Hepadnaviridae (taxid:10404)
VIRION
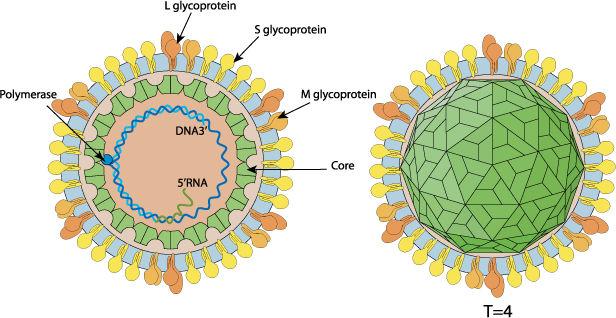
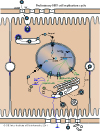
Enveloped, spherical. Diameter from about 42nm. Icosahedric capsid with a T=4 symmetry.
GENOME
Partially dsDNA circular genome, about 3.2 kb in size. Encodes for 7 proteins. On rare non-specific recombination, the viral genome can be integrated in host chromosome. This inactivates the integrated virus but can gives the host cell a replicative advantage sometimes leading to hepatocarcinoma.
GENE EXPRESSION
The minichromosome is transcribed by cellular RNA polymerase II under the control of three to four promoters (the core, pre-S1, pre-S2/S promoters, and the X promoter in mammalian viruses) and two enhancer regions (ENH1 and ENH2). The pre-genomic RNA is alternatively spliced. The unspliced form is exported from the nucleus through a PRE motif possibly by capsid protein. The Polymerase and short S proteins are expressed by leaky scanning from the pg mRNA and the S mRNA respectively.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [P]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC/NUCLEAR
- Virus attaches to host receptors through major surface antigen and enters the cell by an unknown mechanism.
- Relaxed circular DNA (RC-DNA) and capsid are transported via microtubules to the nucleus where DNA is released through the nuclear pore, and repaired to form covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA).
- Transcription by RNA polymerase II of the pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) and subgenomic mRNAs, inducing synthesis of all the viral proteins.
- pgRNA is encapsidated, together with the P protein, and reverse-transcribed inside the nucleocapsid in (-)DNA covalently linked to P protein.
- (+)DNA synthesis from the (-)DNA template generates new RC-DNA.
- Transport to the nucleus of new RC-DNA leads to cccDNA amplification; alternatively, the RC-DNA containing nucleocapsids are enveloped at the ER, and new virions are released by exocytosis.
Host-virus interaction
Primary receptor
HBV L surface protein can bind to heparan sulfate
Entry receptor
HBV L surface protein Binds to SLC10A1/NTCP  in order to enter hepatocytes.
in order to enter hepatocytes.
Autophagy modulation
HBV protein HBx seems to be able to increase autophagy through the up-regulation of host beclin 1 expression  .
.
Cell-cycle modulation
HBV protein HBx protein deregulates cell cycle checkpoint controls
at G0/G1 and G2/M  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
HBV protein HBx directly interacts with and inhibits host MAVS protein by inducing its ubiquitination and targeting it for degradation  .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)292 entries grouped by strain
7 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate France/Tiollais/1979) (HBV-D) reference strain
5 entries
Ground squirrel hepatitis virus (strain 27) (GSHV) reference strain
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ayr (isolate Human/Japan/Okamoto/-) (HBV-C) reference strain
5 entries
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 7) (WHV) reference strain
5 entries
Woolly monkey hepatitis B virus (isolate Louisville) (WMHBV) reference strain
4 entries
Duck hepatitis B virus (isolate Shanghai/DHBVQCA34) (DHBV) reference strain
4 entries
Heron hepatitis B virus (HHBV) reference strain
5 entries
Chimpanzee hepatitis B virus (isolate United Kingdom/LSH/1988) (HBVcpz)
5 entries
Gibbon hepatitis B virus subtype ayw3q (isolate Hope) (HBVgbn)
5 entries
Gorilla hepatitis B virus (isolate Cameroon/gor97) (HBVgor)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A1 subtype adw2 (isolate South Africa/84/2001) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 (isolate Japan/11D11HCCW/1998) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 subtype adw (isolate Japan/Nishioka/1983) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 subtype adw2 (isolate Germany/991/1990) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A2 subtype adw2 (strain Rutter 1979) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A3 (isolate Cameroon/CMR711/1994) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A3 (isolate Cameroon/CMR983/1994) (HBV-A)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B/C subtype adw (isolate Okinawa/pODW282/1998) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B1 (isolate Japan/Ry30/2002) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B1 (isolate Japan/Yamagata-2/1998) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B1 subtype adw (isolate Japan/pJDW233/1988) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 (isolate Indonesia/pIDW420/1988) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 (isolate Vietnam/9873/1997) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 subtype adw (isolate China/patient4/1996) (HBV-B)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C (isolate Vietnam/3270/2000) (HBV-C)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate Japan/Nishioka/1983) (HBV-C)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (strain Japan/adr4/1983) (HBV-C)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ar (isolate Japan/S-207/1988) (HBV-C)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ayw (isolate Australia/AustRC/1992) (HBV-C)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ayw (isolate China/Tibet127/2002) (HBV-C)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D (isolate France/alpha1/1989) (HBV-D)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D (isolate Germany/1-91/1991) (HBV-D)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate Australia/AustKW/1991) (HBV-D)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate Italy/CI/1992) (HBV-D)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate Japan/JYW796/1988) (HBV-D)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype F2 (isolate Brazil/w4B) (HBV-F)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype F2 subtype adw4q (isolate Senegal/9203) (HBV-F)
5 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype H subtype adw4 (isolate Nicaragua/2928Nic/1997) (HBV-H)
5 entries
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 1) (WHV)
5 entries
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 2) (WHV)
5 entries
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 59) (WHV)
5 entries
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate 8) (WHV)
4 entries
Arctic squirrel hepatitis virus (ASHV)
4 entries
Duck hepatitis B virus (isolate brown Shanghai duck S5) (DHBV)
4 entries
Duck hepatitis B virus (isolate white Shanghai duck S31) (DHBV)
4 entries
Duck hepatitis B virus (strain China) (DHBV)
4 entries
Duck hepatitis B virus (strain Germany/DHBV-3) (DHBV)
4 entries
Duck hepatitis B virus (strain United States/DHBV-16) (DHBV)
4 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype A1 subtype adw (isolate Philippines/pFDW294/1988) (HBV-A)
4 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype ad (isolate Japan/S-179/1988) (HBV-C)
4 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate Japan/A4/1994) (HBV-C)
4 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate Korea/Kim/1989) (HBV-C)
4 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype G (isolate IG29227/2000) (HBV-G)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype B2 (isolate Vietnam/16091/1992) (HBV-B)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype E (isolate Cote d'Ivoire/ABI-129/2003) (HBV-E)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype E (isolate Cote d'Ivoire/ABI-212/2003) (HBV-E)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype E subtype ayw4 (isolate Kou) (HBV-E)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype F2 (isolate Argentina/sa16/2000) (HBV-F)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype H (isolate United States/LAS2523/2002) (HBV-H)
3 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype H subtype adw4 (isolate Nicaragua/1853Nic/1997) (HBV-H)
3 entries
Orangutan hepatitis B virus (isolate Somad) (HBVoru)
2 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979) (HBV-D)
2 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype E (isolate Chimpanzee/Ch195/1999) (HBV-E)
2 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype F1 (isolate Argentina/sa11/2000) (HBV-F)
2 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype F1 subtype adw4 (isolate El Salvador/1116Sal/1997) (HBV-F)
2 entries
Hepatitis B virus genotype G (isolate United States/USG17/2002) (HBV-G)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype A1 subtype adw2 (isolate Southern-Africa/Cai) (HBV-A)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype C subtype adr (isolate China/NC-1/1988) (HBV-C)
1 entry
Hepatitis B virus genotype G subtype adw2 (isolate United States/sf/1990) (HBV-G)
1 entry
Woodchuck hepatitis B virus (isolate w64/pWS23) (WHV)
 (ModelArchive).
(ModelArchive).
Hepatitis B virus taxid:10407
Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate France/Tiollais/1979) taxid:490133
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein (Core antigen) (Core protein) (HBcAg) (p21.5) | ma-jd-viral-16247 |
Horseshoe bat hepatitis B virus taxid:1508711
Parrot hepatitis B virus taxid:1128118
Roundleaf bat hepatitis B virus taxid:1508710
Sheldgoose hepatitis B virus taxid:259898
Snow goose hepatitis B virus taxid:89623
Tent-making bat hepatitis B virus taxid:1508712
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Core protein | ma-jd-viral-16240 |
| Protein P (EC 2.7.7.49) (EC 2.7.7.7) | ma-jd-viral-49618 |
| Protein X (HBx) (Peptide X) (pX) | ma-jd-viral-29348 |
| Surface protein | ma-jd-viral-48178 |
White sucker hepatitis B virus taxid:1690672
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Large envelope protein | ma-jd-viral-48096 |
| PreC/core protein | ma-jd-viral-16238 |
| Protein P (EC 2.7.7.49) (EC 2.7.7.7) (EC 3.1.26.4) | ma-jd-viral-49619 |