Pseudoviridae (taxid:186670)
Retrotransposon:DNA sequences that can be integrated into the host genome and generate virus particles. Most of them cannot leave the cell, so that new copies of the transposon are created in the host genome during replication.
Molecular biology
VIRION
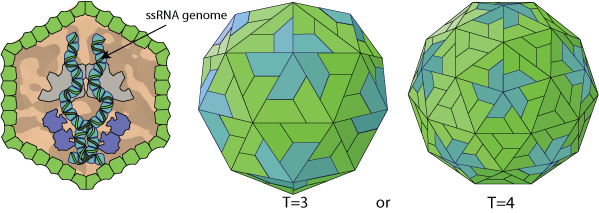
Virions are icosahedral T = 3 and might be enveloped or T=4 of 30-40nm in diameter.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, dimeric, ssRNA(+) genome of about 4-10 kb
GENE EXPRESSION
The integrated transposon utilizes the promoter elements in the 5' LTR to drive transcription primed with a host-encoded tRNA. This gives rise to the full length mRNA that will serve as genomic RNA to be packaged into virions or used as a template for translation of gag-pol polyprotein.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [RT]
- Polyprotein protease (Peptidase A) [PRO]
- Integrase [INT]
REPLICATION
- Transcription of retrotransposon to form viral RNAs.
- Translation of the RNAs to form precursor polyproteins.
- Assembly of the virion and packaging of the viral RNA genome.
- Proteolytic processing of the precursors polyproteins by viral protease and maturation of the virions.
- ssRNA is copied into a linear dsDNA molecule by the reverse transcriptase.
- Nuclear entry of the viral dsDNA which is covalently and randomly integrated into the cell's genome by the viral integrase.
