Molecular biology
VIRION
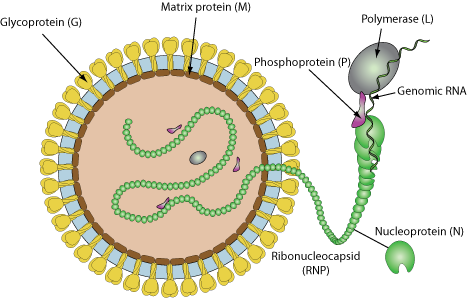
Enveloped, spherical. Diameter from 70 to 130 nm.
GENOME
Negative-stranded RNA linear genome, about 9 kb in size. Encodes for six proteins proteins.
Enzymes: RNA dependent RNA polymerase, RNA guanylyl transferase, mRNA methyltransferase.
GENE EXPRESSION
The viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase binds the encapsidated genome at the leader region, then sequentially transcribes each genes by recognizing start and stop signals flanking viral genes. mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by the L protein during synthesis. the third transcript encodes M, G and L by alternative splicing.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [L]
- Mononega-type capping
- RNA TPase, GTase, N7 Mtase, 2'O Mtase [L]
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
- Attachement of the viral GP glycoproteins to host receptors mediates Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the virus into the host cell
- Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane; ribonucleocapsid is released and migrates to the nucleus.
- Sequential transcription, viral mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by polymerase stuttering in the cytoplasm. M, G and L proteins are produced by alternative splicing.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- Neo-synthesized ribo-nucleocapsids exit out of the nucleus by nuclear pore export.
- Cytoplasmic ribo-nucleocapsids bind to the matrix protein under cell membrane, inducing particle budding.
- Release of new virions.

