RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Naming: By convention viral polymerases are called RNA/DNA-dependent whereas cellular polymerases are called RNA/DNA-directed.
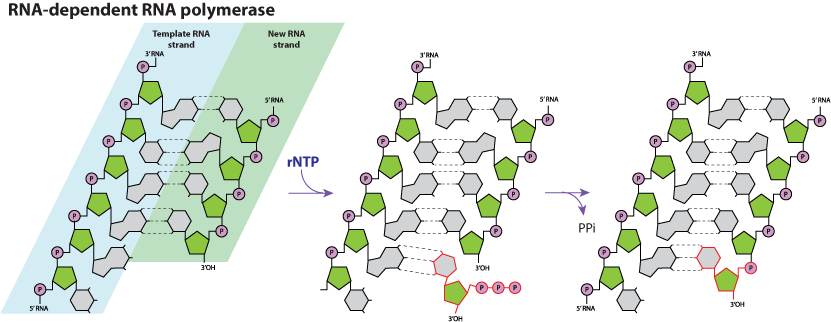
- Primer independent (Kitrinoviricota, Lernaviricota, Haploviricotina, Nidovirales)
- RNA-3'OH (Polynega-type Cap-snatching, Toti-type cap-snatching)
- Protein Vpg
Enzymatic reaction:
- RNA nucleotidyltransferase (RNA-dependent) EC 2.7.7.48 RHEA:21248
 . Subsequently, the 3'-oxygen acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphate bond and eventually releases a pyrophosphate.
. Subsequently, the 3'-oxygen acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphate bond and eventually releases a pyrophosphate.
Motifs
RdRp are characterized by up to six conserved motifs: A,B,C,D,E and F. Motifs A and C carries the catalytic aspartic acids (on orange background).
Source: 

Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements
O Poch 1, I Sauvaget, M Delarue, N Tordo
EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867-74
A Structural Overview of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases from the Flaviviridae Family
Jiqin Wu, Weichi Liu, and Peng Gong
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun; 16(6): 12943?12957
Multiple deprotonation paths of the nucleophile 3'-OH in the DNA synthesis reaction
Mark T Gregory, Yang Gao, Qiang Cui, Wei Yang
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 8;118(23):e2103990118.
