Suppressor of RNA silencing (kw:KW-0941)
RNA-mediated gene silencing (also known as RNA interference, RNAi) is a conserved sequence-specific gene regulation system, which has an essential role in the maintenance of cell genome integrity, and, in higher plants and insects, it also operates as an adaptive inducible antiviral defense mechanism. It consists in sequence-specific recognition and inhibition of target genes expression by endogenous (gene, development, stress response regulation) or virus-derived short silencing RNAs (sRNAs)  .
.
Target genes expression can be inhibited post-translationally (post-transcriptional gene silencing or PTGS): target dsRNAs are recognized by Dicer-like enzymes (DCL) and diced into small interfering RNAs duplexes (siRNA) of about 21- to 24-nt, which interact with Argonaute (AGO) proteins and associated proteins to form RNA-induced complexes (RISCs) to target homologous RNAs for destruction.
PTGS can also be performed by endogenous microRNAs (miRNAs). miRNAs differ from siRNAs in that they are encoded by cellular genes and generally base pair imperfectly with homologous RNAs to target them for destruction or inhibit their translation.
Target genes expression can also be inhibited by heavy methylation of concerned DNA loci (transcriptional gene silencing or TGS).
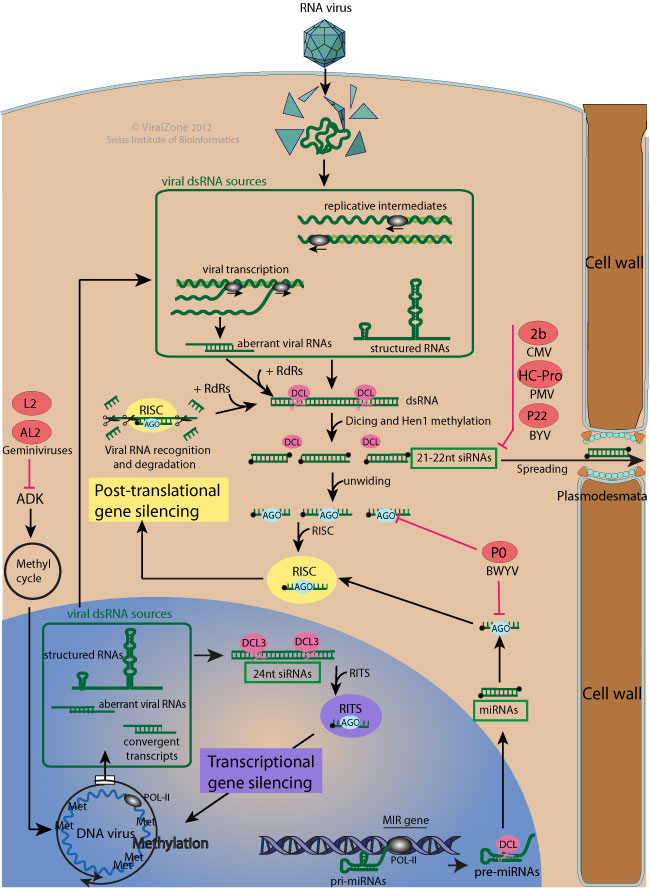
To counteract host RNAi antiviral defense, viruses from almost all plant virus genera (and also from some animal viruses) encode viral suppressors of RNA silencing (VSRs) which inhibit key steps of cellular RNAi system 
 . They are often multifunctional and play important roles in viral replication, coating, movement, and pathogenesis, in addition to suppressing host RNA silencing-based antiviral immunity.
. They are often multifunctional and play important roles in viral replication, coating, movement, and pathogenesis, in addition to suppressing host RNA silencing-based antiviral immunity.
VSRs suppress RNA silencing pathways mainly:
-through dsRNA binding. Sequestering siRNA duplexes prevents small RNA loading into the AGO effector proteins to assemble the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Sequestering long dsRNA duplexes inhibits siRNA biogenesis.

-by interacting with and inhibiting components of the host RISC machinery.
-by inhibiting enzymes necessary for host cell-mediated DNA methylation.
| Family/Genus | Virus | Viral proteins | Reference | Mechanism of action |
| Alphaflexiviridae, Potexvirus | Triple gene block protein 1 |
 |
- | |
| Betaflexiviridae, Carlavirus | Potato virus M | Triple gene block protein 1, ORF6 |
 |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes (ORF6) |
| Betaflexiviridae, Citrivirus | Citrus leaf blotch virus | Movement protein |

| |
| Betaflexiviridae, Trichovirus | Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus | 50 kDa movement protein |

| |
| Betaflexiviridae, Vitivirus | Grapevine virus A | ORF5 p10 |
 |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Bromoviridae, Cucumovirus | Cucumber mosaic virus | Protein 2b |
 |
sequestering siRNA and long dsRNA |
| Tomato aspermy virus | Protein 2b |
 |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes | |
| Bromoviridae, Ilarvirus | Tobacco streak virus | Protein 2b | - | - |
| Bunyaviridae, Tospovirus | Tomato spotted wilt virus | NSs | 
|
Sequesters both long dsRNA and double-stranded siRNA or miRNA |
| Closteroviridae, Closterovirus | Beet yellows virus | P21 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Citrus tristeza virus | p23, capsid protein, p20 |  |
- | |
| Closteroviridae, Crinivirus | Sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus | P22 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Tomato chlorosis virus | P22 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes | |
| Dicistroviridae, Cripavirus | Drosophila C virus | DCV-1A |  |
Sequesters long dsRNA and inhibits siRNA biogenesis |
| Cricket paralysis virus | CrPV-1A |  |
Interaction with Argonaute 2 and inhibition of RISC | |
| Geminiviridae, Begomovirus | Mungbean yellow mosaic virus-Vigna | TrAP/AC2 |
 |
- |
| Tomato leaf curl Java virus | V2 |  |
- | |
| Tomato leaf curl China virus | V2 |  |
?Sequesters siRNA duplexes | |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl virus | C4 |  |
- | |
| Luteoviridae , Polerovirus | Beet western yellows virus | P0 protein |


|
Targets AGO1 to degradation |
| Luteoviridae, Enamovirus | Pea enation mosaic virus-1 | P0 protein |

|
Targets AGO1 to degradation |
| Nanoviridae , Babuvirus | Banana bunchy top virus | Clink , MP |


|
- |
| Nodaviridae, Alphanodavirus | Flock house virus | B2 protein |  |
Interaction with Dicer leads to suppression of siRNA biogenesis |
| Nodaviridae, Alphanodavirus | Flock house virus | B2 protein |  |
Interaction with Dicer leads to suppression of siRNA biogenesis |
| Nodamura virus | B2 protein |  |
Interaction with Dicer leads to suppression of siRNA biogenesis | |
| Potyviridae, Potyvirus | HC-Pro |
 |
Prevents accumulation of siRNA | |
| Potyviridae, Ipomovirus | Cucumber vein yellowing virus | P1b protein |  |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Potyviridae, Poacevirus | Triticum mosaic virus | P1 protein |  |
- |
| Potyviridae, Tritimovirus | Wheat streak mosaic virus | P1 protein |  |
- |
| Reoviridae, Phytoreovirus | Rice gall dwarf virus | Pns11, Pns12 | 
 |
- |
| Rice dwarf virus | Pns10 |  |
- | |
| Reoviridae, Oryzavirus | Rice ragged stunt virus | Pns6 |  |
- |
| Rice dwarf virus | Pns10 |  |
- | |
| Secoviridae, Comovirus | Cowpea mosaic virus | small capsid protein |  |
- |
| Tenuivirus | Rice stripe virus | NS3 |

| Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Sobemovirus | Cocksfoot mottle virus | P1 |

| |
| Rice yellow mottle virus | P1 |

| ||
| Tombusviridae, Tombusvirus | Carnation Italian ringspot virus | p19 |   |
Sequesters siRNA duplexes |
| Tombusviridae, Aureusvirus | Pothos latent virus | Protein p14 |

| Sequesters both long dsRNA and double-stranded siRNA |
| Tombusviridae, Dianthovirus | Red clover necrotic mosaic virus | MP |  |
- |
| Tombusviridae, Carmovirus | Turnip crinkle virus | Capsid protein P38 |

| Competes for and inhibits Argonaute 1 |
| Tymoviridae, Tymovirus | Turnip yellow mosaic virus | p69 |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Furovirus | Soil-borne wheat mosaic virus | P19 |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Pecluvirus | Peanut clump virus | P15 |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Hordeivirus | Barley stripe mosaic virus | Gamma-B |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, tobamovirus | Tobacco mosaic virus | Small replicase subunit |  |
- |
| Virgaviridae, Tobravirus | Tobacco rattle virus | P16 |  |
- |
| Hypovirus | Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 | P29 |

| - |
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)298 entries grouped by protein
4 entries
Suppressor of silencing 2b (Protein 2b)
19 entries
Protein AC4 (Protein AL4)
10 entries
Protein V2
4 entries
Protein B2
2 entries
Protein C2 (Protein L2)
1 entry
Capsid protein (Coat protein) (p38)
1 entry
Cell cycle link protein (Clink)
1 entry
Putative movement protein (MP) (Cell-to-cell transport protein)
4 entries
Movement protein (MP)
30 entries
P3N-PIPO polyprotein
2 entries
Non-structural protein NS-S
4 entries
Suppressor of silencing P0 (28 kDa protein) (Protein ORF0)
1 entry
RNA silencing suppressor p14
14 entries
RNA silencing suppressor p19 (19 kDa symptom severity modulator)
1 entry
RNA silencing suppressor (21 kDa protein) (p21)
1 entry
Early 35 kDa protein (Apoptosis-preventing protein) (p35)
3 entries
69 kDa protein (p69)
7 entries
RNA2 polyprotein (119kDa protein) (Genome polyprotein M)
2 entries
Polyprotein p69 (ORFA polyprotein)
85 entries
Genome polyprotein
2 entries
Replicase polyprotein
21 entries
Replicase large subunit (EC 2.1.1.-) (EC 2.7.7.-) (EC 2.7.7.48) (EC 3.6.4.13) (183 kDa protein) (RNA-directed RNA polymerase)
21 entries
Movement and silencing protein TGBp1 (25 kDa protein) (Silencing suppressor P25) (Triple gene block 1 protein) (TGBp1)
19 entries
Transcriptional activator protein (TrAP) (Protein AC2) (Protein AL2)
5 entries
Transcriptional activator VP30 (EbolaVP30) (eVP30) (Minor nucleoprotein VP30)
5 entries
Polymerase cofactor VP35
6 entries
Matrix protein VP40 (Ebola VP40) (eVP40) (Membrane-associated protein VP40)
23 entries
