Betaentomopoxvirus (taxid:10286)
VIRION
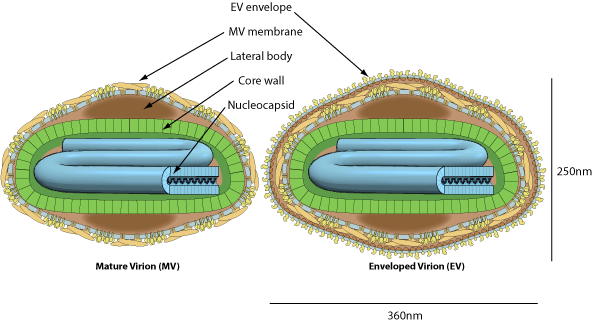
Enveloped, ovoid virion about 350x250nm in size. Two distinct infectious virus particles exists: the intracellular mature virus (IMV) and the extracellular enveloped virus (EEV).
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome about 225kb. The linear genome is flanked by inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequences which are covalently-closed at their extremities.
Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus strain Moyer genome
at Poxvirus Bioinformatics Ressource center
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA dependent DNA polymerase
- DNA dependent RNA polymerase
- Cell-type capping
- RNA TPase
- GTase
- N7MTase
- 2'O methylase
- Core protease (Peptidase C57)
- Metalloprotease (Peptidase M44)
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment of the viral proteins to host glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion with the plasma membrane to release the core into the host cytoplasm.
- Early phase: early genes are transcribed in the cytoplasm by viral RNA polymerase. Early expression begins at 30 minutes post-infection.
- Core is completely uncoated as early expression ends, viral genome is now free in the cytoplasm.
- Intermediate phase: Intermediate genes are expressed, triggering genomic DNA replication at approximately 100 minutes post-infection.
- Late phase: Late genes are expressed from 140 min to 48 hours post-infection, producing all structural proteins.
- Assembly of progeny virions starts in cytoplasmic viral factories, producing an spherical immature particle. This virus particle matures into brick-shaped intracellular mature virion (IMV).
- IMV virion can be released upon cell lysis, or can acquire a second double membrane from trans-Golgi and bud as external enveloped virion (EEV).
- Mature virion can be occluded in spheroids comprised of spheroidin protein.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
The Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus encodes AMV p33, a functional homolog of the baculovirus apoptosis inhibitor p35  . P33 is a direct inhibitor of caspases.
. P33 is a direct inhibitor of caspases.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)19 entries grouped by strain
11 entries
Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus (AmEPV) reference strain
4 entries
Choristoneura biennis entomopoxvirus (CbEPV)
2 entries
Choristoneura fumiferana entomopoxvirus (CfEPV)
2 entries
