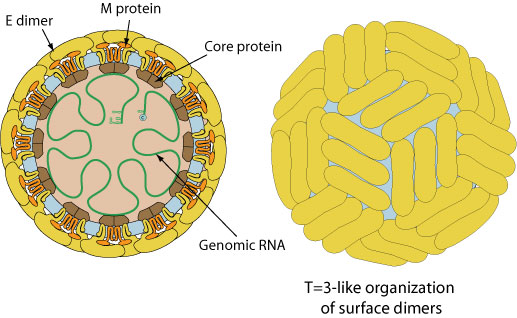
Enveloped, spherical, about 50 nm in diameter. The surface proteins are arranged in an icosahedral-like symmetry. Mature virions contain two virus-encoded membrane proteins (M and E), while immature virions contain a membrane protein precursor.
Source: Zhang et al("Pubmed":http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14528291)
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome of of 10-11 kb. The genome 5' end has a methylated nucleotide cap for canonical cellular translation. The 3' terminus is not polyadenylated but forms a loop structure. This secondary structure leads to the formation of a subgenomic flavivirus RNA (sfRNA) through genomic RNA degradation by host XRN1. sfRNA is essential for pathogenicity , and may play a role in inhibiting host RIG-I antiviral activity as shown for Dengue virus
, and may play a role in inhibiting host RIG-I antiviral activity as shown for Dengue virus
GENE EXPRESSION
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and the viral messenger RNA. The whole genome is translated in a polyprotein, which is processed co- and post-translationally by host and viral proteases.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [NS5]
- Cell-type capping
- Polyprotein major protease (Peptidase S7) [NS3]
REPLICATION
- Attachement of the viral envelope protein E to host receptors mediates internalization into the host cell by clathrin-mediated endocytosis, or by apoptotic mimicry
- Fusion of virus membrane with host endosomal membrane. RNA genome is released into the cytoplasm.
- The positive-sense genomic ssRNA is translated into a polyprotein, which is cleaved into all structural and non structural proteins (to yield the replication proteins).
- Replication takes place at the surface of endoplasmic reticulum in cytoplasmic viral factories. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Virus assembly occurs at the endoplasmic reticulum. The virion buds at the endoplasmic reticulum and is transported to the Golgi apparatus.
- The prM protein is cleaved in the Golgi, thereby maturing the virion which is fusion competent.
- Release of new virions by exocytosis.
Host-virus interaction
Adaptive immune response inhibition
Dengue NS1 protein inhibits host complement by binding C4 and reducing C4b deposition and C3 convertase activity. Through this mechanism, NS1 protects DENV from complement-dependent neutralization in solution
 .
.
Apoptosis modulation
Flaviviruses NS3 induces apoptosis through host caspases activation

 .
.
Autophagy modulation
Flaviviruses NS4A and NS4B induces autophagy signaling
 .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Dengue virus blocks STAT2  .
.
| VMR1009056 | Orthoflavivirus apoiense | ICTV19710089 | E | Apoi virus | APOIV | ApMAR | AF160193 | Complete genome | vertebrates | Q9J9C2 | ||
| VMR1009057 | Orthoflavivirus aroaense | ICTV19990811 | E | Aroa virus | AROAV | BeAn 4073 | AY632536 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q32ZE0 | ||
| VMR1012783 | Orthoflavivirus aroaense | ICTV19990811 | A | Aroa virus | AROAV | VenA-1809 | AF013362 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55786 | ||
| VMR1012784 | Orthoflavivirus aroaense | ICTV19990811 | A | Bussuquara virus | BSQV | BeAn 4073 | AF013366 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55790 | ||
| VMR1012785 | Orthoflavivirus aroaense | ICTV19990811 | A | Iguape virus | IGUV | SP An71686 | AF013375 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55799 | ||
| VMR1012786 | Orthoflavivirus aroaense | ICTV19990811 | A | Naranjal virus | NJLV | 25008 | AF013390 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55814 | ||
| VMR1009058 | Orthoflavivirus bagazaense | ICTV19790887 | E | Bagaza virus | BAGV | DakAr B209 | AY632545 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q32ZD1 | ||
| VMR1009059 | Orthoflavivirus banziense | ICTV19710090 | E | Banzi virus | BANV | SAH 366 | DQ859056 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPA8 | ||
| VMR1009060 | Orthoflavivirus boubouiense | ICTV19760589 | E | Bouboui virus | BOUV | DAK AR B490 | DQ859057 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPA9 | ||
| VMR1009061 | Orthoflavivirus bravoense | ICTV19760625 | E | Rio Bravo virus | RBV | RiMAR | AF144692 | Complete genome | vertebrates | Q9JAD5 | ||
| VMR1009062 | Orthoflavivirus bukalasaense | ICTV19710091 | E | Bukalasa bat virus | BBV | UGBP-111 | AF013365 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55789 | ||
| VMR1009063 | Orthoflavivirus cacipacoreense | ICTV19990816 | E | Cacipacor? virus | CPCV | BeAn 3276000 | KF917536 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0A0C4PNF2 | ||
| VMR1009064 | Orthoflavivirus careyense | ICTV19760592 | E | Carey Island virus | CIV | P70-1215 | AF013368 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55792 | ||
| VMR1009065 | Orthoflavivirus cowboneense | ICTV19710093 | E | Cowbone Ridge virus | CRV | W-10986 | AF013370 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55794 | ||
| VMR1009066 | Orthoflavivirus dakarense | ICTV19710094 | E | Dakar bat virus | DBV | 209 | AF013371 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55795 | ||
| VMR1009067 | Orthoflavivirus denguei | ICTV19990820 | E | dengue virus type 2 | DENV-2 | 16681 | U87411 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O09234 | ||
| VMR1012787 | Orthoflavivirus denguei | ICTV19990820 | A | dengue virus type 1 | DENV-1 | 45AZ5 | U88536 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P17763 | ||
| VMR1012788 | Orthoflavivirus denguei | ICTV19990820 | A | dengue virus type 3 | DENV-3 | H87 | M93130 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P27915 | ||
| VMR1012789 | Orthoflavivirus denguei | ICTV19990820 | A | dengue virus type 4 | DENV-4 | 814669 | AF326573 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P09866 | ||
| VMR1009068 | Orthoflavivirus edgehillense | ICTV19710099 | E | Edge Hill virus | EHV | YMP 48 | DQ859060 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPB2 | ||
| VMR1009069 | Orthoflavivirus encephalitidis | ICTV19790934 | E | tick-borne encephalitis virus-European subtype | TBEV-Eur | Neudoerfl | U27495 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P14336 | ||
| VMR1012790 | Orthoflavivirus encephalitidis | ICTV19790934 | A | tick-borne encephalitis virus - Far Eastern subtype | TBEV-FE | Sofjin | X07755 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P07720 | ||
| VMR1012791 | Orthoflavivirus encephalitidis | ICTV19790934 | A | tick-borne encephalitis virus-Siberian subtype | TBEV-Sib | Vasilchenko | L40361 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q9DUT7 | ||
| VMR1009070 | Orthoflavivirus entebbeense | ICTV19710100 | E | Entebbe bat virus | ENTV | UgIL-30 | DQ837641 | Complete genome | vertebrates | Q32ZD9 | ||
| VMR1012792 | Orthoflavivirus entebbeense | ICTV19710100 | A | Sokuluk virus | SOKV | LEIV-400K | AF013405 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55829 | ||
| VMR1009071 | Orthoflavivirus flavi | ICTV19710125 | E | yellow fever virus | YFV | 17D | X03700 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P03314 | ||
| VMR1009072 | Orthoflavivirus gadgetsense | ICTV19990823 | E | Gadgets Gully virus | GGYV | Aus | DQ235145 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0EKU2 | ||
| VMR1009073 | Orthoflavivirus ilheusense | ICTV19990824 | E | Ilh?us virus | ILHV | Original | AY632539 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q32ZD7 | ||
| VMR1012793 | Orthoflavivirus ilheusense | ICTV19990824 | A | Rocio virus | ROCV | H-34675 | AF013397 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55821 | ||
| VMR1009074 | Orthoflavivirus israelense | ICTV19710102 | E | Israel turkey meningoencephalomyelitis virus | ITV | AF013377 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55801 | |||
| VMR1009075 | Orthoflavivirus japonicum | ICTV19710103 | E | Japanese encephalitis virus | JEV | JaOArS982 | M18370 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P32886 | ||
| VMR1009076 | Orthoflavivirus jugraense | ICTV19990827 | E | Jugra virus | JUGV | P-9-314 | DQ859066 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPB8 | ||
| VMR1009077 | Orthoflavivirus jutiapaense | ICTV19760607 | E | Jutiapa virus | JUTV | JG-128 | KJ469371 | Complete genome | vertebrates | A0A0C4W3V9 | ||
| VMR1009078 | Orthoflavivirus kadamense | ICTV19990829 | E | Kadam virus | KADV | Uganda | DQ235146 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0EKU3 | ||
| VMR1009079 | Orthoflavivirus kedougouense | ICTV19990830 | E | K?dougou virus | KEDV | DakAar D1470 | AY632540 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q32ZD6 | ||
| VMR1009080 | Orthoflavivirus kokoberaorum | ICTV19990831 | E | Kokobera virus | KOKV | AusMRM 32 | AY632541 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q32ZD5 | ||
| VMR1012794 | Orthoflavivirus kokoberaorum | ICTV19990831 | A | Stratford virus | STRV | AUSC-338 | AF013407 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55831 | ||
| VMR1009081 | Orthoflavivirus koutangoense | ICTV19760611 | E | Koutango virus | KOUV | Dak Ar D1470 | AF013384 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55808 | ||
| VMR1009082 | Orthoflavivirus kyasanurense | ICTV19710106 | E | Kyasanur Forest disease virus | KFDV | AY323490 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | D7RF80 | |||
| VMR1012795 | Orthoflavivirus kyasanurense | ICTV19710106 | A | Alkhumra hemorrhagic fever virus | AHFV | 1176 | AF331718 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q91B85 | ||
| VMR1009083 | Orthoflavivirus langatense | ICTV19710107 | E | Langat virus | LGTV | TP21 | AF253419 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q9IG40 | ||
| VMR1009084 | Orthoflavivirus louisense | ICTV19710117 | E | St. Louis encephalitis virus | SLEV | Kern217 | DQ525916 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A1BQD2 | ||
| VMR1009085 | Orthoflavivirus loupingi | ICTV19710108 | E | louping ill virus | LIV | 369/T2 | Y07863 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P22338 | ||
| VMR1012800 | Orthoflavivirus loupingi | ICTV19710108 | A | Greek goat encephalitits virus subtype | GGEV | Vergina | DQ235153 | Coding-complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | |||
| VMR1012796 | Orthoflavivirus loupingi | ICTV19710108 | A | louping ill virus-British subtype | LIV-Brit | LI/31 | D12937 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P35764 | ||
| VMR1012797 | Orthoflavivirus loupingi | ICTV19710108 | A | louping ill virus-Irish subtype | LIV-Ir | LI/MA54 | X86784 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O40972 | ||
| VMR1012798 | Orthoflavivirus loupingi | ICTV19710108 | A | louping ill virus-Spanish subtype | LIV-Spain | 87/2617 | DQ235152 | Coding-complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | |||
| VMR1012799 | Orthoflavivirus loupingi | ICTV19710108 | A | Turkish sheep encephalitis virus subtype | TSEV | TTE80 | DQ235151 | Coding-complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0EKU8 | ||
| VMR1009086 | Orthoflavivirus meabanense | ICTV19910741 | E | Meaban virus | MEAV | France | DQ235144 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0EKU1 | ||
| VMR1009087 | Orthoflavivirus modocense | ICTV19710109 | E | Modoc virus | MODV | M544 | AJ242984 | Complete genome | vertebrates | Q8QL64 | ||
| VMR1009088 | Orthoflavivirus montanaense | ICTV19990838 | E | Montana myotis leukoencephalitis virus | MMLV | USA | AJ299445 | Complete genome | vertebrates | Q8JJZ3 | ||
| VMR1009089 | Orthoflavivirus murrayense | ICTV19990839 | E | Murray Valley encephalitis virus | MVEV | 18629 | AF161266 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P05769 | ||
| VMR1012801 | Orthoflavivirus murrayense | ICTV19990839 | A | Alfuy virus | ALFV | MRM-3929 | AF013360 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0A7G0QMU0 | ||
| VMR1009090 | Orthoflavivirus nilense | ICTV19990858 | E | West Nile virus | WNV | 956 | M12294 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P06935 | ||
| VMR1012802 | Orthoflavivirus nilense | ICTV19990858 | A | Kunjin virus | KUNV | MRM61C | D00246 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P14335 | ||
| VMR1009091 | Orthoflavivirus ntayaense | ICTV19710113 | E | Ntaya virus | NTAV | IPDIA | JX236040 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | K0BRZ6 | ||
| VMR1009092 | Orthoflavivirus omskense | ICTV19710114 | E | Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus | OHFV | Bogoluvovska | AY193805 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q7T6D2 | ||
| VMR1009093 | Orthoflavivirus perlitaense | ICTV19910755 | E | San Perlita virus | SPV | 71V-1251 | AF013402 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55826 | ||
| VMR1009094 | Orthoflavivirus phnompenhense | ICTV19760623 | E | Phnom Penh bat virus | PPBV | CAMA-38D | AF013394 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55818 | ||
| VMR1012803 | Orthoflavivirus phnompenhense | ICTV19760623 | A | Batu Cave virus | BCV | P70-1459 | AF013369 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55793 | ||
| VMR1009095 | Orthoflavivirus powassanense | ICTV19710115 | E | Powassan virus | POWV | LB | L06436 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q04538 | ||
| VMR1012804 | Orthoflavivirus powassanense | ICTV19710115 | A | deer tick virus | DTV | ctb30 | AF311056 | Coding-complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q8VBK7 | ||
| VMR1009096 | Orthoflavivirus royalense | ICTV19990845 | E | Royal Farm virus | RFV | Afghanistan | DQ235149 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0EKU6 | ||
| VMR1009097 | Orthoflavivirus saboyaense | ICTV19760628 | E | Saboya virus | SABV | Dak AR D4600 | DQ859062 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPB4 | ||
| VMR1012805 | Orthoflavivirus saboyaense | ICTV19760628 | A | Potiskum virus | POTV | IBAN 10069 | DQ859067 | Coding-complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPB9 | ||
| VMR1009098 | Orthoflavivirus saumarezense | ICTV19790927 | E | Saumarez Reef virus | SREV | Australia | DQ235150 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0EKU7 | ||
| VMR1009099 | Orthoflavivirus sepikense | ICTV19990850 | E | Sepik virus | SEPV | MK7148 | DQ837642 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A1Y2M8 | ||
| VMR1009100 | Orthoflavivirus tembusu | ICTV19760634 | E | Tembusu virus | TMUV | JS804 | JF895923 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | G1CRV4 | ||
| VMR1009101 | Orthoflavivirus tyuleniyense | ICTV19760635 | E | Tyuleniy virus | TYUV | LEIV-6C | KF815939 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | W5VK97 | ||
| VMR1009102 | Orthoflavivirus ugandaense | ICTV19710120 | E | Uganda S virus | UGSV | Uganda | DQ859065 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C8XPB7 | ||
| VMR1009103 | Orthoflavivirus usutuense | ICTV19710122 | E | Usutu virus | USUV | Vienna 2001 | AY453411 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | Q5WPU5 | ||
| VMR1009104 | Orthoflavivirus viejaense | ICTV19910756 | E | Sal Vieja virus | SVV | 38TWM-106 | AF013401 | Partial genome | vertebrates | O55825 | ||
| VMR1009105 | Orthoflavivirus wesselsbronense | ICTV19990857 | E | Wesselsbron virus | WESSV | SAH177 | EU707555 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | C5H431 | ||
| VMR1009106 | Orthoflavivirus yaoundeense | ICTV19990859 | E | Yaound? virus | YAOV | DakArY 276 | AF013413 | Partial genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | O55837 | ||
| VMR1009107 | Orthoflavivirus yokoseense | ICTV19910772 | E | Yokose virus | YOKV | Oita 36 | AB114858 | Complete genome | vertebrates | Q7T918 | ||
| VMR1009108 | Orthoflavivirus zikaense | ICTV19990862 | E | Zika virus | ZIKV | MR 766 | AY632535 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | P0DXN9 | ||
| VMR1012806 | Orthoflavivirus zikaense | ICTV19990862 | A | Zika virus | ZIKV | Pf13/251013-18 | KY766069 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0A2H4GY08 | ||
| VMR1012807 | Orthoflavivirus zikaense | ICTV19990862 | A | Zika virus | ZIKV | H/PF/2013 | KJ776791 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0A024B7W1 | ||
| VMR1012808 | Orthoflavivirus zikaense | ICTV19990862 | A | Zika virus | ZIKV | PRVABC59 | KX377337 | Complete genome | invertebrates, vertebrates | A0AA97PZD4 |
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)69 entries grouped by protein
2 entries
uORF1 protein
2 entries
uORF2 protein
60 entries
Genome polyprotein
4 entries
Structural polyprotein
1 entry
