HIV-1 VPR protein
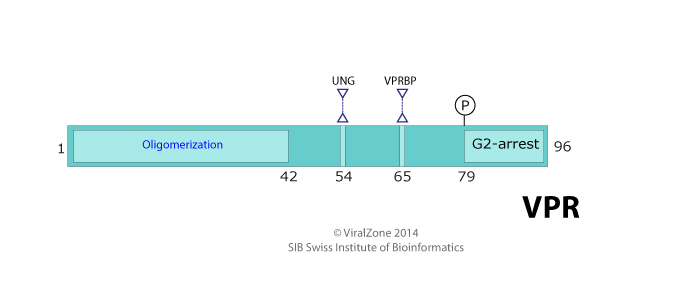
| FUNCTION |
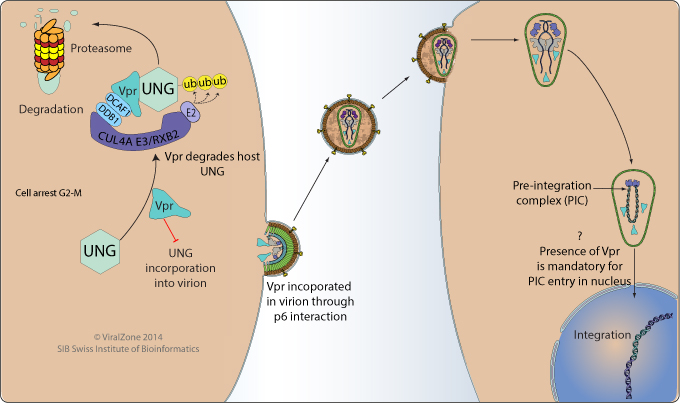
Plays an essential role in the entry of the viral cDNA genome into the host nucleus during infection of quiescent cells  . During virus entry, Vpr colocalizes with the capsid until the latter reaches the nucleus membrane . During virus entry, Vpr colocalizes with the capsid until the latter reaches the nucleus membrane
During virus exit, induces host cell G2 arrest possibly through degradation of host repair proteins, stopping cell division in G2-M damage checkpoint. The lymphocytes stopped in G2-M eventually go into apoptosis  , which is thought to be the main cause of AIDS disease. , which is thought to be the main cause of AIDS disease.
|
| INTERACTIONS |
Host UNG ,
VPRBP (DCAF1) ,
VPRBP (DCAF1)
|
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION |
|
| TIMING OF EXPRESSION |
|
HIV-1 Vpr-a still enigmatic multitasker
Carolin A. Guenzel, C?cile H?rate, Serge Benichou
Front Microbiol 2014; 5: 127
Carolin A. Guenzel, C?cile H?rate, Serge Benichou
Front Microbiol 2014; 5: 127
HIV-1 Vpr-induced apoptosis is cell cycle dependent and requires Bax but not ANT
Joshua L. Andersen, Jason L. DeHart, Erik S. Zimmerman, Orly Ardon, Baek Kim, Guillaume Jacquot, Serge Benichou, Vicente Planelles
PLoS Pathog. December 2006; 2: e127
Joshua L. Andersen, Jason L. DeHart, Erik S. Zimmerman, Orly Ardon, Baek Kim, Guillaume Jacquot, Serge Benichou, Vicente Planelles
PLoS Pathog. December 2006; 2: e127
Visualization of the intracellular behavior of HIV in living cells
David McDonald, Marie A. Vodicka, Ginger Lucero, Tatyana M. Svitkina, Gary G. Borisy, Michael Emerman, Thomas J. Hope
J. Cell Biol. November 11, 2002; 159: 441?452
David McDonald, Marie A. Vodicka, Ginger Lucero, Tatyana M. Svitkina, Gary G. Borisy, Michael Emerman, Thomas J. Hope
J. Cell Biol. November 11, 2002; 159: 441?452
Uracil DNA glycosylase specifically interacts with Vpr of both human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus of sooty mangabeys, but binding does not correlate with cell cycle arrest
L. Selig, S. Benichou, M. E. Rogel, L. I. Wu, M. A. Vodicka, J. Sire, R. Benarous, M. Emerman
J. Virol. June 1997; 71: 4842?4846
L. Selig, S. Benichou, M. E. Rogel, L. I. Wu, M. A. Vodicka, J. Sire, R. Benarous, M. Emerman
J. Virol. June 1997; 71: 4842?4846
HIV1 Vpr arrests the cell cycle by recruiting DCAF1/VprBP, a receptor of the Cul4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase
Catherine Transy, Florence Margottin-Goguet
Cell Cycle August 15, 2009; 8: 2489?2490
Catherine Transy, Florence Margottin-Goguet
Cell Cycle August 15, 2009; 8: 2489?2490