Orthoherpesviridae (taxid:3044472)
VIRION
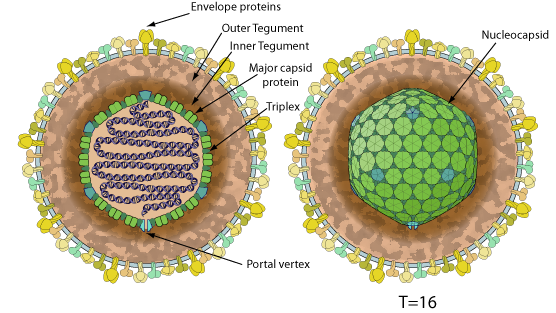
Enveloped, spherical to pleomorphic, 150-200 nm in diameter, T=16 icosahedral symmetry. Capsid consists of 162 capsomers and is surrounded by an amorphous tegument. Glycoproteins complexes are embed in the lipid envelope.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, dsDNA genome of 120-240 kb. The genome contains terminal and internal reiterated sequences.
GENE EXPRESSION
Each viral transcript usually encodes a single protein and has a promoter/regulatory sequence, a TATA box, a transcription initiation site, a 5' leader sequence of 30-300 bp (not translated), a 3' non-translated sequence of 10-30 bp, and a poly A signal. There are many gene overlaps. There are only few spliced genes. Some of the expressed ORFs are antisense to each other. Some ORFs can be accessed from more than one promoter. Certain proteins are downregulated translationaly by a leaky scanning from an upstream ORF.
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
Lytic replication:
- Attachment of the viral gB, gC, gD and gH proteins to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the core and the tegument proteins into the host cytoplasm.
- The capsid is transported to the nuclear pore where viral DNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcription of immediate early genes which promote transcription of early genes and protect the virus against innate host immunity.
- Transcription of early viral mRNA by host polymerase II, encoding proteins involved in replication of the viral DNA.
- A first round of circular genome amplification occurs by bidirectional replication
- Synthesis of linear concatemer copies of viral DNA by rolling circle.
- Transcription of late mRNAs by host polymerase II, encoding structural proteins.
- Assembly of the virus in nuclear viral factories and budding through the inner lamella of the nuclear membrane which has been modified by the insertion of herpes glycoproteins, throughout the Golgi and final release at the plasma membrane.
Latent replication : replication of circular viral episome in tandem with the host cell DNA using the host cell replication machinery.
Host-virus interaction
Adaptive immune response inhibition
Herpesviruses have evolved different strategies to inhibit the host adaptive immune response. For example, Herpes simplex protein US12 binds specifically to transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP), blocking peptide-binding to TAP and subsequent loading of peptides onto MHC class I molecules  . HCMV instead encodes a protein termed US3 that directly binds and inhibits host tapasin.
. HCMV instead encodes a protein termed US3 that directly binds and inhibits host tapasin.
Apoptosis modulation
Apoptosis is very often modulated (and usually inhibited) by herpesviridae. The mechanisms used can be caspase-dependent such as HCMV vICA that prevents host caspase-8 activation, or can involved the inhibition other cellular proteins involved in apoptosis such as EBV protein BHRF1, a viral homologue of the Bcl-2 that protect the infected cell against apoptosis.
Autophagy modulation
Several herpesvirus are able to inhibit host cell autophagy process  , such as HHV-1 ICP34.5 that interacts with Beclin-1 and stop autophagosomes development.
, such as HHV-1 ICP34.5 that interacts with Beclin-1 and stop autophagosomes development.
Cell-cycle modulation
The UL24 protein that is present in all herpesvirus subfamilies ( alpha, beta and gamma-herpesviruses) induces a cell cycle arrest at G2/M transition through inactivation of the host cyclinB/cdc2 complex  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Herpes viruses inhibit the cascade leading to production of interferon-beta by mainly targeting the host IRF3 protein. Thus, herpes simplex virus, varicella virus, or HCMV all possess proteins to prevent IRF3 activation.
Host splicing inhibition
HSV-1 ICP27 is an alternative splicing regulator of host mRNA. This protein is conserved in several herpesviridae genera. It has been shown to act as a splicing silencer at the 3' splice site of the PML intron 7a  .
.
Species
Synonyms
| 2016 naming | 1970's naming | Other common name |
|---|---|---|
| Human alphaherpesvirus 1 | Human herpesvirus 1 (HHV-1) | Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) |
| Human alphaherpesvirus 2 | Human herpesvirus 2 (HHV-2) | Herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV-2) |
| Human alphaherpesvirus 3 | Human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3) | Varicella Zoster virus (VZV) |
| Human gammaherpesvirus 4 | Human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4) | Epstein Barr virus (EBV) |
| Human betaherpesvirus 5 | Human herpesvirus 5 (HHV-5) | Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) |
| Human betaherpesvirus 6A | Human herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) | |
| Human betaherpesvirus 6B | Human herpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B) | |
| Human betaherpesvirus 7 | Human herpesvirus 7 (HHV-7) | |
| Human gammaherpesvirus 8 | Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) | Kaposi syndrome herpesvirus (KSHV) |
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
Alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 1 taxid:35252
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| A2 | ma-jd-viral-12263 |
| AHV-sema | ma-jd-viral-54620 |
Alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 2 taxid:138184
Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 (strain C500) taxid:654901
Aotine betaherpesvirus 1 taxid:50290
Bovine gammaherpesvirus 6 taxid:1504288
Bovine herpesvirus 1 taxid:10320
Bovine herpesvirus 1.1 (strain Cooper) taxid:10323
Bovine herpesvirus 1.1 (strain Jura) taxid:31518
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ICP0 (EC 2.3.2.27) (IER 2.9/ER2.6) (P135 protein) (RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase... | ma-jd-viral-58609 |
Bovine herpesvirus 1.1 (strain P8-2) taxid:10324
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein D (gD) (Glycoprotein IV) | ma-jd-viral-07522 |
Bovine herpesvirus type 1.1 taxid:79889
Canid alphaherpesvirus 1 taxid:170325
Caviid betaherpesvirus 2 taxid:33706
Cercopithecine alphaherpesvirus 2 taxid:10317
Cercopithecine alphaherpesvirus 9 taxid:35246
Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1 taxid:10325
Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1 (strain E2490) taxid:260965
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ICP47 protein (Immediate-early protein IE12) (Immediate-early-5) (Infected cell protein 47) (US12 protein)... | ma-jd-viral-62159 |
Cercopithecine herpesvirus 16 taxid:340907
Cercopithecine herpesvirus 9 (strain DHV) taxid:36348
Chimpanzee herpesvirus strain 105640 taxid:332937
Cricetid gammaherpesvirus 2 taxid:1605972
Cynomolgus cytomegalovirus taxid:1919083
Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 4 taxid:548914
Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 5 taxid:768738
Elephantid herpesvirus 1 taxid:146015
Elephantid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Asian elephant/Berlin/Kiba/1998) taxid:654902
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Protein ORF A | ma-jd-viral-36498 |
| Protein ORF B | ma-jd-viral-13328 |
| Protein U4 | ma-jd-viral-13325 |
| Protein U68 | ma-jd-viral-52996 |
| Tegument protein UL51 homolog | ma-jd-viral-35765 |
Epstein-Barr virus (strain AG876) taxid:82830
Epstein-Barr virus (strain B95-8) taxid:10377
Epstein-Barr virus (strain GD1) taxid:10376
Equid alphaherpesvirus 1 taxid:10326
Equid alphaherpesvirus 3 taxid:80341
Equid alphaherpesvirus 4 taxid:10331
Equid alphaherpesvirus 8 taxid:39637
Equid alphaherpesvirus 9 taxid:55744
Equid gammaherpesvirus 2 taxid:12657
Equid gammaherpesvirus 5 taxid:10371
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain AB1) taxid:10328
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein E (gE) | ma-jd-viral-00326 |
| Envelope glycoprotein I | ma-jd-viral-06387 |
| Packaging protein UL32 homolog (Glycoprotein 300) (GP300) | ma-jd-viral-40921 |
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain Ab4p) taxid:31520
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain HH1) taxid:310537
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized gene 1 protein | ma-jd-viral-40542 |
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain HVS25A) taxid:10327
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein H (gH) | ma-jd-viral-16908 |
| Thymidine kinase (EC 2.7.1.21) | ma-jd-viral-05904 |
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain Kentucky A) taxid:10329
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain Kentucky D) taxid:10330
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein B (gB) | ma-jd-viral-31223 |
| Envelope glycoprotein C (gC) (Glycoprotein 13) | ma-jd-viral-01823 |
| Envelope protein UL45 homolog | ma-jd-viral-16456 |
Equine herpesvirus 1 (strain V592) taxid:310273
Equine herpesvirus 2 (strain 86/87) taxid:82831
Equine herpesvirus 2 (strain T400/3) taxid:82832
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Viral interleukin-10 homolog (vIL-10) | ma-jd-viral-13428 |
Equine herpesvirus 4 (strain 1942) taxid:10333
Falconid herpesvirus 1 taxid:1510155
Gallid alphaherpesvirus 2 taxid:10390
Gallid alphaherpesvirus 3 taxid:35250
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain Chicken/Md5/ATCC VR-987) taxid:10389
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain GA) taxid:10388
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein L (gL) | ma-jd-viral-09079 |
| Virion protein US10 homolog | ma-jd-viral-16121 |
Gallid herpesvirus 2 (strain RB-1b) taxid:33707
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein B (gB) | ma-jd-viral-31201 |
Guinea pig cytomegalovirus (strain 22122) taxid:103920
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein B (gB) | ma-jd-viral-31188 |
| Envelope glycoprotein H (gH) | ma-jd-viral-16930 |
| Envelope glycoprotein L (gL) | ma-jd-viral-00343 |
| Protein GP96 | ma-jd-viral-18507 |
Hawaiian green turtle herpesvirus taxid:70564
Human betaherpesvirus 6A taxid:32603
Human betaherpesvirus 7 taxid:10372
Human cytomegalovirus taxid:10359
Human cytomegalovirus (strain 5508) taxid:69168
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein L (gL) | ma-jd-viral-00341 |
Human cytomegalovirus (strain AD169) taxid:10360
Human cytomegalovirus (strain Merlin) taxid:295027
Human cytomegalovirus (strain Toledo) taxid:311339
Human cytomegalovirus (strain Towne) taxid:10363
Human herpesvirus 1 taxid:10298
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain 17) taxid:10299
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain MP) taxid:10307
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein K (Syncytial protein) | ma-jd-viral-49381 |
Human herpesvirus 1 (strain R15) taxid:36345
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein K (Syncytial protein) | ma-jd-viral-49381 |
Human herpesvirus 2 taxid:10310
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain 333) taxid:10313
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain G) taxid:10314
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Virion host shutoff protein (Vhs) (EC 3.1.27.-) | ma-jd-viral-22425 |
Human herpesvirus 2 (strain HG52) taxid:10315
Human herpesvirus 3 taxid:10335
Human herpesvirus 4 type 2 taxid:12509
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Latent membrane protein 1 (Protein p63) | ma-jd-viral-30641 |
Human herpesvirus 6A (strain GS) taxid:10369
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein H (gH) | ma-jd-viral-16932 |
Human herpesvirus 6A (strain Uganda-1102) taxid:10370
Human herpesvirus 6B taxid:32604
Human herpesvirus 6B (strain Z29) taxid:36351
Human herpesvirus 7 (strain JI) taxid:57278
Human herpesvirus 7 (strain MUK) taxid:57279
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Triplex capsid protein 2 | ma-jd-viral-04783 |
Human herpesvirus 7 (strain RK) taxid:262398
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| U21 glycoprotein (gp60) | ma-jd-viral-36538 |
Human herpesvirus 8 taxid:37296
Human herpesvirus 8 type P (isolate GK18) taxid:868565
Infectious laryngotracheitis virus taxid:10386
Infectious laryngotracheitis virus (strain Thorne V882) taxid:10344
Leporid alphaherpesvirus 4 taxid:481315
Macropodid alphaherpesvirus 1 taxid:137443
Meleagrid herpesvirus 1 taxid:37108
Murid herpesvirus 1 taxid:10366
Murid herpesvirus 1 (strain Smith) taxid:10367
Murine roseolovirus taxid:1940555
Ovine gammaherpesvirus 2 taxid:10398
Panine betaherpesvirus 2 taxid:188763
Papio ursinus cytomegalovirus taxid:1667587
Psittacid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Amazon parrot/-/97-0001/1997) taxid:670426
Pteropodid alphaherpesvirus 1 taxid:1343901
Rat cytomegalovirus (isolate England) taxid:1261657
Rhesus cytomegalovirus (strain 68-1) taxid:47929
Saimiriine betaherpesvirus 4 taxid:1535247
Simian cytomegalovirus (strain Colburn) taxid:50292
Suid herpesvirus 1 taxid:10345
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Indiana-Funkhauser / Becker) taxid:31523
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein B (gB) | ma-jd-viral-31207 |
| Tripartite terminase subunit 1 | ma-jd-viral-61489 |
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Kaplan) taxid:33703
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain NIA-3) taxid:10349
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Protein US2 homolog (28 kDa protein) | ma-jd-viral-21068 |
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase UL13 (EC 2.7.11.1) | ma-jd-viral-24774 |
| Tegument protein UL14 | ma-jd-viral-14631 |
Suid herpesvirus 1 (strain Rice) taxid:10350
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelope glycoprotein G (gG) | ma-jd-viral-64437 |
