Viral Helicases
 .
.- dsDNA viruses either encode their own helicase or utilise cellular activity when replicating in the nucleus.
- ssDNA viruses Rep protein show SF3 helicase activity to initiate the rolling circle.
- Reverse transcription viruses do not encode a helicase because RNAseH breaks the DNA /RNA duplex during reverse transcription.
- dsRNA viruses encode several unknown helicases for transcription of dsRNA templates.
- ssRNA+ viruses encode SF1, SF2 and SF3 to unwind their dsRNA replication template.
- ssRNA- viruses do not encode a helicase as their genome is always enveloped by a nucleocapsid and does not produce dsRNA.
Understanding helicases as a means of virus control
D N Frick, A M I Lam
Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(11):1315-38.
Enzymatic reaction:
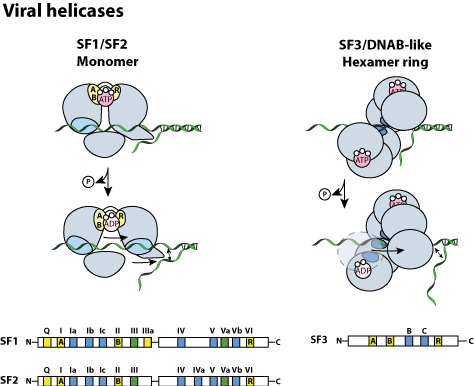
Domain:
| Class | Interpro | Viruses | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF1 | PF01443 | Monomer | SSRNA+ viruses: Pisuviricota and kitriniviricota | |
| SF2 | IPR001650 | Monomer | ssRNA+, hepacivirus; dsDNA viruses, Duplodnaviria, varidnaviria | |
| IPR034711 | Monomer | dsDNA Herpesvirales | ||
| SF3 | IPR014759 | Ring hexamer | ssRNA+ viruses: Pisuviricota | see Rep | Homo-oligomer | ssDNA viruses |
| DnaB-like/SF4 | IPR007694 | Ring hexamer | dsDNA caudoviruses | |
| Unknown | IPR054176 | Pentamers | dsRNA viruses |  |
| Unknown | IPR011181 | Tetramers | dsRNA viruses |  |
Characterization of the nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase and helicase activities of the reovirus lambda1 protein
M Bisaillon 1, J Bergeron, G Lemay
J Biol Chem. 1997 Jul 18;272(29):18298-303.
Characterization of the reovirus lambda1 protein RNA 5'-triphosphatase activity.
Bisaillon M, Lemay G.
J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 21;272(47):29954-7.
2.7 A cryo-EM structure of rotavirus core protein VP3, a unique capping machine with a helicase activity
Dilip Kumar, Xinzhe Yu, Sue E Crawford, Rodolfo Moreno, Joanita Jakana, Banumathi Sankaran, Ramakrishnan Anish, Soni Kaundal, Liya Hu, Mary K Estes, Zhao Wang, B V Venkataram Prasad
Sci Adv. 2020 Apr 15;6(16)
Mechanism : Helicases are characterized by an ATPase that provides the energy to unwind ds nucleic acids. A conserved motif binds a magnesium ion. The reaction begins with the deprotonation of a water molecule, which attacks the phosphate bond as a nucleophile and finally releases a free phosphate.
