Orthoebolavirus (taxid:3044781)
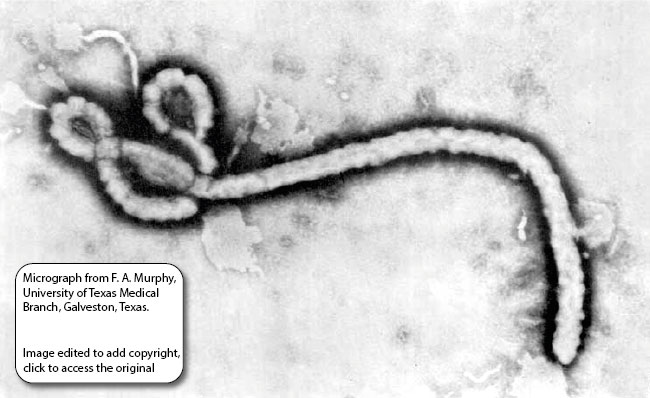
Filamentous 970 nm long for Ebolavirus. Diameter is about 80nm.
GENOME
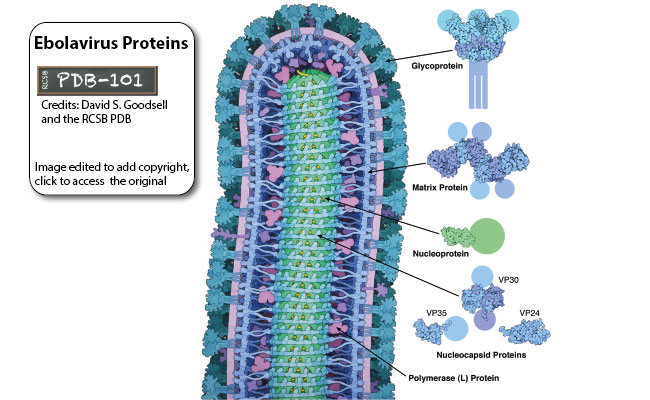
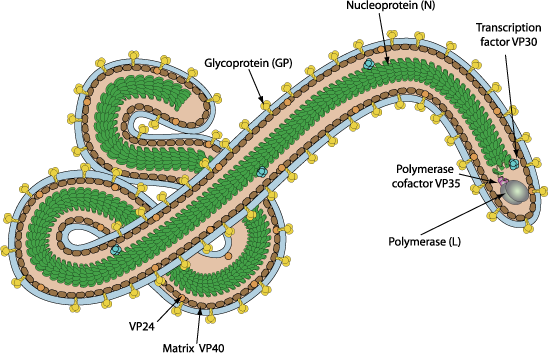
Negative-stranded RNA linear genome, about 18-19 kb in size. Encodes for seven proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase binds the encapsidated genome at the leader region, then sequentially transcribes each genes by recognizing start and stop signals flanking viral genes. mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by the L protein during synthesis.
The primary product of the unedited transcript of GP gene yields a smaller non-structural glycoprotein sGP which is efficiently secreted from infected cells. RNA editing allows expression of full-length GP.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L
- Mononega-type capping
- RNA TPase, GTase, N7 Mtase, 2'O Mtase L
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment to host receptors through GP glycoprotein like DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR

- Cellular receptor like HAVCR1(TIM1) binds phosphatidyl serine on virion membrane and a signal is transduced into the cell that trigger the macropinocytosis program by apoptotic mimicry.
- The virion enters the cell by Macropinocytosis


 . In some culture cells, GP glycoprotein can be processed by host Cathepsin L and Cathepsin B into 19kDa GP1
. In some culture cells, GP glycoprotein can be processed by host Cathepsin L and Cathepsin B into 19kDa GP1 . But this processing is not happening in all cells or for all ebolavirus
. But this processing is not happening in all cells or for all ebolavirus .
. - GP1 interacts with host NPC1, in late macropinosome and promotes Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane
 . The ribonucleocapsid is then released into the cytoplasm.
. The ribonucleocapsid is then released into the cytoplasm. - Sequential transcription, viral mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by polymerase stuttering in the cytoplasm.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid interacts with the matrix protein, and buds via the host ESCRT complexes from the plasma membrane

 , releasing the virion .
, releasing the virion .
Judith M. White, Kathryn L. Schornberg
Nat. Rev. Microbiol. May 2012; 10: 317?322
Carmen P. Alvarez, F?tima Lasala, Jaime Carrillo, Oscar Mu?iz, Angel L. Corb?, Rafael Delgado
J. Virol. July 2002; 76: 6841?6844
Emily Happy Miller, Gregor Obernosterer, Matthijs Raaben, Andrew S. Herbert, Maika S. Deffieu, Anuja Krishnan, Esther Ndungo, Rohini G. Sandesara, Jan E. Carette, Ana I. Kuehne, Gordon Ruthel, Suzanne R. Pfeffer, John M. Dye, Sean P. Whelan, Thijn R. Brummelkamp, Kartik Chandran
The EMBO Journal April 18, 2012; 31: 1947?1960
Asuka Nanbo, Masaki Imai, Shinji Watanabe, Takeshi Noda, Kei Takahashi, Gabriele Neumann, Peter Halfmann, Yoshihiro Kawaoka
PLoS Pathog. 2010; 6: e1001121
Catherine L. Hunt, Andrey A. Kolokoltsov, Robert A. Davey, Wendy Maury
J. Virol. January 2011; 85: 334?347
Andrea Marzi, Thomas Reinheckel, Heinz Feldmann
PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2012; 6: e1923
R. N. Harty, M. E. Brown, G. Wang, J. Huibregtse, F. P. Hayes
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. December 5, 2000; 97: 13871?13876
Jillian M. Licata, Martha Simpson-Holley, Nathan T. Wright, Ziying Han, Jason Paragas, Ronald N. Harty
J. Virol. February 2003; 77: 1812?1819
Host-virus interaction
Inhibition of host Interferon induction
Vp35 protein prevents host interferon induction by Inhibition of host IKBKE by virus 
Inhibition of host interferon signaling
Vp24 protein block interferon signaling by preventing STAT1 signaling. May act by binding host karyopherin ? proteins, thereby preventing them from transporting the tyrosine-phosphorylated transcription factor STAT1 to the nucleus. May directly bind to STAT1 to prevent its signaling  .
.
Antigenic subvertion
Small Glycoprotein (sGP) is a secreted truncated version of GP that prevent host antibodies anti-GP to effectively neutralize it  .
.
Inhibition of acquired immune response
Ebolavirus may encode for a superantigen, thereby inhibiting Vbeta t cells 
Eric M Leroy, Pierre Becquart, Nadia Wauquier, Sylvain Baize
J. Virol. April 2011; 85: 4041?4042
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)62 entries grouped by strain
9 entries
Reston ebolavirus (strain Reston-89) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus) reference strain
9 entries
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Human/Uganda/Gulu/2000) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus) reference strain
9 entries
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Mayinga-76) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus) reference strain
9 entries
Reston ebolavirus (strain Philippines-96) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
9 entries
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Kikwit-95) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
5 entries
Zaire ebolavirus (strain Gabon-94) (ZEBOV) (Zaire Ebola virus)
3 entries
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Boniface-76) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus)
3 entries
Sudan ebolavirus (strain Maleo-79) (SEBOV) (Sudan Ebola virus)
2 entries
Reston ebolavirus (strain Siena/Philippine-92) (REBOV) (Reston Ebola virus)
2 entries
Tai Forest ebolavirus (strain Cote d'Ivoire-94) (TAFV) (Cote d'Ivoire Ebola virus)
2 entries