Viral short tail ejection system (kw:KW-1244)
 .
.
Upon binding to the host cell surface, podoviruses display a tube-like extension of their short tail that penetrates both host membranes. This tail extension comes from the release of viral core proteins with channel forming properties
 .
.
The source of the forces that drive viral genome ejection is probably in part due to osmotic pressure imbalance between the virus inside and the host cytoplasm
 .
.
Gram(-) hosts:
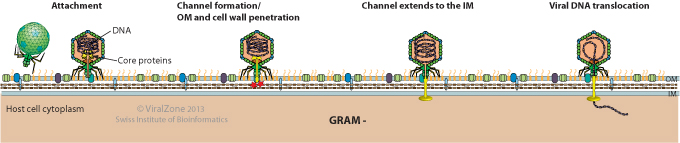
- Attachment to a host cell outer membrane (OM) receptor.
- Ejection proteins in the head form a channel that penetrates the OM. Virion-associated exolysin (if present) hydrolyzes the peptidoglycan layer.
- Channel extends through the inner membrane (IM). Some viruses may use an IM receptor.
- Viral DNA translocation into the host cytoplasm.
Gram(+) hosts:
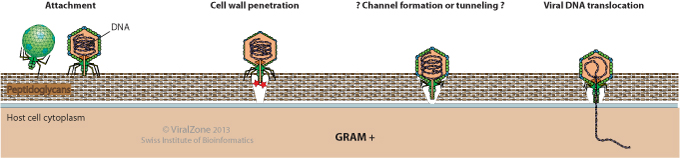
- Attachment to a host cell wall receptor.
- Virion-associated exolysin (if present)hydrolyzes the peptidoglycan layer.
- ? Channel formation or tunneling of a way through the host cell wall ?
- Viral DNA translocation into the host cytoplasm.
Short noncontractile tail machines: adsorption and DNA delivery by podoviruses
Casjens SR, Molineux IJ
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;726:143-79
Casjens SR, Molineux IJ
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;726:143-79
Structural characterization of the bacteriophage T7 tail machinery
Cuervo A, Pulido-Cid M, Chagoyen M, Arranz R, Gonzalez-Garcia VA, Garcia-Doval C, Caston JR, Valpuesta JM, van Raaij MJ, Martin-Benito J, Carrascosa JL
J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):26290-9
Cuervo A, Pulido-Cid M, Chagoyen M, Arranz R, Gonzalez-Garcia VA, Garcia-Doval C, Caston JR, Valpuesta JM, van Raaij MJ, Martin-Benito J, Carrascosa JL
J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):26290-9
The bacteriophage t7 virion undergoes extensive structural remodeling during infection
Bo Hu, William Margolin, Ian J Molineux, Jun Liu
Science February 1, 2013; 339: 576-579
Bo Hu, William Margolin, Ian J Molineux, Jun Liu
Science February 1, 2013; 339: 576-579
A conformational switch in bacteriophage p22 portal protein primes genome injection
Hongjin Zheng, Adam S Olia, Melissa Gonen, Simeon Andrews, Gino Cingolani, Tamir Gonen
Mol. Cell February 15, 2008; 29: 376-383
Hongjin Zheng, Adam S Olia, Melissa Gonen, Simeon Andrews, Gino Cingolani, Tamir Gonen
Mol. Cell February 15, 2008; 29: 376-383
Long noncontractile tail machines of bacteriophages
Alan R Davidson, Lia Cardarelli, Lisa G Pell, Devon R Radford, Karen L Maxwell
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012; 726: 115-142
Alan R Davidson, Lia Cardarelli, Lisa G Pell, Devon R Radford, Karen L Maxwell
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012; 726: 115-142
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)35 entries grouped by strain
6 entries
Escherichia phage T7 (Bacteriophage T7) reference strain
4 entries
Bacillus phage phi29 (Bacteriophage phi-29) reference strain
4 entries
Salmonella phage P22 (Bacteriophage P22) reference strain
2 entries
Acyrthosiphon pisum secondary endosymbiont phage 1 (Bacteriophage APSE-1) reference strain
2 entries
Enterobacteria phage SP6 (Bacteriophage SP6) reference strain
2 entries
Pseudomonas phage phiKMV reference strain
1 entry
Bacillus phage Nf (Bacteriophage Nf) reference strain
1 entry
Bordetella phage BPP-1 reference strain
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage HK620 (Bacteriophage HK620) reference strain
1 entry
Enterobacteria phage N4 (Bacteriophage N4) reference strain
1 entry
Helicobacter pylori bacteriophage KHP30 reference strain
1 entry
Salmonella phage epsilon15 reference strain
1 entry
Shigella phage Sf6 (Shigella flexneri bacteriophage VI) (Bacteriophage SfVI) reference strain
1 entry
Staphylococcus phage 44AHJD reference strain
3 entries
Bacillus phage B103 (Bacteriophage B103)
3 entries
Bacillus phage PZA (Bacteriophage PZA)
1 entry
