Parapoxvirus (taxid:10257)
VIRION
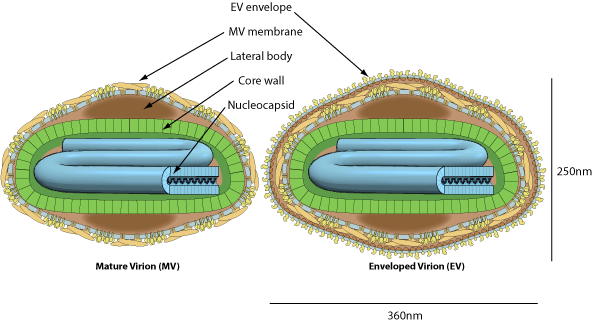
Enveloped, ovoid virion, 220-300nm long and 140-170nm wide. The surface membrane displays surface filaments. Two distinct infectious virus particles exists: the intracellular mature virus (IMV) and the extracellular enveloped virus (EEV).
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome of 130-150kb. The linear genome is flanked by inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequences which are covalently-closed at their extremities.
_Bovine papular stomatitis virus strain BV-AR02_genome at Poxvirus Bioinformatics Ressource center
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA-directed DNA polymerase [OPG071]
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase [DdRp]
- Cell-type capping
- Core protease (Peptidase C57) [OPG083]
- Metalloprotease (Peptidase M44) [Protease (OPG085)]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement of the viral proteins to host glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the core into the host cytoplasm.
- Early phase: early genes are transcribed in the cytoplasm by viral RNA polymerase. Early expression begins at 30 minutes post-infection.
- Core is completely uncoated as early expression ends, viral genome is now free in the cytoplasm.
- Intermediate phase: Intermediate genes are expressed, triggering genomic DNA replication at approximately 100 minutes post-infection.
- Late phase: Late genes are expressed from 140 min to 48 hours post-infection, producing all structural proteins.
- Assembly of progeny virions starts in cytoplasmic viral factories, producing an spherical immature particle. This virus particle matures into brick-shaped intracellular mature virion (IMV).
- IMV virion can be released upon cell lysis, or can acquire a second double membrane from trans-Golgi and bud as external enveloped virion (EEV).
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
The orf virus encodes a viral bcl-2 protein (v-Bcl2) that prevents host apoptosis  .
.
NF-kappa-B modulation
Orf virus ORFV121 physically interacts with NF-kappaB-p65 in the cell cytoplasm and thereby inhibits host NF-kappaB signaling pathway  .
.
Cell cycle modulation
The poxvirus anaphase promoting complex regulator (PACR) promotes viral replication by manipulating the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), thus promoting the host differentiated G0 cells to enter G1  .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)7 entries grouped by strain
1 entry
Orf virus (strain Goat/Texas/SA00/2000) (OV-SA00) (Orf virus-San Angelo 2000) reference strain
5 entries
Orf virus (strain NZ2) (OV NZ-2)
1 entry
