Inovirus (taxid:10861)
VIRION
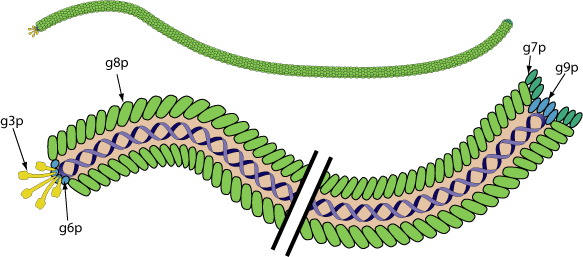
Non-enveloped, rod of filaments of 7nm in diameter and 700 to 2000nm in length. Helical capsid with adsorption proteins on one end.
GENOME
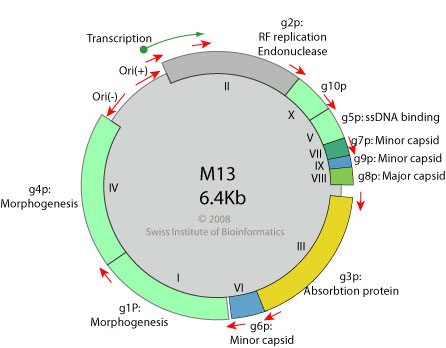
Circular, ssDNA genome (+) of 4.5 to 8kb encoding for 4 to 10 proteins. Replication occurs via dsDNA intermediate and rolling circle.
GENE EXPRESSION
Each gene is transcribed by host cellular machinery, via a specific promoter. Some genes end by a transcription terminator.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Viral g3p protein mediates pilus-mediated adsorption of the virus onto host cell. Pilus retraction pulls the virion to the host internal membrane to allow and subsequent interaction of g3p with the integral membrane protein TolA (coreceptor).
- The proteins of the capsid perform the injection of the viral DNA through bacterial membranes into cell cytoplasm.
- Host polymerase convert the (+)ssDNA viral genome into a covalently closed dsDNA called replicative form DNA (RF).
- dsDNA transcription by host RNA polymerase gives rise to viral mRNAs.
- Viral g2p protein nicks RF DNA strand at the origin of replication.
- (+) strand replication occurs by rolling circle.
- New (+)ssDNA genomes are converted into new RF molecules, and further transcription occurs.
- When enough g5p protein is synthesized, conversion into RF dsDNA is inhibited, as neo-synthesized genomic ssDNA is covered with g5p.
- g5p are replaced by g8p proteins to trigger the assembly of the viral capsid.
- New virions are secreted from host cell.
- Infected cells continue to divide and produce virions indefinitely.
replication cycle
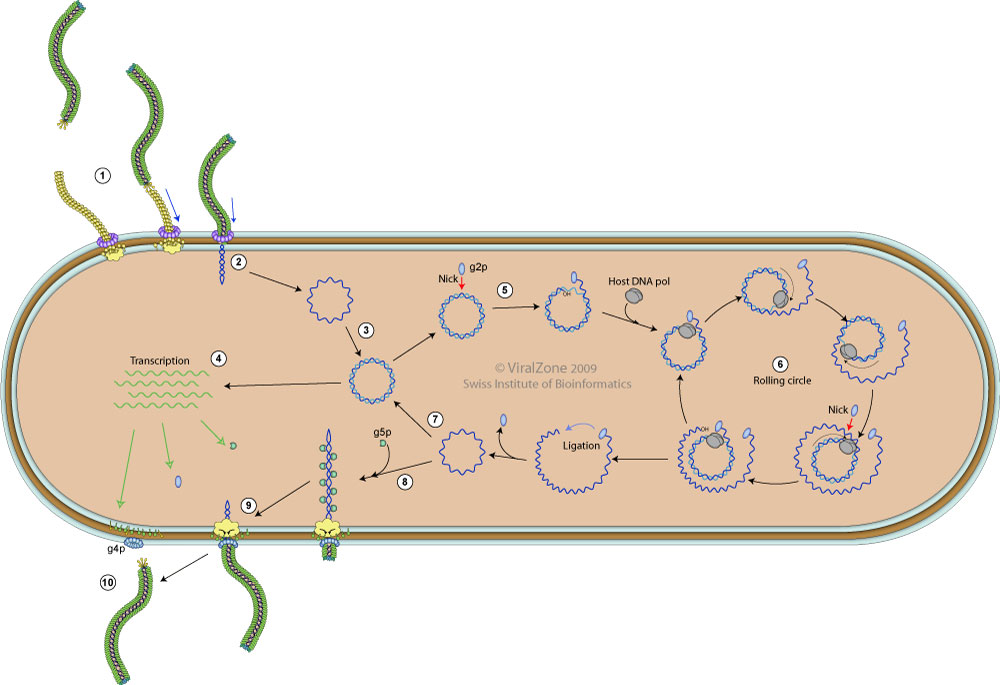
- Viral g3p protein mediates pilus-mediated adsorption of the virus onto host cell. Pilus retraction pulls the virion to the host internal membrane to allow and subsequent interaction of g3p with the integral membrane protein TolA (coreceptor).
- The proteins of the capsid mediate the Injection of the viral DNA through bacterial membranes into cell cytoplasm.
- Host polymerase convert the (+)ssDNA viral genome into a covalently closed dsDNA called replicative form DNA (RF).
- dsDNA transcription by host RNA polymerase gives rise to viral mRNAs.
- Viral g2p protein nicks RF DNA strand at the origin of replication.
- (+) strand replication occurs by rolling circle.
- New (+)ssDNA genomes are converted into new RF molecules, and further transcription occurs.
- When enough g5p protein is synthesized, conversion into RF dsDNA is inhibited, as neo-synthesized genomic ssDNA is covered with g5p.
- g5p are replaced by g8p proteins to trigger the assembly of the viral capsid.
- New virions are secreted from host cell.
- Infected cells continue to divide and produce virions indefinitely.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)27 entries grouped by protein
3 entries
Capsid protein G8P (Coat protein B) (Gene 8 protein) (G8P) (Major coat protein) (pVIII)
3 entries
Gene 1 protein (G1P) (pI)
3 entries
Attachment protein G3P (Gene 3 protein) (G3P) (Minor coat protein) (pIII)
3 entries
Virion export protein (Gene 4 protein) (G4P)
3 entries
DNA-Binding protein G5P (G5P) (GPV) (Single-stranded DNA-binding protein) (pV)
3 entries
Head virion protein G6P (Coat protein D) (G6P) (pVI)
3 entries
Tail virion protein G7P (Coat protein C, polypeptide I) (Gene 7 protein) (G7P) (pVII)
3 entries
Tail virion protein G9P (Coat protein C, polypeptide II) (G9P) (pIX)
3 entries
