Proboscivirus (taxid:548689)
VIRION
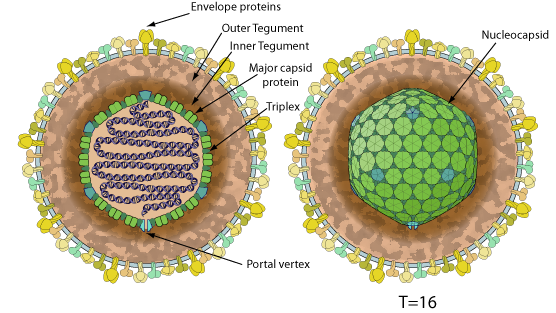
Enveloped, spherical to pleomorphic, 150-200 nm in diameter, T=16 icosahedral symmetry. Capsid consists of 162 capsomers and is surrounded by an amorphous tegument. Glycoproteins complexes are embeded in the lipid envelope.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, dsDNA genome.
GENE EXPRESSION
ENZYMES
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- DNA primase
- Tegument deneddylase (Peptidase C76)
- Assemblin (Peptidase S21)
- Kinase
- Helicase
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase
- Thymidine kinase
- Uracil-DNA glycosylase
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
Lytic replication:
- Attachment of the viral glycoproteins to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Entry into host cell is still unclear and may depend on the host cell type, i.e. endocytosis versus fusion at the plasma membrane.
- The capsid is transported to the nuclear pore where the viral DNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcription of immediate early genes which promote transcription of early genes and protect the virus against innate host immunity.
- Transcription of early viral mRNA by host polymerase II, encoding proteins involved in replication of the viral DNA.
- A first round of circular genome amplification occurs by bidirectional replication
- Synthesis of linear concatemer copies of viral DNA by rolling circle.
- Transcription of late mRNAs by host polymerase II, encoding structural proteins.
- Assembly of the virus in nuclear viral factories and budding through the inner lamella of the nuclear membrane which has been modified by the insertion of herpes glycoproteins, throughout the Golgi and final release at the plasma membrane.
Latent replication : replication of circular viral episome in tandem with the host cell DNA using the host cell replication machinery.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)34 entries grouped by strain
34 entries
Elephantid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Asian elephant/Berlin/Kiba/1998) (EIHV-1) (Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus)
Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 4 taxid:548914
Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 5 taxid:768738
Elephantid herpesvirus 1 taxid:146015
Elephantid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Asian elephant/Berlin/Kiba/1998) taxid:654902
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Protein ORF A | ma-jd-viral-36498 |
| Protein ORF B | ma-jd-viral-13328 |
| Protein U4 | ma-jd-viral-13325 |
| Protein U68 | ma-jd-viral-52996 |
| Tegument protein UL51 homolog | ma-jd-viral-35765 |
