Sinsheimervirus (taxid:1910954)
VIRION
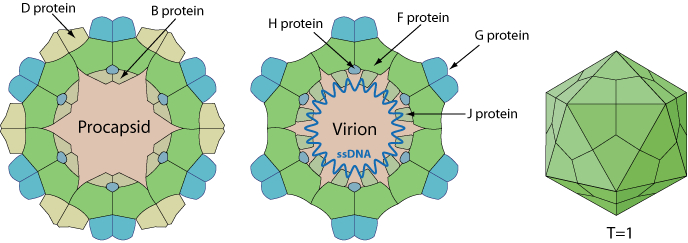
Non-enveloped, round, T=1 icosahedral symmetry, about 30 nm in diameter. The capsid consists of 12 pentagonal trumpet-shaped pentomers.
The virion is composed of 60 copies each of the F, G, and J proteins, and 12 copies of the H protein. There are 12 spikes which are each composed of 5 G and one H proteins.
GENOME
Circular, ssDNA(+) genome of 4.4 to 6.1kb. replication occurs via dsDNA intermediate and rolling circle.
GENE EXPRESSION
Early and late genes promoters tightly regulate the timing of gene expression, which is crucial for the replication cycle.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- The viral particle attaches to host cell by binding host lipopolysaccharides.
- The proteins of the capsid perform Injection of the viral DNA through bacterial membranes into cell cytoplasm.
- Host polymerase convert the (+)ssDNA viral genome into a covalently closed dsDNA called replicative form DNA I (RF-I).
- Early viral genes are transcribed by host RNA polymerase, producing viral replication proteins.
- Viral protein A cleaves RF-I(+) DNA strand at the origin of replication and covalently attaches itself to the DNA.
- (+)strand replication occurs by rolling circle, which is converted to dsDNA by host polymerase, generating RF-II molecules (amplification of RF-I).
- Late viral genes are transcribed by host RNA polymerase.
- Procapsid assembly in the cytoplasm.
- Viral protein C binds to replication complex, inducing synthesis and packaging of neo-synthesized (+)ssDNA genomes (RF-III) into procapsids.
- Procapsids maturation occurs in host cytoplasm
- Mature virions are released from the cell by lysis.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)20 entries grouped by strain
10 entries
Enterobacteria phage S13 (Bacteriophage S13) reference strain
10 entries
