Activation of host caspases by virus (kw:KW-1073)
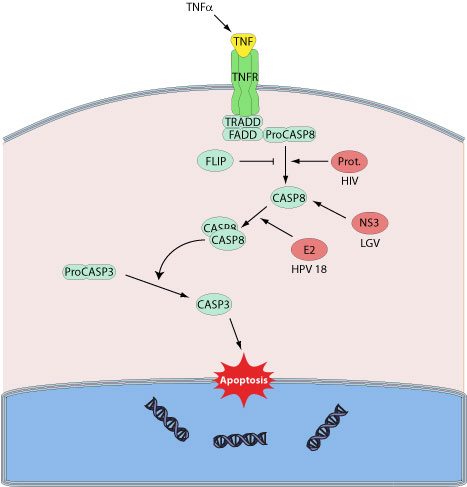
Apoptosis (or programmed cell death) is a controlled process leading to cell death characterized by chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, cell shrinkage, and compartimentalization of the dead cells to apoptotic bodies. The host immune system uses apoptosis to eliminate cells infected by pathogens. Apoptosis of infected cells is caused either by cytolytic cells activated during the anti-viral response, or directly by viral infection. Host caspases, constitute an evolutionary conserved family of aspartate-specific cysteine proteases that are at the heart of the apoptotic machinery.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)44 entries grouped by protein
36 entries
Gag-Pol polyprotein (Pr160Gag-Pol)
1 entry
Genome polyprotein
1 entry
Tyrosine phosphatase H2 (PTP-H2) (EC 3.1.3.48)
6 entries
