Caulimovirus (taxid:10639)
VIRION
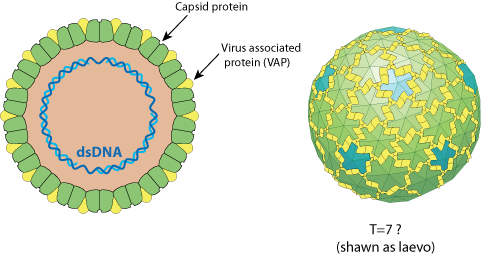
Non enveloped, large (50 nm diameter) icosahedral particles composed of 420 subunits with a T=7 symmetry  . The virion shell is covered with virion associated protein (VAP)
. The virion shell is covered with virion associated protein (VAP)  .
It has not been described whether handedness of capsid is laevo or dextro, here the pictures dsplays a laevo form.
.
It has not been described whether handedness of capsid is laevo or dextro, here the pictures dsplays a laevo form.
GENOME
Monopartite, open circular, double stranded DNA of about 8000 base pairs with discontinuities in both strands: one in the transcribed strand and one to three in the non-transcribed strand. Codes for 6 to 7 proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The 35s RNA and its spliced derivatives serves as polycistronic mRNA for viral proteins. Polycistronic translation depends on Tav which is believed to be a translation reinitiation factor. Tav is produced from the monocistronic 19S RNA, the second major viral transcript. Translation of 35S RNA is initiated by ribosome shunt, in which scanning ribosomes bypass leader sequence and multiple short ORFs.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [RT]
- Polyprotein protease (Peptidase A3) [PRO]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC / NUCLEAR
- Attachment of viral proteins to host receptors mediates entry into the host cell.
- The viral dsDNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcribed by host RNA polymerase II.
- mRNA translation produces viral proteins.
- Genomic RNA is retrotranscribed into new dsDNA genomes in the cytoplasm.
- Genomes are encapsidated by the capsid protein and form new virions.
- The virion infects either a new cell by plasmodesmata movement, or by insect vector uptake.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)49 entries grouped by strain
6 entries
Carnation etched ring virus (CERV) reference strain
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain Strasbourg) (CaMV) reference strain
6 entries
Figwort mosaic virus (strain DxS) (FMV) reference strain
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain BBC) (CaMV)
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain CM-1841) (CaMV)
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain D/H) (CaMV)
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain NY8153) (CaMV)
2 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain PV147) (CaMV)
2 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain W260) (CaMV)
1 entry
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain Bari 1) (CaMV)
1 entry
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain D4) (CaMV)
1 entry
