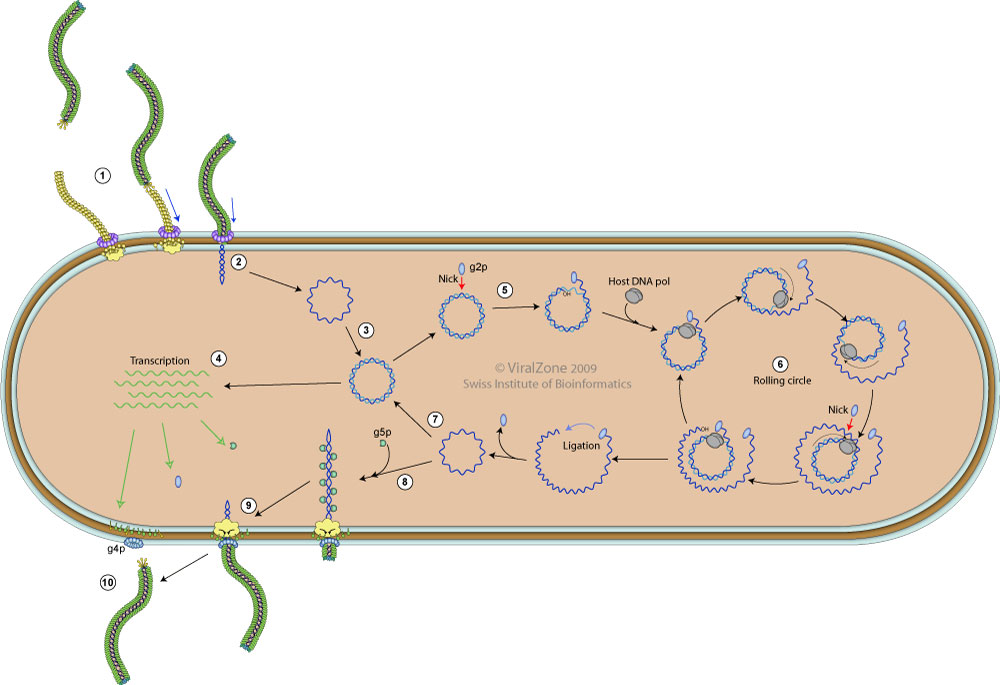
Inovirus replication cycle
back to virus description page
- Virus particle attaches to target cell by g3p protein binding of host F pilus. Pilus retraction pulls the virion to the host internal membrane.
- The proteins of the capsid inject the DNA core into cell cytoplasm.
- Host polymerase convert the (+)ssDNA viral genome into a covalently closed dsDNA called replicative form DNA RF.
- viral genes are transcribed by host RNA polymerase.
- Viral g2p protein nicks RF DNA strand at the origin of replication.
- (+)strand replication occurs by rolling circle.
- New (+)ssDNA genomes are converted into new RF molecules, and further transcription occurs.
- When enough g5p protein is synthsized, convertion into RF dsDNA is inhibited, as neo-synthesized genomic ssDNA is covered with g5p.
- g5p are replaed by g8p proteins to assemble the viral capsid.
- new virions bud out from host cell.
- Infected cells continue to divide and produces virion indefinetely.