Asfivirus (taxid:39743)
VIRION
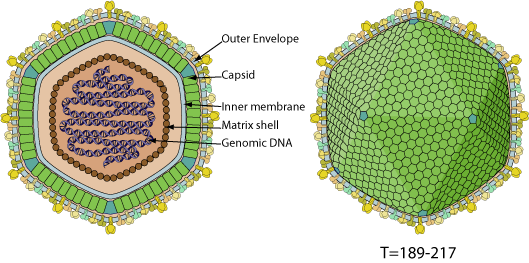
Enveloped, spherical to pleomorphic, 175-215 nm in diameter. Capsid is round, exhibits icosahedral symmetry (T=189-217) corresponding to 1892-2172 capsomers.
- Hexons: Double jelly roll-fold major capsid protein [Ba71V-081]
- Pentons: Single jelly roll-fold [Ba71V-120]
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome of 170-190 kb. End sequences are complementary. Encodes for at least 150 ORF.
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA-directed DNA polymerase B [DNApolbeta]
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase [RBP1, RBP2, RBP3-11, RBP5, RBP6, RBP7, RBP10]
- Cell-type capping
- Poly(A) polymerase [Ba71V-067]
- Peptidase C48 [Ba71V-111]
- mRNA-decapping [Ba71V-102]
- Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 [UBC
- Trans-prenyltransferase [Ba71V-074]
- DNA ligase [LIG]
- Repair DNA polymerase X [Ba71V-097]
- Deoxyuridine 5'-triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase [Ba71V-131]
- DNA topoisomerase 2 [TOP]
- Thymidylate kinase [TMK]
- Thymidine kinase [Ba71V-050]
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase [Small SU, Large SU]
- FAD-linked sulfhydryl oxidase [Ba71V-073]
- Helicase [Ba71V-072, Ba71V-123, Ba71V-040, primase]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment of the viral proteins to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the endocytic vesicle membrane occurs; DNA genome is released into the cytoplasm.
- Transcription of early viral genes; replication of the DNA genome in the cytoplasm begins about 6 hours post-infection.
- Following DNA replication, late viral genes are transcribed including structural proteins.
- Assembly of new virions occurs in cytoplasmic viral factories. Endoplasmic reticulum cisternae are recruited and transformed to give rise to precursor viral membranes, which represent the first identifiable viral structures. Viral membranes become icosahedral particles by the gradual assembly of the outer capsid layer formed by protein p72. At the same time, the matrix shell is formed underneath the viral envelope and the viral DNA and nucleoproteins are packaged and condensed.
- Virions migrate to plasma membrane on microtubules and bud.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
Several viral proteins from ASFV are dedicated to the modulation of apoptosis. For example, A224L prevent apoptosis of host cell by inhibiting caspase-3/CASP3 activation. Another viral protein, A179L, is a bcl-2 homolog and suppresses apoptosis.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)821 entries grouped by strain
160 entries
African swine fever virus (strain Badajoz 1971 Vero-adapted) (Ba71V) (ASFV) reference strain
159 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Warthog/Namibia/Wart80/1980) (ASFV)
158 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Pig/Kenya/KEN-50/1950) (ASFV)
158 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/South Africa/Pretoriuskop Pr4/1996) (ASFV)
156 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/Malawi/Lil 20-1/1983) (ASFV)
12 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Portugal/Lis 57/1957) (ASFV)
5 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Pig/Portugal/OURT88/1988) (ASFV)
3 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Pig/Portugal/Lis 60/1960) (ASFV)
2 entries
African swine fever virus (isolate Pig/Spain/E-75/1975) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Pig/Haiti/H811/1981) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/South Africa/Crocodile Cr1/1996) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/South Africa/Crocodile Cr3/1996) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/South Africa/Pretoriuskop Pr5/1996) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/South Africa/Wildebeeslaagte M1/1996) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (isolate Tick/Zimbabwe/Chiredzi Ch1/1983) (ASFV)
1 entry
African swine fever virus (strain E-70 MS16) (ASFV)
1 entry
