mRNA Methyltransferase
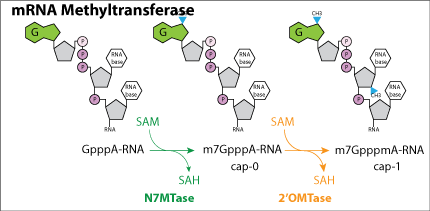
Enzymatic reactions N7methyltransferase: Rhea 67008 2'O Methyltransferase: Rhea 67020
Mechanism All methyltransferases function by transferring methyl from S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM).
Most viral 2'O methyltransferases are class I, containing a Rossmann fold.
| virus | N7MTaseRhea 67008 | 2'O methylaseRhea 67020 |
|---|---|---|
| Host metazoan | RMNT | CMTR1 |
| Iridovirus | 235L? | 235L? |
| Baculovirus | Ac69 | |
| Vaccinia (Poxvirus) | D1R: TTM TPase +D12L | J3R/VP39 |
| Orthoflavivirus (Dengue virus) | NS5 + SLA RNA  | NS5 + SLA RNA  |
| Mammalian orthoreovirus | Lambda2 | Lambda2 |
| Orbivirus(Bluetongue virus) | VP4  | VP4  |
Conventional and unconventional mechanisms for capping viral mRNA
Etienne Decroly, Francois Ferron, Julien Lescar, Bruno Canard.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Dec 5;10(1):51-65
Characterization of a trifunctional mimivirus mRNA capping enzyme and crystal structure of the RNA triphosphatase domain
Delphine Benarroch, Paul Smith, Stewart Shuman
Structure. 2008 Apr;16(4):501-12
Crystal Structures of Flavivirus NS5 Guanylyltransferase Reveal a GMP-Arginine Adduct
Hengxia Jia, Yao Zhong, Chao Peng and Peng Gong
J Virol. 2022 Jul; 96(14)
Bluetongue virus VP4 is an RNA-capping assembly line
Geoff Sutton 1, Jonathan M Grimes, David I Stuart, Polly Roy
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 May;14(5):449-51.
Nucleoside and RNA triphosphatase activities of orthoreovirus transcriptase cofactor mu2
Jonghwa Kim 1, John S L Parker, Kenneth E Murray, Max L Nibert
J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 6;279(6):4394-403.
Characterization of the reovirus lambda1 protein RNA 5'-triphosphatase activity
M Bisaillon, G Lemay
J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 21;272(47):29954-7.
Structures of dengue virus RNA replicase complexes
Takuo Osawa , Mari Aoki , Haruhiko Ehara , Shun-Ichi Sekine
Mol Cell. 2023 Aug 3;83(15):2781-2791.e4.
