Fibrovirus (taxid:1977139)
VIRION
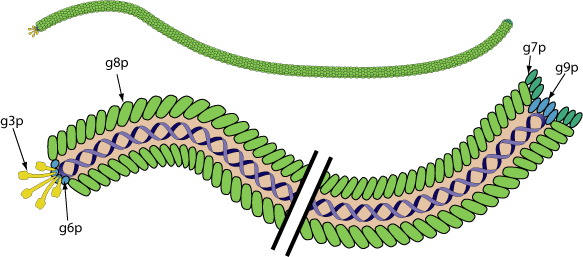
Non-enveloped, rod of filaments of 7 nm in diameter and 1000 to 1200nm long in length. Helical capsid with adsorption proteins on one end.
GENOME
Circular, ssDNA genome (+) of 6.3 to 7.5 kb encoding for 12 to 15 proteins. Replication occurs via dsDNA intermediate and rolling circle.
GENE EXPRESSION
Each gene is transcribed by host cellular machinery, via a specific promoter. Some genes end by a transcription terminator.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Virus mediates pilus-mediated adsorption of the virus onto host cell. Pilus retraction pulls the virion to the host internal membrane.
- The proteins of the capsid perform the injection of the viral DNA through bacterial membranes into cell cytoplasm.
- Host polymerase convert the (+)ssDNA viral genome into a covalently closed dsDNA called replicative form DNA (RF).
- dsDNA transcription by host RNA polymerase gives rise to viral mRNAs.
- A viral protein may nick RF DNA strand at the origin of replication.
- (+) strand replication occurs by rolling circle.
- New (+)ssDNA genomes are converted into new RF molecules, and further transcription occurs.
- A conversion into RF dsDNA is inhibited, as neo-synthesized genomic ssDNA is covered with a viral protein.
- Assembly of the viral capsid.
- New virions are secreted from host cell.
- Infected cells continue to divide and produce virions indefinitely.
