Inhibition of host STAT1 by virus (kw:KW-1105)
The signal transducer and activator of transcription STAT1 protein is a cytoplasmic latent transcription factor that becomes activated by various extracellular stimuli, including cytokines and growth factors that bind to specific cell surface receptors. The activation of STAT1 in IFN-γ and IFN-α/β signaling pathways is largely mediated by phosphorylation of conserved tyrosine and serine residues in the C-terminal region. While IFN-γ induces STAT1 homodimerization, IFN-α/β mainly stimulates heterodimerization of STAT1 and STAT2, both leading to STAT1 activation and nuclear localization.
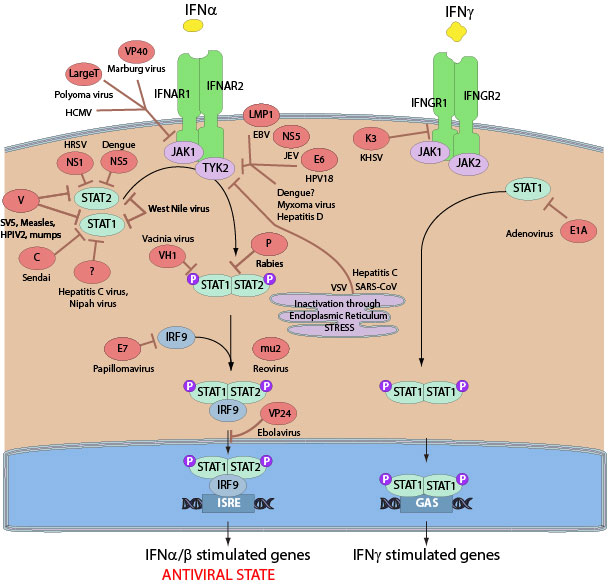
Many viruses modulate the interferon mediated response by acting on STAT1 using different strategies. The V protein of simian virus 5 inhibits interferon signalling by targeting STAT1 for proteasome-mediated degradation. Sendai virus C protein also physically associates with STAT1 and send it to degradation. Vaccinia VH1 phosphatase instead reverses STAT1 activation by interacting with and dephosphorylating STAT1.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
