Filoviridae (taxid:11266)
VIRION
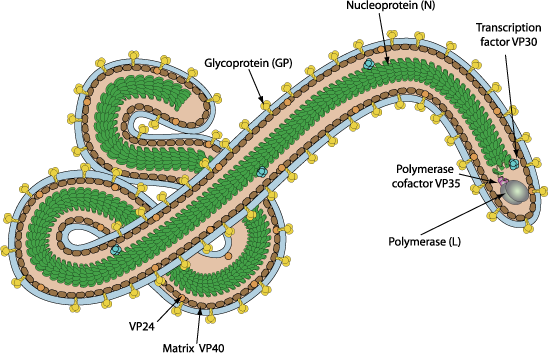
Filamentous 790 nm long for Marburg virus and 970 nm long for Ebolavirus. Diameter is about 80nm.
GENOME
Negative-stranded RNA linear genome, about 18-19 kb in size. Encodes for seven proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase binds the encapsidated genome at the leader region, then sequentially transcribes each genes by recognizing start and stop signals flanking viral genes. mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by the L protein during synthesis.
In Ebolavirus, the primary product of the unedited transcript of GP gene yields a smaller non-structural glycoprotein sGP which is efficiently secreted from infected cells. RNA editing allows expression of full-length GP.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L
- Mononega-type capping
- RNA TPase, GTase, N7 Mtase, 2'O Mtase L
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment to host receptors through GP glycoprotein mediates is endocytosed into vesicles in the host cell by apoptotic mimicry
- Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane; ribonucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm.
- Sequential transcription, viral mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by polymerase stuttering in the cytoplasm.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid interacts with the matrix protein under the plasma membrane, buds via the host ESCRT complexes from the plasma membrane, releasing the virion.
Host-virus interaction
Inhibition of host Interferon induction
Vp35 protein prevents host interferon induction by inhibiting host TBK1-IKBKE-DDX3 complex 
Inhibition of host interferon signaling
Vp24 protein block interferon signaling by preventing STAT1 signaling. May act by binding host karyopherin ? proteins, thereby preventing them from transporting the tyrosine-phosphorylated transcription factor STAT1 to the nucleus. May directly bind to STAT1 to prevent its signaling  .
.
Antigenic subvertion
Small Glycoprotein (sGP) is a secreted truncated version of GP that prevent host antibodies anti-GP to effectively neutralize it  .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)97 entries grouped by protein
11 entries
RNA-directed RNA polymerase L (Protein L) (Large structural protein) (Replicase) (Transcriptase)
12 entries
Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) (Protein N)
16 entries
Envelope glycoprotein (GP1,2) (GP)
11 entries
Membrane-associated protein VP24 (Marburg VP24) (mVP24)
10 entries
Transcriptional activator VP30 (Minor nucleoprotein VP30)
10 entries
Polymerase cofactor VP35 (Marburg VP35) (mVP35)
11 entries
Matrix protein VP40 (Ebola VP40) (eVP40) (Membrane-associated protein VP40)
11 entries
Pre-small/secreted glycoprotein (pre-sGP)
5 entries
Super small secreted glycoprotein (SsGP)
 (ModelArchive).
(ModelArchive).
