Umbravirus (taxid:39734)
Satellite virus: The virus does not encode for a capsid and needs a helper virus for encapsidation and aphid transmission. Infection requires host cell to be co-infected with a Luteoviridae.
VIRION
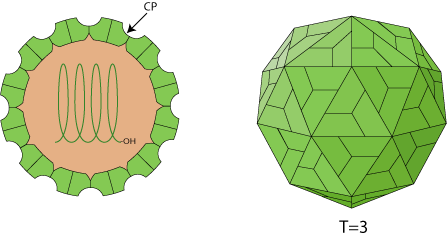
Non-enveloped, T=3 icosahedral particles of 25-30 nm diameter, with 180 copies of the capsid protein (CP).
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome. The genomic RNAs is not capped in 5', not polyadenylated in 3'.
GENE EXPRESSION
Genomic RNAs serve as messenger RNA. Translation is initiated by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) at the 5'end. Subgenomic RNAs may be synthesized during replication. A ribosomal frameshifting induces the translation of the RNA-dependent-RNA polymerase.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Virus penetrates into the host cell.
- Uncoating, and release of the viral genomic RNA into the cytoplasm.
- The viral RNA is translated to produce the two proteins necessary for RNA synthesis (replication and transcription).
- Replication takes place in cytoplasmic viral factories. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Expression of the subgenomic RNAs (sgRNAs).
- In case of Luteoviridae co-infection, the viral genome can be encapsidated by helper virus capsid proteins. If Luteoviridae helper virus is absent, the viral genome forms filamentous ribonucleoproteins thanks to the interaction between ORF3 protein and fibrillarin.
- Viral movement protein probably mediates virion cell-to-cell transfer. Ribonucleoproteins perform long-distance movement leading to systemic infection.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)3 entries grouped by strain
3 entries
Groundnut rosette virus (strain MC1) (GRV) reference strain
Carrot mottle virus taxid:68033
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Cell-to-cell movement protein | ma-jd-viral-28423 |
| Long-distance movement protein | ma-jd-viral-47126 |
| RNA-directed RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.48) | ma-jd-viral-19258 |
Ethiopian tobacco bushy top virus taxid:1538549
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Cell-to-cell movement protein | ma-jd-viral-28425 |
| Long-distance movement protein | ma-jd-viral-37736 |
| RNA-directed RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.48) | ma-jd-viral-19255 |
Opium poppy mosaic virus taxid:473784
Pea enation mosaic virus-2 taxid:193120
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| 26kDa protein | ma-jd-viral-37738 |
| 27kDa protein | ma-jd-viral-28427 |
| 33kDa protein | ma-jd-viral-43194 |
