Roniviridae (taxid:199704)
VIRION
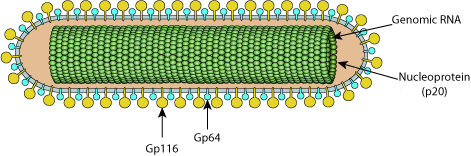
Enveloped, bacilliform-shaped, about 150-200 nm x 40-60 nm. Nucleocapsid have helical symmetry with diameter of 20-30nm.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear ssRNA(+) genome of 26 kb in size. Capped, and polyadenylated.
GENE EXPRESSION
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and viral messenger RNA. Genomic RNA encodes ORF1a, as for ORF1b, it is translated by ribosomal frameshifting. Resulting proteins pp1a and pp1ab are processed into the viral polymerase (RdRp) and other non-structural proteins involved in RNA synthesis. Structural proteins are expressed as subgenomic RNAs. Each RNA (genomic and subgenomic) is translated to yield only the protein encoded by the 5'-most ORF.
ENZYMES
- RNA-directed RNA polymerase [Q9WPZ7]
- Proofreading exoribonuclease (ExoN) [Q9WPZ7]
- Nido-type capping (GDP polyribonucleotidyltransferase, N7methyltransferase, 2'O methylase) [Q9WPZ7]
- Papain-like protease (Peptidase C16) [Q9WPZ7]
- Polyprotein major protease (Peptidase C62) [Q9WPZ7]
REPLICATION
- Attachement to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the endosomal membrane, ssRNA(+) genome is released into the cytoplasm.
- Synthesis and proteolytic cleavage of the replicase polyprotein.
- Replication occurs in viral factories. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Synthesis of structural proteins encoded by subgenomic mRNAs.
- Assembly and budding at membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the intermediate compartments, and/or the Golgi complex.
- Release of new virions.
Gill-associated virus (isolate Giant tiger prawn/Australia) taxid:649894
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-42110 |
| p20 nucleocapsid protein | ma-jd-viral-59058 |
