Host mRNA suppression by virus (kw:KW-1192)
Viruses have evolved ways of suppressing host mRNAs expression to favor their survival and maximize expression of their own mRNAs. Decimating cellular mRNAs eventually leads to shutoff of host proteins expression and gives viruses transcripts a competitive edge for access to the cellular translation machinery.
Preventing the expression of host proteins is also a strategy to counteract the antiviral response.
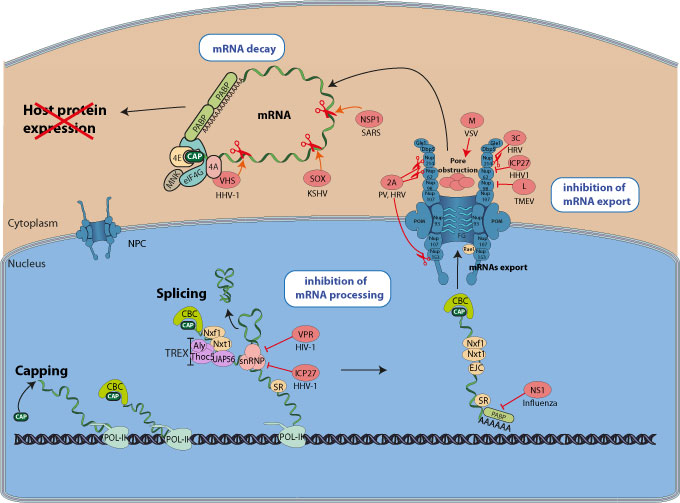
Some viruses interfere with host pre-mRNA processing function (splicing or polyadenylation), whereas other induce the host mRNAs degradation or block their export out of the nucleus.
Viruses inhibiting host mRNA splicing:
| Family | Virus | Viral protein | mRNA suppression strategy | references |
| Orthomyxoviridae | Influenza A virus | NS1 | Inhibition of polyadenylation & nuclear export |




|
| Herpesviridae | HHV1, HHV2 ( Simplexvirus) | ICP27 | Inhibition of splicing & nuclear export |




|
| VHS protein | mRNA decay |
  

|
HHV-8/KSHV ( Gammaherpesvirinae ) | SOX protein (ORF37) | mRNA decay |





|
| MHV68 ( Rhadinovirus ) | SOX protein | mRNA decay |

|
|
| EBV ( Lymphocryptovirus ) | BGLF5 | mRNA decay |

|
|
| Retroviridae | HIV-1 | VPR | Inhibition of splicing |

|
| Coronaviridae | SARS coronavirus | NSP1 | mRNA decay |

|
| Picornaviridae | Poliovirus ( Enterovirus ) | 2A protease | Inhibition of nuclear export |


|
| Theiler's virus ( Cardiovirus ) | Leader protein | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| EMCV ( Cardiovirus ) | Leader protein | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| HRV16 ( Enterovirus ) | 3C protease | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| HRV14 ( Enterovirus ) | ? | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| Rhabdoviridae | Vesicular stomatitis virus ( Vesiculovirus ) | M protein | Inhibition of nuclear export |


|
| Adenoviridae | Adenovirus ( Mastadenovirus ) | ? | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)330 entries grouped by strain
2 entries
Bat coronavirus HKU4 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/HKU4/2004) reference strain
2 entries
Bat coronavirus HKU5 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/HKU5/2004) reference strain
2 entries
Bat coronavirus HKU9 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/HKU9) reference strain
2 entries
Human coronavirus HKU1 (isolate N5) (HCoV-HKU1) reference strain
2 entries
Human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain 17) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1) reference strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain HG52) (HHV-2) (Human herpes simplex virus 2) reference strain
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Goose/Guangdong/1/1996 H5N1 genotype Gs/Gd) reference strain
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1) reference strain
2 entries
Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (isolate United Kingdom/H123990006/2012) (MERS-CoV) (Betacoronavirus England 1) reference strain
2 entries
Murine coronavirus (strain 2) (MHV-2) (Murine hepatitis virus) reference strain
2 entries
Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (MHV-A59) (Murine hepatitis virus) reference strain
2 entries
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) reference strain
2 entries
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (2019-nCoV) (SARS-CoV-2) reference strain
1 entry
Aichi virus (strain Human/A846/88/1989) (AiV) (Aichi virus (strain A846/88)) reference strain
1 entry
Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 (strain C500) (AlHV-1) (Malignant catarrhal fever virus) reference strain
1 entry
Encephalomyocarditis virus (strain Rueckert) (EMCV) reference strain
1 entry
Epstein-Barr virus (strain AG876) (HHV-4) (Human herpesvirus 4) reference strain
1 entry
Epstein-Barr virus (strain B95-8) (HHV-4) (Human herpesvirus 4) reference strain
1 entry
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain Ab4p) (EHV-1) (Equine abortion virus) reference strain
1 entry
Equine herpesvirus 2 (strain 86/87) (EHV-2) reference strain
1 entry
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain Chicken/Md5/ATCC VR-987) (GaHV-2) (Marek's disease herpesvirus type 1) reference strain
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 8 type P (isolate GK18) (HHV-8) (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus) reference strain
1 entry
Human rhinovirus A serotype 89 (strain 41467-Gallo) (HRV-89) reference strain
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Aichi/2/1968 H3N2) reference strain
1 entry
Poliovirus type 1 (strain Mahoney) reference strain
1 entry
Psittacid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Amazon parrot/-/97-0001/1997) (PsHV-1) (Pacheco's disease virus) reference strain
1 entry
Salivirus A (isolate Human/Nigeria/NG-J1/2007) (SV-A) reference strain
1 entry
Varicella-zoster virus (strain Dumas) (HHV-3) (Human herpesvirus 3) reference strain
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain San Juan) (VSIV) reference strain
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus (strain Ogden subtype Concan) (VSNJV) reference strain
2 entries
Bat coronavirus 133/2005 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/133/2005)
2 entries
Bat coronavirus 279/2005 (BtCoV) (BtCoV/279/2005)
2 entries
Bat coronavirus HKU3 (BtCoV) (SARS-like coronavirus HKU3)
2 entries
Bat coronavirus Rp3/2004 (BtCoV/Rp3/2004) (SARS-like coronavirus Rp3)
2 entries
Bovine coronavirus (strain 98TXSF-110-ENT) (BCoV-ENT) (BCV)
2 entries
Bovine coronavirus (strain 98TXSF-110-LUN) (BCoV-LUN) (BCV)
2 entries
Bovine coronavirus (strain Mebus) (BCoV) (BCV)
2 entries
Bovine coronavirus (strain Quebec) (BCoV) (BCV)
2 entries
Human coronavirus HKU1 (isolate N1) (HCoV-HKU1)
2 entries
Human coronavirus HKU1 (isolate N2) (HCoV-HKU1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Ann Arbor/6/1960 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Beijing/39/1975 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Brazil/11/1978 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Brevig Mission/1/1918 H1N1) (Influenza A virus (strain A/South Carolina/1/1918 H1N1))
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Brescia/1902 H7N7)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/220/1997 H5N1 genotype Gs/Gd)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/31.2/2002 H5N1 genotype X1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/715.5/2001 H5N1 genotype E)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/96.1/2002 H5N1 genotype Y)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/YU22/2002 H5N1 genotype Z)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/1/1983 H5N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Scotland/1959 H5N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Victoria/1/1985 H7N7)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chile/1/1983 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/China:Nanchang/11/1996 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Czechoslovakia/1956 H4N6)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/England/1/1956 H11N6)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Germany/1949 H10N7)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Hokkaido/8/1980 H3N8)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Hong Kong/2986.1/2000 H5N1 genotype C)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/England/878/1969 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/London/1416/1973 H7N7)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Tennessee/5/1986 H3N8)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Fort Monmouth/1/1947 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Fowl plague virus/Rostock/8/1934 H7N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Grey teal/Australia/2/1979 H4N4)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Guinea fowl/Hong Kong/38/2002 H5N1 genotype X0)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Maryland/704/1977 H13N6)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Minnesota/945/1980 H13N6)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Henry/1936 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hickox/1940 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/1/1968 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/156/1997 H5N1 genotype Gs/Gd)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/5/1983 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/India/6263/1980 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Japan/305/1957 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Korea/426/1968 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Leningrad/134/17/1957 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Leningrad/134/1957 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Leningrad/134/47/1957 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Malaysia:Malaya/302/1954 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/New York/6750/1978 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/1/1971 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/101/1972 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/102/1972 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/110/1976 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/18/1978 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/2/1978 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Memphis/4/1980 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/New Zealand:South Canterbury/35/2000 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Pintail/Alberta/119/1979 H4N6)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Port Chalmers/1/1973 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Qu/7/1970 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Ruddy Turnstone/New Jersey/47/1985 H4N6)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Russia:St.Petersburg/8/2006 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Seal/Massachusetts/1/1980 H7N7)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Silky Chicken/Hong Kong/SF189/2001 H5N1 genotype A)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Silky Chicken/Hong Kong/YU100/2002 H5N1 genotype X3)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Singapore/1/1957 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Colorado/1/1977 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Iowa/15/1930 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Wisconsin/1/1961 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Tokyo/3/1967 H2N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Ireland/1378/1983 H5N8)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Minnesota/501/1978 H6N8)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Minnesota/833/1980 H4N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Ontario/6118/1968 H8N4)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Wisconsin/1/1966 H9N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Albany/12/1951 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Huston/AA/1945 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Iowa/1943 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Memphis/10/1996 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Phila/1935 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Texas/UR06-0195/2007 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/USSR/90/1977 H1N1)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Udorn/307/1972 H3N2)
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/Wilson-Smith/1933 H1N1) (Influenza A virus (strain A/WS/1933 H1N1))
2 entries
Influenza A virus (strain A/X-31 H3N2)
2 entries
Murine coronavirus (strain JHM) (MHV-JHM) (Murine hepatitis virus)
1 entry
Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) (BEV)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A16 (strain G-10)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A16 (strain Tainan/5079/98)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A21 (strain Coe)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A24 (strain EH24/70)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus A9 (strain Griggs)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B1 (strain Japan)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B2 (strain Ohio-1)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B3 (strain Nancy)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B3 (strain Woodruff)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B4 (strain E2)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B4 (strain JVB / Benschoten / New York/51)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B5 (strain Peterborough / 1954/UK/85)
1 entry
Coxsackievirus B6 (strain Schmitt)
1 entry
Echovirus 1 (strain Human/Egypt/Farouk/1951) (E-1)
1 entry
Echovirus 11 (strain Gregory)
1 entry
Echovirus 12 (strain Travis)
1 entry
Echovirus 30 (strain Bastianni)
1 entry
Echovirus 5 (strain Noyce)
1 entry
Echovirus 6 (strain Charles)
1 entry
Echovirus 9 (strain Barty)
1 entry
Echovirus 9 (strain Hill)
1 entry
Encephalomyocarditis virus
1 entry
Encephalomyocarditis virus (strain emc-b nondiabetogenic)
1 entry
Encephalomyocarditis virus (strain emc-d diabetogenic)
1 entry
Epstein-Barr virus (strain GD1) (HHV-4) (Human gammaherpesvirus 4)
1 entry
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain V592) (EHV-1) (Equine abortion virus)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 70 (strain J670/71) (EV70) (EV-70)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 71 (EV71) (EV-71)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 71 (strain 7423/MS/87) (EV71) (EV-71)
1 entry
Human enterovirus 71 (strain USA/BrCr/1970) (EV71) (EV-71)
1 entry
Human enterovirus D68 (EV68) (EV-68)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain HFEM) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain KOS) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain 333) (HHV-2) (Human herpes simplex virus 2)
1 entry
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain G) (HHV-2) (Human herpes simplex virus 2)
1 entry
Human klassevirus 1 (HKV-1)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 14 (HRV-14)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 16 (HRV-16)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 1A (HRV-1A)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 1B (HRV-1B)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 2 (HRV-2)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus 3 (HRV-3)
1 entry
Human rhinovirus C (strain C15) (HRV-C15)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Alaska/6/1977 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Anas acuta/Primorje/695/1976 H2N3)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Beijing/352/1989 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Blue-winged teal/Minnesota/993/1980 H6N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Budgerigar/Hokkaido/1/1977 H4N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Germany/n/1949 H10N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/37.4/2002 H5N1 genotype X2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/FY150/2001 H5N1 genotype D)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Hong Kong/YU562/2001 H5N1 genotype B)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/1370/1983 H5N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Chicken/Shantou/4231/2003 H5N1 genotype V)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Duck/Alberta/60/1976 H12N5)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Alaska/1/1991 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Jillin/1/1989 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/New Market/1/1977 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Equine/Prague/1/1956 H7N7)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Fort Warren/1/1950 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Goose/Guangxi/345/2005 H5N1 genotype G)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Maryland/1824/1978 H13N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Gull/Massachusetts/26/1980 H13N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Herring gull/DE/677/1988 H2N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Hong Kong/212/2003 H5N1 genotype Z+)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Kitakyushu/159/1993 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Leningrad/1/1954 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/Alberta/827/1978 H8N4)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/Alberta/88/1976 H3N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/New York/6874/1978 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Mallard/Ohio/556/1987 H5N9)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Northern Territory/60/1968 H3N2) (Influenza A virus (strain NT60)) (Influenza A virus (strain A/NT/60/1968 H3N2))
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Pintail/Alberta/121/1979 H7N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Pintail/Alberta/268/1978 H6N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Pintail/Alberta/358/1979 H3N6)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Seal/Massachusetts/133/1982 H4N5)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Shearwater/Australia/1972 H6N5)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Hong Kong/126/1982 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Hong Kong/81/1978 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Tennessee/26/1977 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Swine/Wisconsin/1/1967 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Tern/Turkmenia/18/1972 H3N3)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Bethlehem-Glilit/1492-B/1982 H1N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Canada/1963 H6N8)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Ontario/7732/1966 H5N9)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Turkey/Oregon/1971 H7N3)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Vietnam/1203/2004 H5N1)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Wa-182)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/Whale/Maine/328/1984 H13N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain A/wyoming/03/2003 H3N2)
1 entry
Influenza A virus (strain swl A/California/04/2009 H1N1)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 1 (strain Sabin)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 2 (strain Lansing)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 2 (strain W-2)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 3 (strain 23127)
1 entry
Poliovirus type 3 (strains P3/Leon/37 and P3/Leon 12A[1]B)
1 entry
Porcine enterovirus 9 (strain UKG/410/73)
1 entry
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Kaplan) (SuHV-1) (Pseudorabies virus (strain Kaplan))
1 entry
Swine vesicular disease virus (strain H/3 '76) (SVDV)
1 entry
Swine vesicular disease virus (strain UKG/27/72) (SVDV)
1 entry
Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (strain GDVII) (TMEV)
1 entry
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (strain Trinidad donkey) (VEEV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 85CLB South America) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 94GUB Central America) (VSIV)
1 entry
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 98COE North America) (VSIV)
1 entry
