Inhibition of host MDA5 by virus (kw:KW-1089)
Upon viral infection, the cytosolic receptor MDA5 recognizes long viral dsRNAs and initiates an antiviral signaling cascade by interacting with the downstream partner MAVS, located to the mitochondria. This signaling pathway leads to the establishment of an antiviral state characterized by expression of antiviral cytokines and interferons. The MDA5 protein belongs to the RNA helicase family.
ISGylation of MDA5 would be crutial for its function  .
.
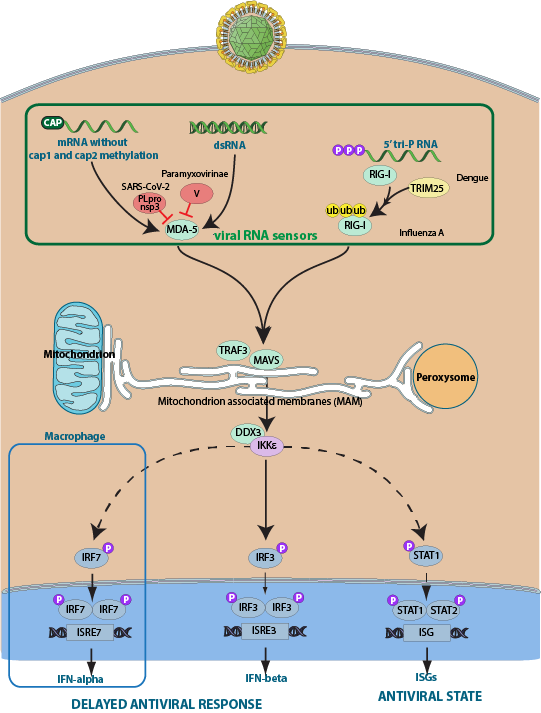
Several viruses encode proteins that directly interfere with MDA5 to decrease interferon production by infected cells. For example, all viruses from paramyxovirinae subfamily encode a protein V able to interact with MDA5 and block MDA5 interaction with MAVS, its downstream partner in the cascade. The interaction has been investigated in detail and the C-terminal domain of the V proteins is responsible for the binding of the helicase domain of protein V.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)56 entries grouped by protein
7 entries
Nucleoprotein (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein)
14 entries
Genome polyprotein
1 entry
Non-structural polyprotein pORF1
3 entries
Accessory factor US11 (Vmw21)
31 entries
