Acid (Asp/Glu) proteases

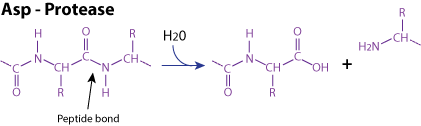
Enzymatic reaction:
- Asp-endopeptidase EC.3.4.23.-
- Glu-endopeptidase EC.3.4.23.-
Mechanism These proteases are characterized by a conserved motif known as a catalytic dyad consisting of two aspartic acid residues or one glutamic and one aspartic acid residues. One carboxylate groups of these two acid residues assist in proton transfers from a water molecule that acts as the nucleophile, to attack the peptide bond of the peptide or protein to be cleaved. A well-known example of an aspartate protease is pepsin, which is found in the stomach and plays a crucial role in the digestion of proteins.
| Genome | Order | Family | Function | Type | MEROPS family | Distribution (low incidence) | Clan (fold) | Interpro | UniProt exemplar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RtRNA | Ortervirales |   Retroviridae, Orthoretrovirinae Retroviridae, Orthoretrovirinae |
Virion maturation | Aspartyl | Peptidase A2 | Virus, (animals, plant, fungi, protozoa) | AA (pepsin fold) | IPR001969 | Gag polyprotein |
| RtRNA | Ortervirales |   Retroviridae, Spumaretrovirinae Retroviridae, Spumaretrovirinae |
Virion maturation | Aspartyl | Peptidase A9 | Virus, animals, fungi | AA (pepsin fold) | IPR001641 | Pro-pol polyprotein |
| RtRNA | Ortervirales |   Caulimoviridae Caulimoviridae |
Virion maturation | Aspartyl | Peptidase A3 | Virus, (plant) | AA (pepsin fold) | IPR000588 | Polyprotein |
| dsDNA | Caudovirales |  Salasmaviridae Salasmaviridae |
Self cleaving, Virion maturation | Glutamine | Peptidase G2 | Bacteria, virus | GB | IPR021865 | Pre-neck appendage protein |
| dsDNA | Algavirales |  Phycodnaviridae Phycodnaviridae |
Self cleaving, Virion maturation | Glutamine | Peptidase G2 | Bacteria, virus | GB | IPR021865 | Chlorovirus glycoprotein repeat domain-containing protein |
Origins of peptidases
Neil D Rawlings, Alex Bateman
Biochimie. 2019 Nov;166:4-18.
