Suppressor of RNA silencing (kw:KW-0941)
RNA-mediated gene silencing (also known as RNA interference, RNAi) is a conserved sequence-specific gene regulation system, which has an essential role in the maintenance of cell genome integrity, and, in higher plants and insects, it also operates as an adaptive inducible antiviral defense mechanism. It consists in sequence-specific recognition and inhibition of target genes expression by endogenous (gene, development, stress response regulation) or virus-derived short silencing RNAs (sRNAs)  .
.
Target genes expression can be inhibited post-translationally (post-transcriptional gene silencing or PTGS): target dsRNAs are recognized by Dicer-like enzymes (DCL) and diced into small interfering RNAs duplexes (siRNA) of about 21- to 24-nt, which interact with Argonaute (AGO) proteins and associated proteins to form RNA-induced complexes (RISCs) to target homologous RNAs for destruction.
PTGS can also be performed by endogenous microRNAs (miRNAs). miRNAs differ from siRNAs in that they are encoded by cellular genes and generally base pair imperfectly with homologous RNAs to target them for destruction or inhibit their translation.
Target genes expression can also be inhibited by heavy methylation of concerned DNA loci (transcriptional gene silencing or TGS).
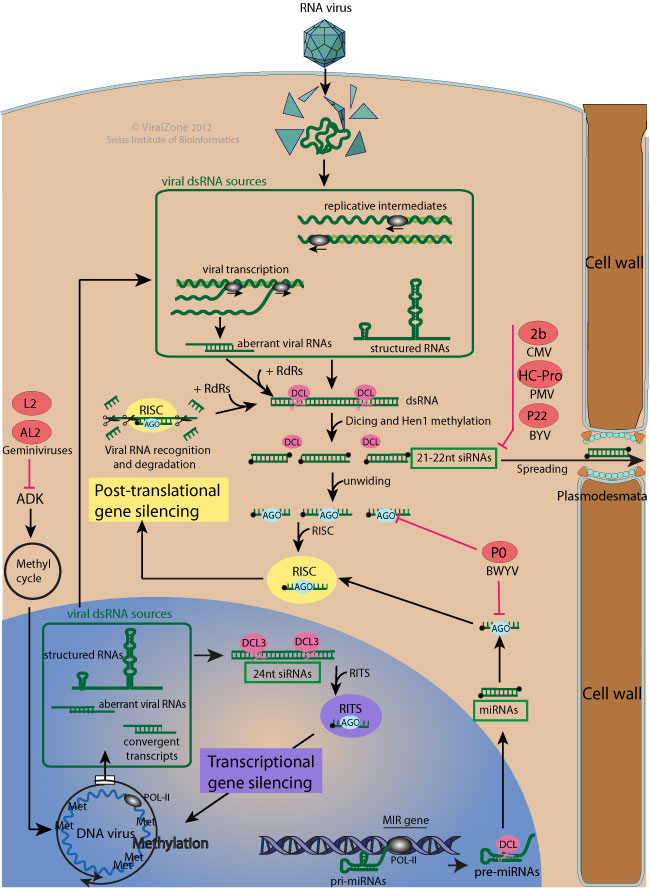
To counteract host RNAi antiviral defense, viruses from almost all plant virus genera (and also from some animal viruses) encode viral suppressors of RNA silencing (VSRs) which inhibit key steps of cellular RNAi system 
 . They are often multifunctional and play important roles in viral replication, coating, movement, and pathogenesis, in addition to suppressing host RNA silencing-based antiviral immunity.
. They are often multifunctional and play important roles in viral replication, coating, movement, and pathogenesis, in addition to suppressing host RNA silencing-based antiviral immunity.
VSRs suppress RNA silencing pathways mainly:
-through dsRNA binding. Sequestering siRNA duplexes prevents small RNA loading into the AGO effector proteins to assemble the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Sequestering long dsRNA duplexes inhibits siRNA biogenesis.

-by interacting with and inhibiting components of the host RISC machinery.
-by inhibiting enzymes necessary for host cell-mediated DNA methylation.
| Family/Genus | Virus | Viral proteins | Reference | Mechanism of action |
| Alphaflexiviridae, Potexvirus | Triple gene block protein 1 |
 |
- | |
| Betaflexiviridae, Carlavirus | Potato virus M | Triple gene block protein 1, ORF6 |
 |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes (ORF6) |
| Betaflexiviridae, Citrivirus | Citrus leaf blotch virus | Movement protein |

| |
| Betaflexiviridae, Trichovirus | Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus | 50 kDa movement protein |

| |
| Betaflexiviridae, Vitivirus | Grapevine virus A | ORF5 p10 |
 |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Bromoviridae, Cucumovirus | Cucumber mosaic virus | Protein 2b |
 |
sequestering siRNA and long dsRNA |
| Tomato aspermy virus | Protein 2b |
 |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes | |
| Bromoviridae, Ilarvirus | Tobacco streak virus | Protein 2b | - | - |
| Bunyaviridae, Tospovirus | Tomato spotted wilt virus | NSs | 
|
Sequesters both long dsRNA and double-stranded siRNA or miRNA |
| Closteroviridae, Closterovirus | Beet yellows virus | P21 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Citrus tristeza virus | p23, capsid protein, p20 |  |
- | |
| Closteroviridae, Crinivirus | Sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus | P22 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Tomato chlorosis virus | P22 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes | |
| Dicistroviridae, Cripavirus | Drosophila C virus | DCV-1A |  |
Sequesters long dsRNA and inhibits siRNA biogenesis |
| Cricket paralysis virus | CrPV-1A |  |
Interaction with Argonaute 2 and inhibition of RISC | |
| Geminiviridae, Begomovirus | Mungbean yellow mosaic virus-Vigna | TrAP/AC2 |
 |
- |
| Tomato leaf curl Java virus | V2 |  |
- | |
| Tomato leaf curl China virus | V2 |  |
?Sequesters siRNA duplexes | |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl virus | C4 |  |
- | |
| Luteoviridae , Polerovirus | Beet western yellows virus | P0 protein |


|
Targets AGO1 to degradation |
| Luteoviridae, Enamovirus | Pea enation mosaic virus-1 | P0 protein |

|
Targets AGO1 to degradation |
| Nanoviridae , Babuvirus | Banana bunchy top virus | Clink , MP |


|
- |
| Nodaviridae, Alphanodavirus | Flock house virus | B2 protein |  |
Interaction with Dicer leads to suppression of siRNA biogenesis |
| Nodaviridae, Alphanodavirus | Flock house virus | B2 protein |  |
Interaction with Dicer leads to suppression of siRNA biogenesis |
| Nodamura virus | B2 protein |  |
Interaction with Dicer leads to suppression of siRNA biogenesis | |
| Potyviridae, Potyvirus | HC-Pro |
 |
Prevents accumulation of siRNA | |
| Potyviridae, Ipomovirus | Cucumber vein yellowing virus | P1b protein |  |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Potyviridae, Poacevirus | Triticum mosaic virus | P1 protein |  |
- |
| Potyviridae, Tritimovirus | Wheat streak mosaic virus | P1 protein |  |
- |
| Reoviridae, Phytoreovirus | Rice gall dwarf virus | Pns11, Pns12 | 
 |
- |
| Rice dwarf virus | Pns10 |  |
- | |
| Reoviridae, Oryzavirus | Rice ragged stunt virus | Pns6 |  |
- |
| Rice dwarf virus | Pns10 |  |
- | |
| Secoviridae, Comovirus | Cowpea mosaic virus | small capsid protein |  |
- |
| Tenuivirus | Rice stripe virus | NS3 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Sobemovirus | Cocksfoot mottle virus | P1 |

| |
| Rice yellow mottle virus | P1 |

| ||
| Tombusviridae, Tombusvirus | Carnation Italian ringspot virus | p19 |   |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Tombusviridae, Aureusvirus | Pothos latent virus | Protein p14 |

| Sequesters both long dsRNA and double-stranded siRNA |
| Tombusviridae, Dianthovirus | Red clover necrotic mosaic virus | MP |  |
- |
| Tombusviridae, Carmovirus | Turnip crinkle virus | Capsid protein P38 |

| Competes for and inhibits Argonaute 1 |
| Tymoviridae, Tymovirus | Turnip yellow mosaic virus | p69 |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Furovirus | Soil-borne wheat mosaic virus | P19 |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Pecluvirus | Peanut clump virus | P15 |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Hordeivirus | Barley stripe mosaic virus | Gamma-B |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, tobamovirus | Tobacco mosaic virus | Small replicase subunit |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Tobravirus | Tobacco rattle virus | P16 |  |
- |
| Hypovirus | Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 | P29 |

| - |
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)298 entries grouped by strain
3 entries
African cassava mosaic virus (isolate Nigerian) (ACMV) (Cassava latent virus (isolate Nigerian)) reference strain
3 entries
Mungbean yellow mosaic virus (strain Vigna) (MYMV) reference strain
3 entries
Tomato leaf curl virus (strain Australia) (ToLCV) reference strain
3 entries
Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus (TYLCCNV) reference strain
3 entries
Tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus (TYLCSV) reference strain
3 entries
Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (strain Israel) (TYLCV) reference strain
3 entries
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Mayinga-76) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus) reference strain
2 entries
Abutilon mosaic virus (isolate West India) (AbMV) reference strain
2 entries
Banana bunchy top virus (isolate Autralia) (BBTV) reference strain
2 entries
Bean golden yellow mosaic virus (isolate Puerto Rico) (BGYMV) (Bean golden mosaic virus (isolate Puerto Rico)) reference strain
2 entries
Bean golden yellow mosaic virus (isolate Puerto Rico-Japan) (BGYMV) reference strain
2 entries
Beet curly top virus (strain California/Logan) (BCTV) reference strain
2 entries
Pepper huasteco yellow vein virus (PHYVV) (Pepper huasteco virus) reference strain
2 entries
Potato virus M (strain Russian) (PVM) reference strain
2 entries
Potato virus Y (strain N) (PVY) reference strain
2 entries
Potato yellow mosaic virus (isolate Venezuela) (PYMV) reference strain
2 entries
Red clover necrotic mosaic virus (RCNMV) reference strain
2 entries
Soybean mosaic virus (strain N) (SMV) reference strain
2 entries
Squash leaf curl virus (SLCV) reference strain
2 entries
Tomato pseudo-curly top virus (TPCTV) reference strain
2 entries
Turnip mosaic virus (strain Japanese) (TuMV) reference strain
1 entry
Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (isolate plum P863) (ACLSV) reference strain
1 entry
Apple stem pitting virus (isolate PA66) (ASPV) reference strain
1 entry
Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) reference strain
1 entry
Barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV) reference strain
1 entry
Barley yellow dwarf virus (isolate PAV) (BYDV) reference strain
1 entry
Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (isolate Japan/S) (BNYVV) reference strain
1 entry
Beet yellows virus (isolate Ukraine) (BYV) (Sugar beet yellows virus) reference strain
1 entry
Blackberry virus Y (isolate Blackberry plant/USA:Arkansas/C3ARK/2005) (BVY) reference strain
1 entry
Brome streak virus (strain 11-Cal) (BStV) (Brome streak mosaic rymovirus) reference strain
1 entry
Carnation ringspot virus (isolate Lommel) (CRSV) reference strain
1 entry
Citrus leaf blotch virus (isolate Nagami kumquat/France/SRA-153/1984) (CLBV) reference strain
1 entry
Cocksfoot mottle virus (isolate Dactylis glomerata/Norway/CfMV-NO/1995) (CfMV) reference strain
1 entry
Cowpea mosaic virus (strain SB) (CPMV) reference strain
1 entry
Cricket paralysis virus (isolate Teleogryllus commodus/Australia/CrPVVIC/1968) (CrPV) reference strain
1 entry
Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 (strain EP713) (CHV-1/EP713) (Chestnut blight fungus hypovirulence-associated virus) reference strain
1 entry
Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (strain watermelon SH) (CGMMV) reference strain
1 entry
Cucumber mosaic virus (strain FNY) (CMV) reference strain
1 entry
Dengue virus type 1 (strain Nauru/West Pac/1974) (DENV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Foxtail mosaic virus reference strain
1 entry
Grapevine virus A (isolate Is 151) (GVA) reference strain
1 entry
Indian citrus ringspot virus (isolate Kinnow mandarin/India/K1/1996) (ICRSV) reference strain
1 entry
Lolium latent virus (isolate Lolium/USA/US1/-) (LoLV) reference strain
1 entry
Narcissus mosaic virus (NMV) reference strain
1 entry
Nodamura virus (strain Mag115) (NoV) reference strain
1 entry
Papaya mosaic potexvirus (PMV) reference strain
1 entry
Pea enation mosaic virus-1 (strain WSG) (PEMV-1) reference strain
1 entry
Peanut clump virus (isolate 87/TGTA2) (PCV) reference strain
1 entry
Plantago asiatica mosaic potexvirus (P1AMV) reference strain
1 entry
Poinsettia latent virus (isolate Euphorbia pulcherrima/Germany/Siepen/2005) (PnLV) (Poinsettia cryptic virus) reference strain
1 entry
Potato leafroll virus (strain Potato/Scotland/strain 1/1984) (PLrV) reference strain
1 entry
Potato virus X (strain X3) (PVX) reference strain
1 entry
Pothos latent virus (isolate Pigeonpea/India) (PoLV) reference strain
1 entry
Rice gall dwarf virus (RGDV) reference strain
1 entry
Rice ragged stunt virus (isolate Thailand) (RRSV) reference strain
1 entry
Rice stripe virus (isolate T) (RSV) reference strain
1 entry
Ryegrass mosaic virus (isolate Denmark/Danish) (RGMV) reference strain
1 entry
Shallot virus X (ShVX) reference strain
1 entry
Soil-borne wheat mosaic virus (strain United States/Nebraska/1981) (SBWMV) reference strain
1 entry
Southern bean mosaic virus (isolate Bean/United States/Arkansas) (SBMV) reference strain
1 entry
Southern cowpea mosaic virus (SCPMV) (Southern bean mosaic virus (strain cowpea)) reference strain
1 entry
Strawberry mild yellow edge-associated virus (SMYEaV) reference strain
1 entry
Sunn-hemp mosaic virus (SHMV) (TMV strain cowpea) reference strain
1 entry
Sweet potato mild mottle virus (isolate Salazar) (SPMMV) reference strain
1 entry
Tobacco mosaic virus (strain OM) (TMV) reference strain
1 entry
Tobacco mosaic virus (strain vulgare) (TMV) (Tobacco mosaic virus (strain U1)) reference strain
1 entry
Tobacco rattle virus (isolate PpK20) (TRV) reference strain
1 entry
Tobacco streak virus (strain WC) (TSV) reference strain
1 entry
Tomato aspermy virus (TAV) reference strain
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain Cherry) (TBSV) reference strain
1 entry
Tomato golden mosaic virus (strain Yellow vein) (TGMV) reference strain
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Brazilian Br-01) (TSWV) reference strain
1 entry
Triticum mosaic virus (isolate Triticum aestivum/United States/U06-123/2006) (TriMV) reference strain
1 entry
Turnip crinkle virus (TCV) reference strain
1 entry
Turnip yellow mosaic virus reference strain
1 entry
Turnip yellows virus (isolate FL-1) (TuYV) (BWYV-FL1) reference strain
1 entry
White clover mosaic virus (strain M) (WCMV) reference strain
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain 17D vaccine) (YFV) reference strain
1 entry
Youcai mosaic virus (YoMV) reference strain
1 entry
Zika virus (ZIKV) reference strain
3 entries
African cassava mosaic virus (isolate West Kenyan 844) (ACMV) (Cassava latent virus (isolate West Kenyan 844))
3 entries
Indian cassava mosaic virus (ICMV)
3 entries
Reston ebolavirus (strain Philippines-96) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
3 entries
Reston ebolavirus (strain Reston-89) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
3 entries
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Human/Uganda/Gulu/2000) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus)
3 entries
Tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus (isolate Spain-1) (TYLCSV)
3 entries
Tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus (isolate Spain-2) (TYLCSV)
3 entries
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Kikwit-95) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
2 entries
Bean common mosaic necrosis virus (strain NL-3) (BCMNV) (Bean common mosaic virus serotype A (strain NL-3))
2 entries
Bean yellow mosaic virus
2 entries
Beet mosaic virus (BtMV)
2 entries
Cabbage leaf curl virus (isolate Jamaica) (CaLCuV)
2 entries
Chrysanthemum virus B (CVB)
2 entries
Lettuce mosaic virus (strain 0 / isolate French) (LMV)
2 entries
Lettuce mosaic virus (strain E) (LMV)
2 entries
Lily symptomless virus (LSV)
2 entries
Papaya ringspot virus (strain P / mutant HA)
2 entries
Pea seed-borne mosaic virus (strain DPD1)
2 entries
Peanut mottle virus (strain M)
2 entries
Pepper mottle virus (isolate California) (PeMV) (PepMoV C)
2 entries
Plum pox potyvirus (isolate NAT) (PPV)
2 entries
Plum pox potyvirus (strain D) (PPV)
2 entries
Plum pox potyvirus (strain SK 68) (PPV)
2 entries
Poplar mosaic virus (isolate ATCC Pv275) (PMV)
2 entries
Potato virus A (PVA)
2 entries
Potato virus S (strain Peruvian)
2 entries
Potato virus Y (strain Hungarian) (PVY)
2 entries
Soybean mosaic virus (strain G2) (SMV)
2 entries
Tobacco etch virus (TEV)
2 entries
Tobacco vein mottling virus (TVMV)
2 entries
Turnip mosaic virus (strain Quebec) (TuMV)
2 entries
Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (strain California) (ZYMV)
2 entries
Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (strain Reunion Island) (ZYMV)
2 entries
Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (strain Singapore) (ZYMV)
1 entry
Alkhumra hemorrhagic fever virus (ALKV) (Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever virus)
1 entry
Andean potato mottle virus (APMV)
1 entry
Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (isolate apple) (ACLSV)
1 entry
Artichoke mottled crinkle virus (AMCV)
1 entry
Banzi virus (BANV)
1 entry
Bean-pod mottle virus (strain Kentucky G7) (BPMV)
1 entry
Black beetle virus (BBV)
1 entry
Boolarra virus (BoV)
1 entry
Broad bean wilt virus 2 (BBWV-2)
1 entry
Bussuquara virus (BUSV)
1 entry
Carnation Italian ringspot virus (CIRV)
1 entry
Carnation latent virus (CLV)
1 entry
Cowpea severe mosaic virus (strain DG) (CPSMV)
1 entry
Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 (strain Euro7) (CHV-1/Euro7) (Chestnut blight fungus hypovirulence-associated virus)
1 entry
Cucumber mosaic virus (strain Q) (CMV)
1 entry
Cucumber necrosis virus (CNV)
1 entry
Cymbidium ringspot virus (CymRSV)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 1 (strain Singapore/S275/1990) (DENV-1)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (isolate Thailand/0168/1979) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain 16681-PDK53) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Jamaica/1409/1983) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Peru/IQT2913/1996) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Puerto Rico/PR159-S1/1969) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Thailand/16681/1984) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 2 (strain Thailand/NGS-C/1944) (DENV-2)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain China/80-2/1980) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Martinique/1243/1999) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Philippines/H87/1956) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Singapore/8120/1995) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 3 (strain Sri Lanka/1266/2000) (DENV-3)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Dominica/814669/1981) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Philippines/H241/1956) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Singapore/8976/1995) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Thailand/0348/1991) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Dengue virus type 4 (strain Thailand/0476/1997) (DENV-4)
1 entry
Drosophila C virus (strain EB) (DCV)
1 entry
Edge Hill virus (EHV)
1 entry
Flock house virus (FHV)
1 entry
Havel river virus (HaRV)
1 entry
Helenium virus S (HelVS)
1 entry
Ilheus virus (ILHV)
1 entry
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain Jaoars982) (JEV)
1 entry
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain M28) (JEV)
1 entry
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain SA(v)) (JEV)
1 entry
Japanese encephalitis virus (strain SA-14) (JEV)
1 entry
Kokobera virus (KOKV)
1 entry
Kunjin virus (strain MRM61C)
1 entry
Kyasanur forest disease virus (KFDV)
1 entry
Langat virus (strain TP21)
1 entry
Lily virus X
1 entry
Louping ill virus (Li)
1 entry
Maize stripe virus (MStV)
1 entry
Murray valley encephalitis virus (strain MVE-1-51) (MVEV)
1 entry
Odontoglossum ringspot virus (isolate Korean Cy) (ORSV-Cy)
1 entry
Odontoglossum ringspot virus (isolate Singapore 1) (ORSV)
1 entry
Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus (OHFV)
1 entry
Pear latent virus (PeLV)
1 entry
Pelargonium necrotic spot virus (PeNSV)
1 entry
Pepper mild mottle virus (strain Japan) (PMMV-J)
1 entry
Pepper mild mottle virus (strain Spain) (PMMV-S)
1 entry
Plum pox potyvirus (strain Rankovic) (PPV)
1 entry
Potato leafroll virus (strain Potato/Netherlands/Wageningen/1989) (PLrV)
1 entry
Potato virus M (strain German) (PVM)
1 entry
Potato virus X (PVX)
1 entry
Potato virus X (strain CP) (PVX)
1 entry
Potato virus X (strain HB) (PVX)
1 entry
Red clover mottle virus (RCMV)
1 entry
Rice dwarf virus (isolate Akita) (RDV)
1 entry
Rice dwarf virus (isolate O) (RDV)
1 entry
Rice hoja blanca virus (strain cr) (RHBV) (Rice hoja blanca virus (strain Costa Rica))
1 entry
Rice stripe virus (isolate M) (RSV)
1 entry
Rocio virus (ROCV)
1 entry
Squash mosaic virus (strain melon) (SqMV)
1 entry
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (strain Hypr) (TBEV)
1 entry
Tick-borne encephalitis virus European subtype (strain Neudoerfl) (NEUV) (Neudoerfl virus)
1 entry
Tick-borne encephalitis virus Far Eastern subtype (strain Sofjin) (SOFV) (Sofjin virus)
1 entry
Tick-borne powassan virus (strain LB) (POWV) (Powassan virus)
1 entry
Tobacco mild green mosaic virus (TMGMV) (TMV strain U2)
1 entry
Tobacco mosaic virus (strain B935A) (TMV)
1 entry
Tobacco mosaic virus (strain Korean NC 82) (TMV)
1 entry
Tobacco mosaic virus (strain Rakkyo) (TMV-R)
1 entry
Tobamovirus Ob
1 entry
Tomato brown rugose fruit virus (isolate TOBRFV/Tomato/Jordan/Tom1-Jo/2015) (ToBRFV)
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain A23) (TBSV)
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain B8) (TBSV)
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain BS-3) (TBSV)
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain Ja6) (TBSV)
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain Ja9) (TBSV)
1 entry
Tomato bushy stunt virus (strain type) (TBSV)
1 entry
Tomato mosaic virus (strain Kazakh K1) (ToMV) (TMV strain K1)
1 entry
Tomato mosaic virus (strain Kazakh K2) (ToMV) (TMV strain K2)
1 entry
Tomato mosaic virus (strain L) (ToMV) (TMV strain tomato)
1 entry
Tomato mosaic virus (strain S-1) (ToMV)
1 entry
Tomato mottle virus (isolate Florida) (ToMoV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Bulgarian L3) (TSWV)
1 entry
Turnip vein-clearing virus (TVCV)
1 entry
Turnip yellow mosaic virus (isolate Australia)
1 entry
Turnip yellow mosaic virus (isolate TYMC)
1 entry
Usutu virus (USUV)
1 entry
Wesselsbron virus (WSLV)
1 entry
West Nile virus (WNV)
1 entry
West Nile virus (strain NY-99) (WNV) (West Nile virus (strain NY-1999))
1 entry
White clover mosaic virus (strain O) (WCMV)
1 entry
Wound tumor virus (WTV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Angola/14FA/1971) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Ethiopia/Couma/1961) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Ivory Coast/1999) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Ivory Coast/85-82H/1982) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (isolate Uganda/A7094A4/1948) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain French neurotropic vaccine FNV) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain Ghana/Asibi/1927) (YFV)
1 entry
Yellow fever virus (strain Trinidad/TRINID79A/1979) (YFV)
1 entry
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Gabon-94) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
1 entry
